5 Essential Tips for Understanding Waves Unit 2 Worksheet 5

Welcome to our deep dive into understanding the Waves Unit 2 Worksheet 5. If you're studying waves in your physics or science class, this worksheet can often be a pivotal point in your learning journey, designed to test your comprehension of wave phenomena. Today, we'll cover five essential tips to not only help you navigate through this worksheet effectively but also to gain a profound understanding of the wave concepts at play.
Tip 1: Review Your Wave Basics
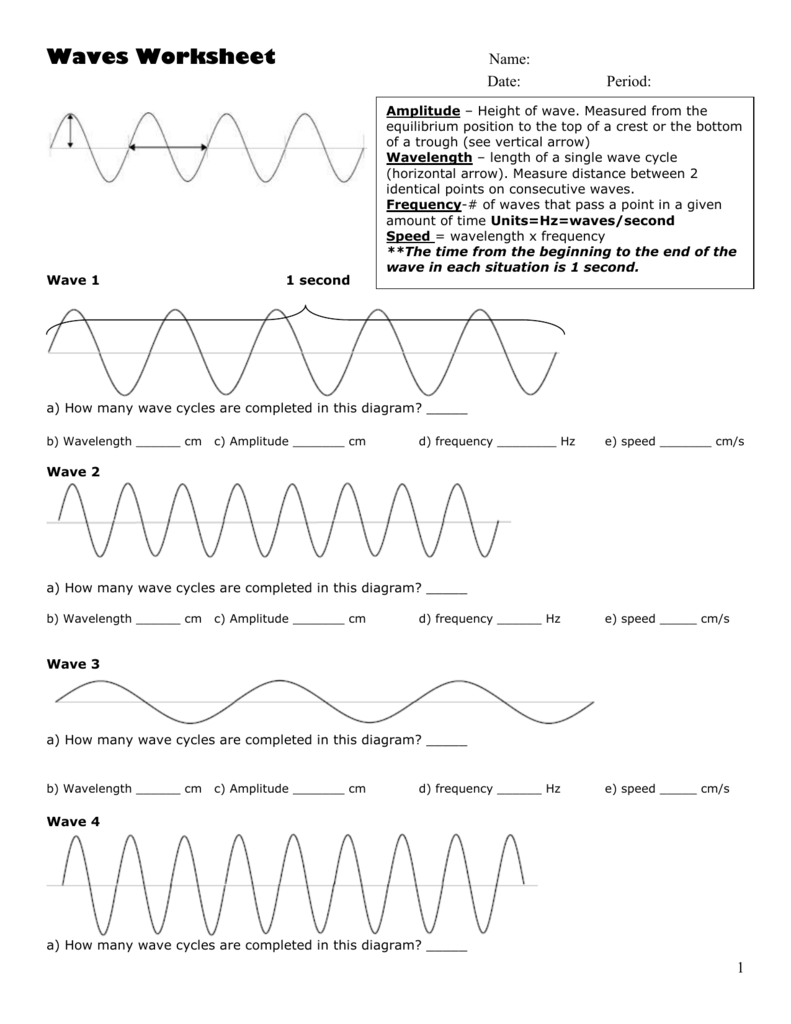
Before you dive into the worksheet, make sure to review the basics of waves:
- Definition of a wave: A disturbance that transfers energy from one place to another.
- Wave types: Mechanical and electromagnetic.
- Properties: Wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and velocity.
- Wave equation: v = fλ, where v is velocity, f is frequency, and λ is wavelength.
✅ Note: Refreshing these fundamental concepts will provide a solid foundation for tackling more complex problems in the worksheet.
Tip 2: Understand the Relationship Between Wave Parameters
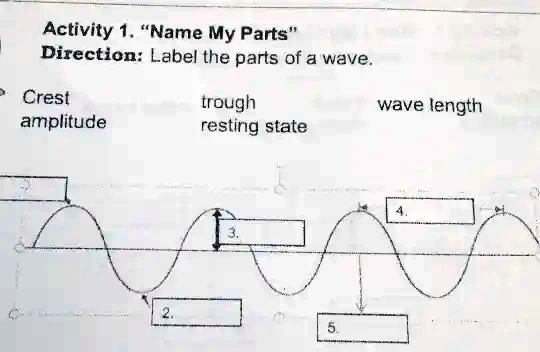
The relationship between wave properties is crucial for solving problems:
- Frequency and wavelength: As frequency increases, wavelength decreases, keeping wave speed constant for a given medium.
- Amplitude and energy: Higher amplitudes transfer more energy.
- Velocity in different media: Wave speed changes when waves move from one medium to another.
💡 Note: Practice converting units and understanding the inverse relationship between frequency and wavelength to solve problems effectively.
Tip 3: Practice Sketching Wave Diagrams
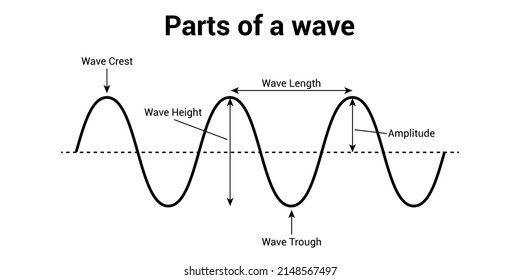
Visual representation aids in understanding:
- Sketch transverse waves with peaks and troughs, labeling amplitude and wavelength.
- Draw longitudinal waves showing compressions and rarefactions.
- Use diagrams to show phase differences and the effect of reflection.
| Wave Type | Amplitude | Wavelength | Energy Transfer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transverse | Distance from equilibrium to crest/trough | Distance between two consecutive crests/troughs | Up/down energy movement |
| Longitudinal | Intensity of compression or rarefaction | Distance between two consecutive compressions or rarefactions | Forward/backward energy movement |

