5 Key Answers for Cladogram Worksheets Revealed

Cladogram worksheets are essential tools in biology education, particularly when teaching evolutionary relationships and taxonomy. Cladograms, or phylogenetic trees, illustrate the evolutionary history of species or other biological entities. Here, we'll discuss the key aspects of cladograms and provide answers to common questions students might face while working on these worksheets:
Understanding Cladograms

Cladograms depict relationships among organisms, showing which groups are most closely related by using nodes and branches to represent evolutionary splits:
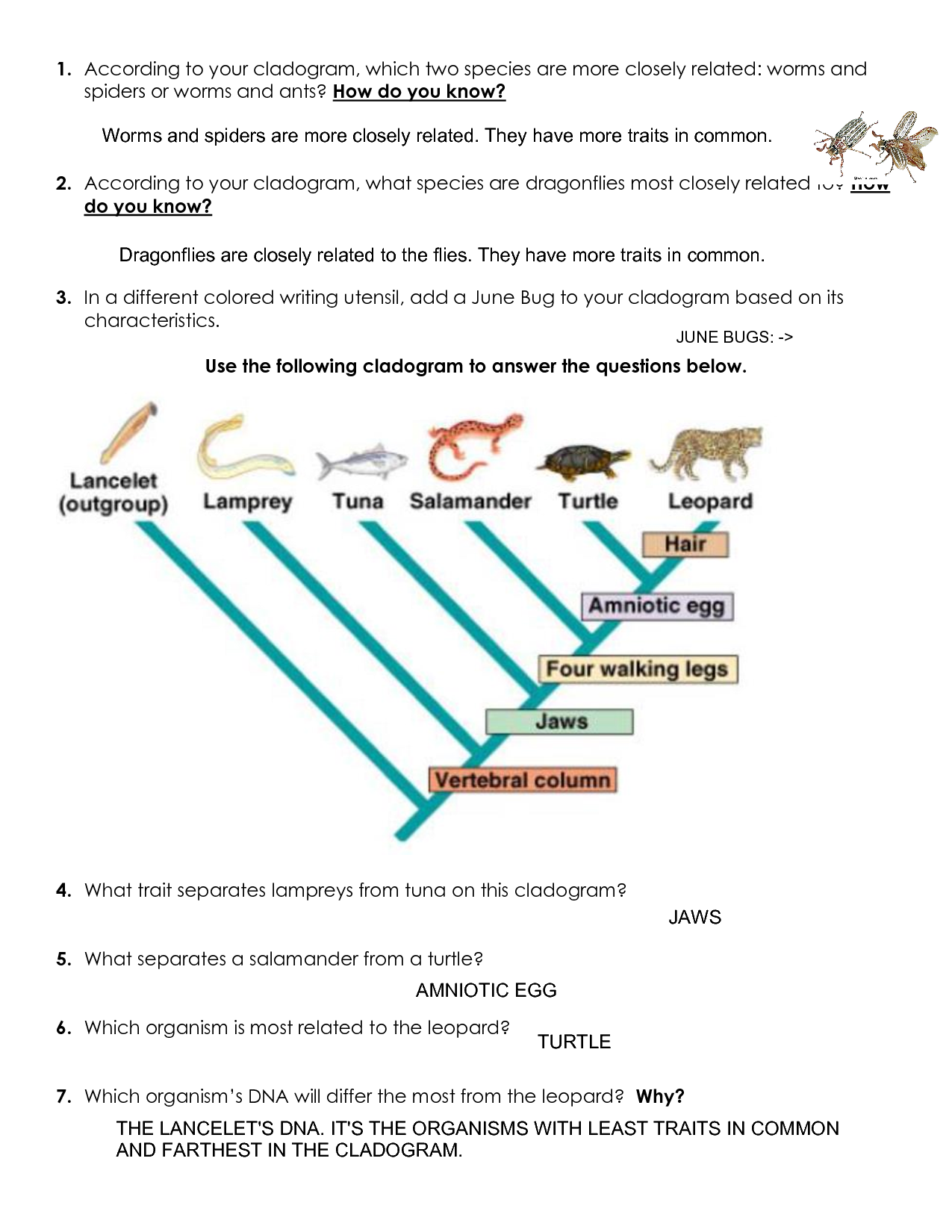
- Nodes: These represent the divergence points, or where a new lineage branches off.
- Branches: They indicate time or a sequence of evolution from one common ancestor to descendant species.
- Derived Traits: Traits that appear in certain organisms but not in their common ancestor are used to construct cladograms.
Reading a Cladogram
To interpret a cladogram:
- Locate the outgroup, which is usually at the base and represents the organism that shares fewer traits with the other organisms.
- Follow the branches to see how traits evolve, where each node indicates the appearance of a new trait.
- Identify the common ancestor at each node; it should possess traits shared by all branches stemming from that node.
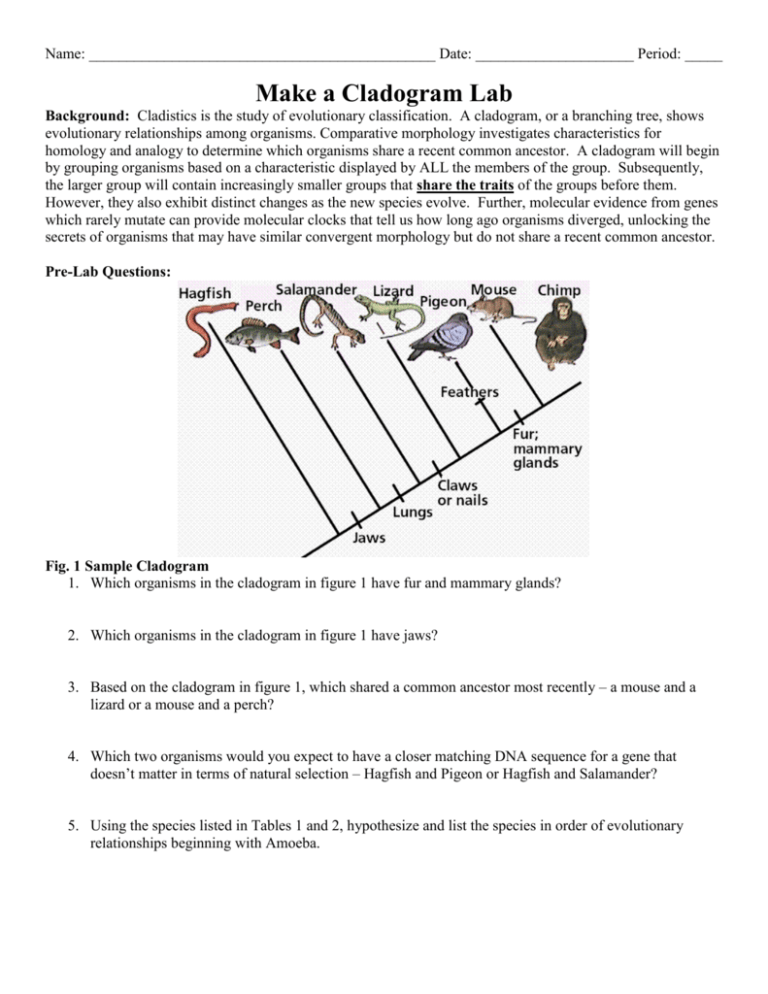
Constructing a Cladogram

