What Do Nuclear Engineers Do

The Role of Nuclear Engineers in Shaping the Energy Landscape

Nuclear engineers play a crucial role in the development, operation, and maintenance of nuclear power plants, as well as in the application of nuclear energy in various fields such as medicine, industry, and research. Their work is critical to ensuring the safe and efficient generation of electricity from nuclear energy, which is a vital component of the global energy mix.
Key Responsibilities of Nuclear Engineers

Nuclear engineers are responsible for a wide range of tasks, including:
- Designing and developing nuclear reactors and fuel cycles: Nuclear engineers design and develop nuclear reactors, fuel cycles, and other equipment to ensure efficient and safe operation.
- Conducting research and development: Nuclear engineers conduct research and development to improve the performance, safety, and efficiency of nuclear reactors and fuel cycles.
- Operating and maintaining nuclear power plants: Nuclear engineers oversee the operation and maintenance of nuclear power plants to ensure safe and efficient electricity generation.
- Ensuring safety and regulatory compliance: Nuclear engineers ensure that nuclear power plants and facilities comply with safety and regulatory requirements.
- Collaborating with other professionals: Nuclear engineers work with other professionals, such as physicists, chemists, and engineers, to ensure the safe and efficient operation of nuclear facilities.
Specializations within Nuclear Engineering

Nuclear engineers can specialize in various areas, including:
- Reactor physics: Reactor physicists design and develop nuclear reactors and fuel cycles.
- Thermal hydraulics: Thermal hydraulic engineers design and develop cooling systems for nuclear reactors.
- Nuclear materials: Nuclear materials engineers develop and test materials used in nuclear reactors.
- Nuclear safety: Nuclear safety engineers ensure that nuclear power plants and facilities comply with safety and regulatory requirements.
Education and Training Requirements

To become a nuclear engineer, one typically needs to:
- Earn a bachelor’s degree in nuclear engineering or a related field: A bachelor’s degree in nuclear engineering or a related field, such as physics or engineering, is typically required.
- Gain relevant work experience: Many nuclear engineers gain relevant work experience through internships or co-op programs.
- Obtain professional certification: Professional certification, such as the Certified Nuclear Engineer (CNE) certification, can demonstrate expertise and knowledge in nuclear engineering.
📚 Note: Many nuclear engineers also pursue advanced degrees, such as master's or Ph.D.s, to specialize in a particular area or to move into leadership positions.
Tools and Technologies Used by Nuclear Engineers

Nuclear engineers use a variety of tools and technologies, including:
- Computer simulations: Computer simulations are used to model and analyze nuclear reactor behavior.
- Data analysis software: Data analysis software is used to analyze data from nuclear reactors and facilities.
- Radiation detection equipment: Radiation detection equipment is used to detect and measure radiation levels.
- Robotics and automation: Robotics and automation are used to perform tasks that are too hazardous for humans.
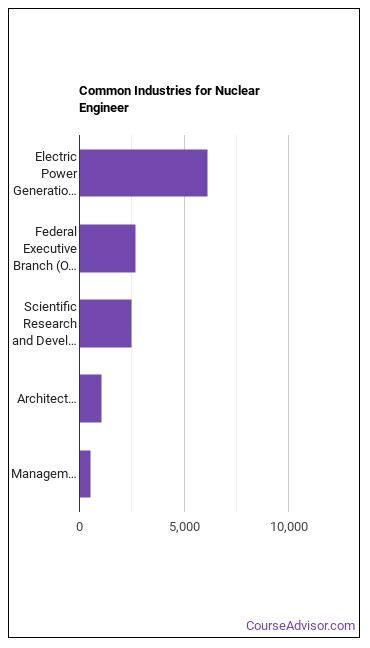
Work Environment and Salary

Nuclear engineers typically work in:
- Nuclear power plants: Nuclear engineers work in nuclear power plants, overseeing the operation and maintenance of the facility.
- Research institutions: Nuclear engineers work in research institutions, conducting research and development to improve nuclear energy.
- Government agencies: Nuclear engineers work in government agencies, ensuring that nuclear facilities comply with safety and regulatory requirements.
The median salary for nuclear engineers is around $105,000 per year, although salaries can vary depending on location, experience, and employer.
Challenges and Opportunities in Nuclear Engineering

Nuclear engineers face a variety of challenges, including:
- Public perception: Many people have concerns about the safety of nuclear energy.
- Waste management: Nuclear engineers must ensure that nuclear waste is disposed of safely and securely.
- Regulatory requirements: Nuclear engineers must ensure that nuclear facilities comply with safety and regulatory requirements.
Despite these challenges, nuclear engineering offers many opportunities, including:
- Career advancement: Nuclear engineers can advance to leadership positions or specialize in a particular area.
- Job security: Nuclear engineers are in high demand, and job security is generally good.
- Opportunity to make a difference: Nuclear engineers have the opportunity to make a difference in the world by contributing to the development of clean and sustainable energy.
To summarize, nuclear engineers play a critical role in the development, operation, and maintenance of nuclear power plants, as well as in the application of nuclear energy in various fields. Their work is crucial to ensuring the safe and efficient generation of electricity from nuclear energy.
A Bright Future for Nuclear Engineers

As the world continues to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, the demand for nuclear engineers is likely to increase. With the development of new nuclear technologies and the expansion of existing nuclear power plants, nuclear engineers will play a vital role in shaping the energy landscape of the future.
What is the primary responsibility of a nuclear engineer?

+
The primary responsibility of a nuclear engineer is to ensure the safe and efficient operation of nuclear power plants and facilities.
What kind of education and training do nuclear engineers need?
+
Nuclear engineers typically need a bachelor’s degree in nuclear engineering or a related field, as well as relevant work experience and professional certification.
What are some of the challenges faced by nuclear engineers?

+
Nuclear engineers face challenges such as public perception, waste management, and regulatory requirements.