Mastering the Electromagnetic Spectrum: Waves Worksheet Guide

In this guide, we delve into the fascinating world of the electromagnetic spectrum, a topic that not only forms the backbone of modern physics but also intersects with daily technology and natural phenomena. Here, we'll provide a detailed exploration through a "Waves Worksheet Guide" to help you understand electromagnetic waves better. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or just someone curious about how these invisible waves shape our lives, this guide will serve as an invaluable resource.
What is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?

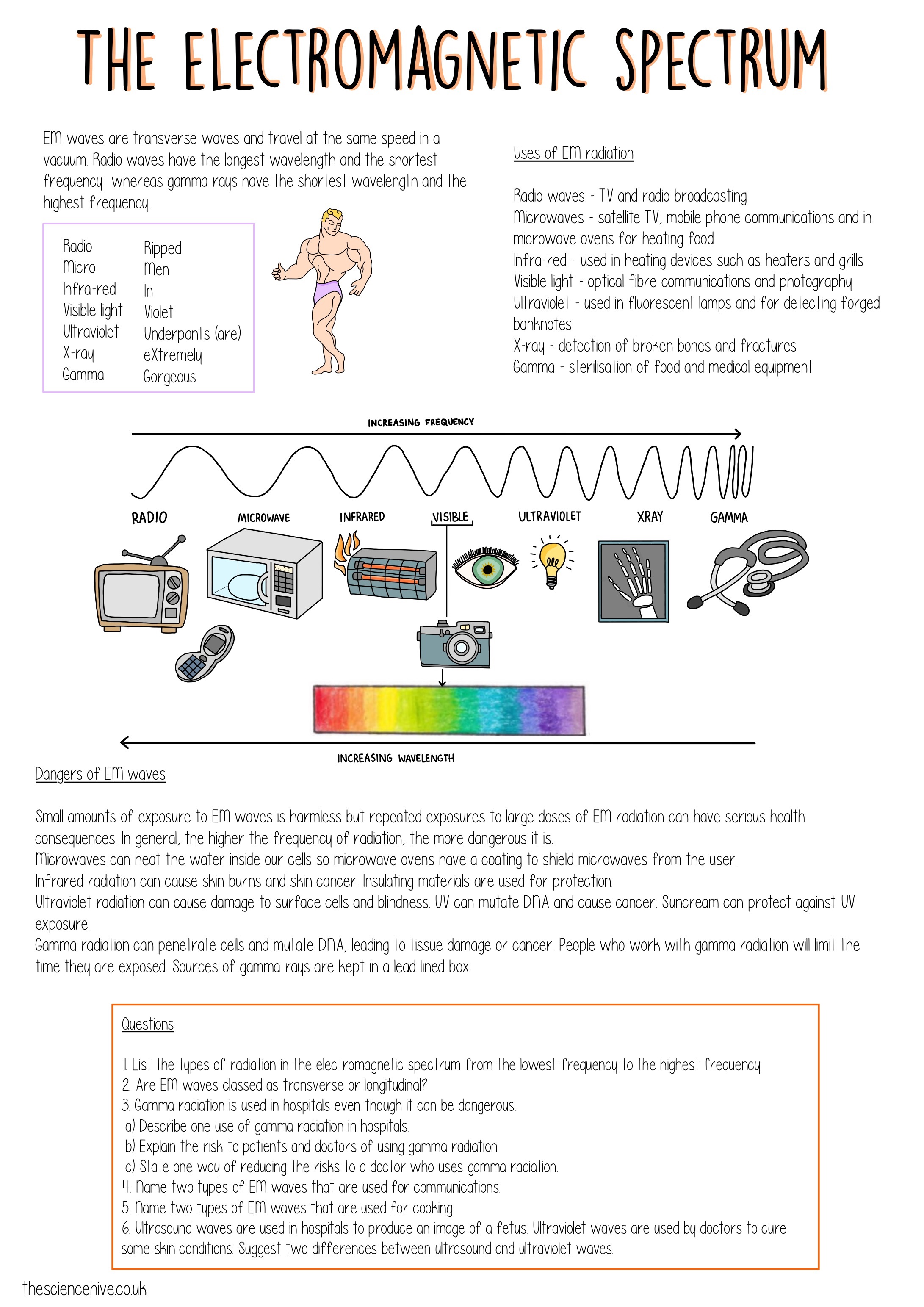
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all the different types of electromagnetic waves arranged according to their wavelengths and frequencies. Here’s a brief overview:
- Radio Waves - Longest wavelengths, used in communication technologies like radio, TV, and mobile phones.
- Microwaves - Known for heating food but also used in satellite communications.
- Infrared Radiation - Felt as heat, this form of energy is emitted by objects warmer than the environment.
- Visible Light - The only part of the spectrum we can see, ranging from red to violet.
- Ultraviolet Radiation - Causes sunburns and is utilized in various sterilization processes.
- X-rays - Used in medical imaging to see inside the body.
- Gamma Rays - The shortest wavelengths, associated with radioactivity and nuclear events.