To construct a cladogram:
- Identify the traits to be used. These should be consistent and clear.
- Determine the polarity of these traits (ancestral or derived).
- Group the organisms according to their shared derived traits.
- Draw the cladogram by starting from the most ancient node and branching out to represent the evolutionary changes.
🧠 Note: When constructing cladograms, consider using a computer program to streamline the process, especially for complex data sets.
Common Misconceptions in Cladograms

- Cladograms Show Time: While they can represent relative time, cladograms are not intended to show exact chronological time.
- Common Ancestry: All branches on a cladogram share a common ancestor, not just the ones closest to each other.
- Cladograms vs. Phylogenetic Trees: Phylogenetic trees might imply time and may include other information like genetic distances, while cladograms are strictly about trait-based relationships.
Answer Key for Cladogram Worksheets

| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the purpose of a cladogram? | Cladograms are used to illustrate the evolutionary relationships between species or other biological entities. |
| How do you determine the polarity of traits? | Polarity is determined by comparing traits to outgroups, where ancestral traits are present in both in-group and outgroup species, and derived traits are only in the in-group. |
| Can time be accurately represented in a cladogram? | Cladograms typically don’t show precise time; they’re more about the order and pattern of divergence. |
| Why might a cladogram not match a traditional classification system? | Cladograms reflect shared derived traits and evolutionary relationships, whereas traditional classification systems might group organisms by general morphology or ecological roles, which can lead to different groupings. |
| What information should you look for when comparing cladograms? | When comparing, look for consistency in shared derived traits, the arrangement of nodes, and the representation of common ancestors. |

