5 Ways to Understand Percentile
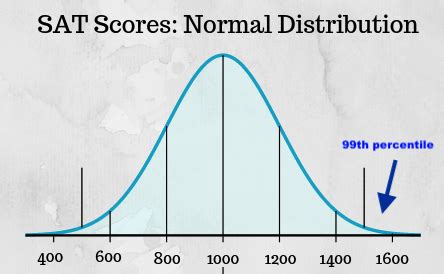
Introduction to Percentiles

Percentiles are a statistical measure used to understand the distribution of data. They are particularly useful in understanding how a particular data point compares to the rest of the data set. In this post, we will delve into the world of percentiles, exploring what they are, how they are calculated, and most importantly, how to understand them. Percentiles are essentially a way to measure the position of a value within a dataset, indicating the percentage of observations that fall below that value.
What are Percentiles?

To grasp the concept of percentiles, let’s start with a basic definition. A percentile is a measure used in statistics indicating the value below which a given percentage of observations in a group of observations falls. For example, if a student scored in the 85th percentile on a test, it means that the student scored better than 85% of the other students who took the test. This does not mean the student scored 85% on the test; rather, it means the student’s score was higher than 85% of the other scores.
Calculating Percentiles

Calculating percentiles involves arranging the data in ascending or descending order and then finding the percentage of data points that fall below a specific value. The formula for calculating the percentile (P) of a value (X) in a dataset is given by: - First, arrange the data in ascending order. - Then, calculate the position of the percentile using the formula: (P/100) * N, where N is the number of items in the dataset. - If the result is a whole number, the percentile value is the average of the two values around that position. - If the result is not a whole number, the percentile value is the value at the next highest position.
Understanding Percentiles with Examples

Let’s consider a few examples to better understand percentiles: - Example 1: In a class of 10 students, the scores are 50, 60, 70, 75, 80, 85, 90, 92, 95, 98. To find the 75th percentile, we first arrange the scores in ascending order (already done). Then, we calculate (75⁄100)*10 = 7.5. Since 7.5 is not a whole number, we look at the 8th score (because 7.5 rounds up to 8), which is 92. Thus, the 75th percentile score is 92, meaning 75% of the scores are below 92. - Example 2: Suppose we have a dataset of exam scores, and we want to find the score that marks the 90th percentile. If our dataset consists of 100 students, the calculation would be (90⁄100)*100 = 90. This means we look at the 90th score when the data is arranged in ascending order.
Applications of Percentiles

Percentiles have numerous applications in real life: - Education: Percentiles are used to compare students’ performances in exams and tests, helping to identify top performers and those who need extra support. - Business: Companies use percentiles to analyze customer satisfaction ratings, employee performance, and market trends. - Medicine: Percentiles are crucial in understanding growth charts for children, indicating how a child’s height or weight compares to the average.
Common Percentiles and Their Meanings

Some percentiles are more commonly referenced than others: - 25th Percentile (Q1): 25% of the data falls below this value. - 50th Percentile (Median): 50% of the data falls below this value, dividing the data into two equal parts. - 75th Percentile (Q3): 75% of the data falls below this value. - 90th Percentile: Often used as a cutoff for top performers. - 95th Percentile: Used in various statistical analyses to identify outliers.
| Percentile | Description |
|---|---|
| 25th Percentile | First Quartile (Q1), 25% of data below |
| 50th Percentile | Median, 50% of data below |
| 75th Percentile | Third Quartile (Q3), 75% of data below |

📝 Note: Understanding percentiles requires a solid grasp of statistical concepts and how data is distributed. It's essential to practice calculating percentiles with different datasets to become proficient.
In summary, percentiles are a powerful tool for understanding data distribution and comparing individual data points within a larger dataset. By grasping how percentiles work and how to calculate them, individuals can make more informed decisions in various fields, from education to business and beyond. The key is to remember that percentiles measure the relative position of a data point, not its absolute value, and to use this understanding to interpret data effectively.
What is the difference between percentile and percentage?
+
A percentile is a measure used in statistics indicating the value below which a given percentage of observations in a group of observations falls. A percentage, on the other hand, is a fraction of a whole as a percentage of the whole. For example, scoring in the 90th percentile does not mean scoring 90% on a test but rather scoring higher than 90% of the other test-takers.
How are percentiles used in real-life applications?
+
Percentiles are used in various real-life applications such as in education to compare student performances, in business to analyze customer satisfaction and employee performance, and in medicine to understand growth charts for children and identify health trends.
What does it mean to be in a higher percentile in a test?
+
Being in a higher percentile in a test means that you scored better than a higher percentage of the other test-takers. For instance, being in the 95th percentile means you scored better than 95% of the other test-takers, indicating a very high performance compared to the group.