Understanding Waves through Worksheets
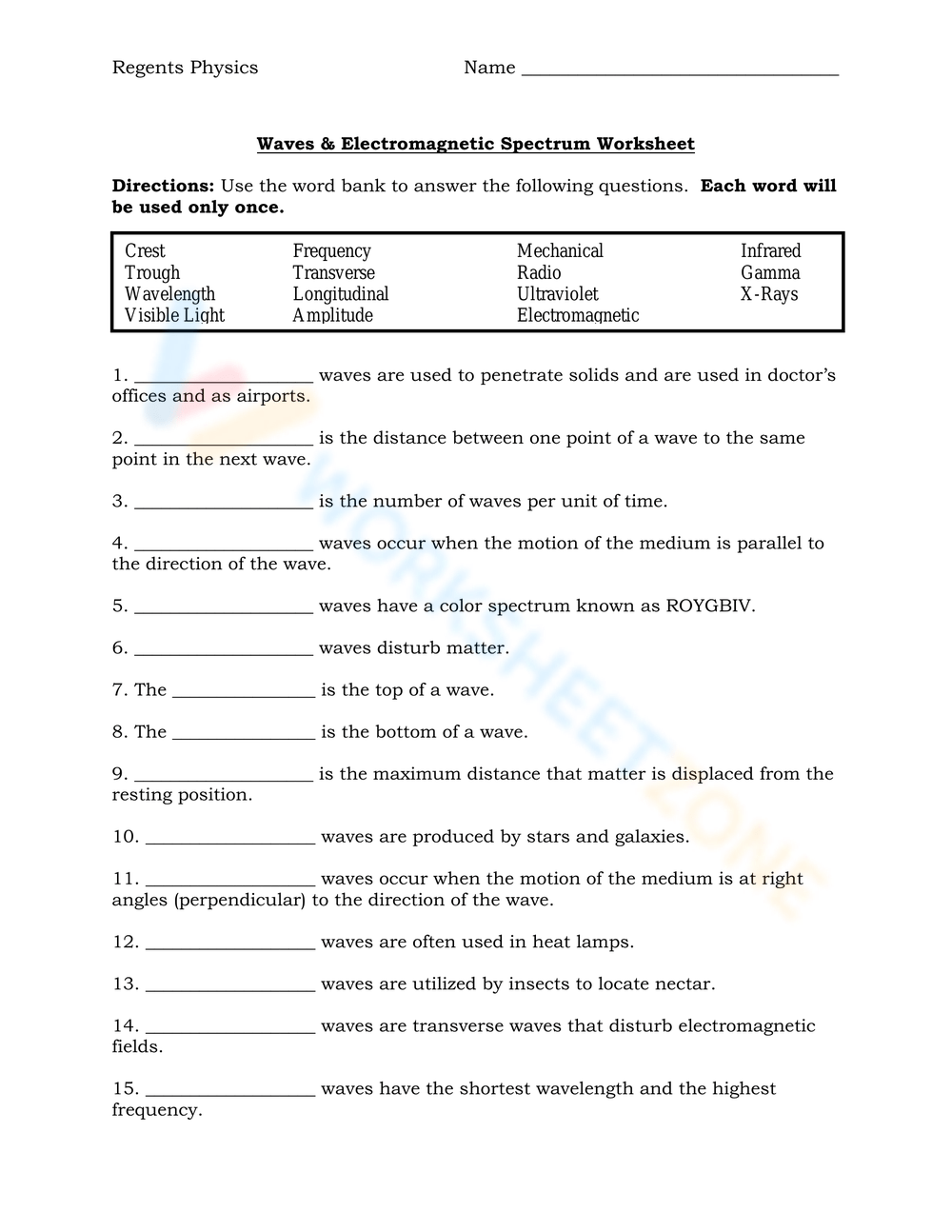
Worksheets are an excellent way to solidify your understanding of electromagnetic waves. Here’s how you can use them effectively:
1. Identify Components of Waves

Each wave has:
- Wavelength - The distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs.
- Frequency - How many cycles of the wave pass a given point per second, measured in Hertz (Hz).
- Amplitude - Reflects the intensity or energy of the wave.
📝 Note: Understanding these components is crucial as they define the properties and behavior of electromagnetic waves.
2. Speed of Light and Wave Equation

Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light ©, which is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second in a vacuum. Use the wave equation c = f * λ (where c is the speed of light, f is frequency, and λ is wavelength) in worksheets to calculate unknown variables.
3. Exploring Frequency and Wavelength Relationship

Inverse Proportionality:
- As frequency increases, wavelength decreases, and vice versa.
| Frequency (Hz) | Wavelength (m) |
|---|---|
| 1 * 109 | 0.3 |
| 3 * 109 | 0.1 |
| 5 * 109 | 0.06 |

4. Energy and Electromagnetic Waves
The energy (E) carried by an electromagnetic wave is directly related to its frequency (f) and the Planck’s constant (h):
E = h * f
Worksheet exercises might involve:
- Calculating the energy of photons across different parts of the spectrum.
- Relating energy levels to the potential hazards or applications of each wave type.
5. Practical Applications

Apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios:
- Medical applications - MRI scans use radio waves and magnetic fields.
- Communication - Understanding how satellites and WiFi operate.
To wrap up our journey through the electromagnetic spectrum, it's evident that these invisible waves are not just theoretical constructs but integral to many aspects of our daily lives. From understanding how light travels to harnessing the power of waves for various applications, this guide has highlighted key components, relationships, and practical uses of electromagnetic waves. By working through worksheets, one can gain a deeper appreciation and comprehension of this vast and vibrant spectrum.
What is the difference between frequency and wavelength?

+
Frequency measures how many cycles of a wave pass a point per second, while wavelength is the distance between two consecutive points on a wave that are in phase.
How does the energy of an electromagnetic wave relate to its frequency?

+
Energy of an electromagnetic wave is directly proportional to its frequency, calculated as E = h * f, where h is Planck’s constant and f is the frequency of the wave.
What are some harmful effects of high-frequency electromagnetic waves?

+
High-frequency electromagnetic waves like ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays can damage biological tissues because they carry enough energy to ionize atoms or molecules, leading to potential health issues like radiation sickness or cancer.