Cladograms provide a visual representation of the evolution of life on Earth, illustrating the patterns of divergence from common ancestors. By understanding how to read and construct cladograms, students gain insights into the dynamic nature of biological classification and evolutionary biology. These tools not only help in organizing information but also in fostering a deeper understanding of how species are interconnected through time. This comprehension of evolutionary relationships is fundamental for those studying biology or related fields, as it informs conservation efforts, medical research, and our understanding of biodiversity.
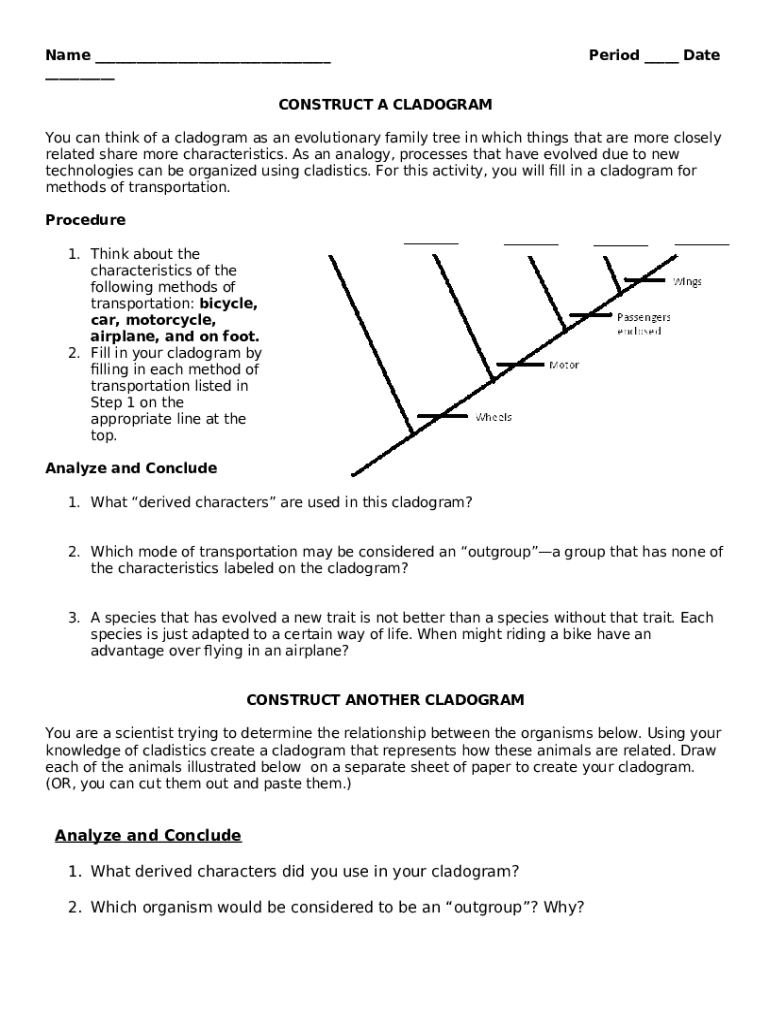
What is the difference between a cladogram and a phylogeny?
+
A cladogram specifically illustrates relationships based on shared derived traits, while a phylogeny can include other aspects like genetic distances and might infer time. A phylogeny might also use different kinds of trees (like a dendrogram) to show hierarchical relationships rather than just evolutionary divergence.
How do you know which traits are derived or ancestral?

+
Derived traits are determined by comparing traits to an outgroup. If the outgroup lacks a trait that is present in the in-group, that trait is considered derived. Conversely, if the outgroup has the same trait, it’s considered ancestral.
Can cladograms be used to predict future evolutionary trends?

+
Cladograms themselves do not predict future evolution. However, understanding patterns of divergence can inform hypotheses about evolutionary potential based on existing genetic variation, ecological pressures, and other biological factors.