👁 Note: Drawing waves helps visualize the relationships and can make solving problems more intuitive.
Tip 4: Solve Problems Systematically

To navigate through problems:
- Identify knowns and unknowns: Clearly list what is given and what you need to find.
- Apply formulas: Use the appropriate wave equations step by step.
- Check dimensions and units: Ensure your answers make physical sense in terms of units.
- Review each step: It's easy to make mistakes in calculations, so double-check your work.
🔍 Note: Taking a systematic approach not only increases your accuracy but also builds a methodical problem-solving mindset.
Tip 5: Utilize Study Aids and Examples

Harnessing resources effectively:
- Use textbooks, online resources, or previous worksheets to practice similar problems.
- Work through past student solutions to see how others have approached problems.
- Join or form study groups to discuss and solve wave problems collaboratively.
💬 Note: Peer learning can provide different perspectives and enhance your understanding through discussion.
To wrap up, mastering the Waves Unit 2 Worksheet 5 is not just about completing a task; it's about grasping how waves behave, interact, and transfer energy. The tips we've explored provide you with tools to approach wave phenomena systematically, whether you're sketching, solving, or studying. With these strategies in your toolkit, you'll find yourself not only solving the problems with more ease but also appreciating the elegance of wave theory. Remember, understanding waves is a step towards comprehending many other natural phenomena, from sound to light, and even quantum mechanics. Keep these tips in mind, and you'll find yourself riding the wave of knowledge with confidence.
Why do waves sometimes behave differently in different media?

+
Waves change speed when they pass through different media because of changes in the medium’s density or elastic properties. The wavelength adjusts to keep the frequency constant.
How does amplitude affect the energy of a wave?
+
The energy of a wave is proportional to the square of its amplitude. Thus, doubling the amplitude will quadruple the energy.
Can I apply these wave principles to all types of waves?

+
Yes, although there might be specific behaviors for different types of waves, the fundamental principles like frequency-wavelength relationships are universal to all waves.