Mastering Wave Interference: A Comprehensive Worksheet Guide

Wave interference is a fascinating subject within physics that deals with the behavior of waves when they meet. When two waves travel simultaneously through the same medium, their superposition leads to either an increase or decrease in the amplitude of the resultant wave, known as interference. Understanding wave interference is not just crucial for academic physics but also has practical implications in fields ranging from acoustics to optics and beyond.
Understanding Wave Interference


Before diving into the practical applications and hands-on exercises, let's get a firm grasp on the concept:
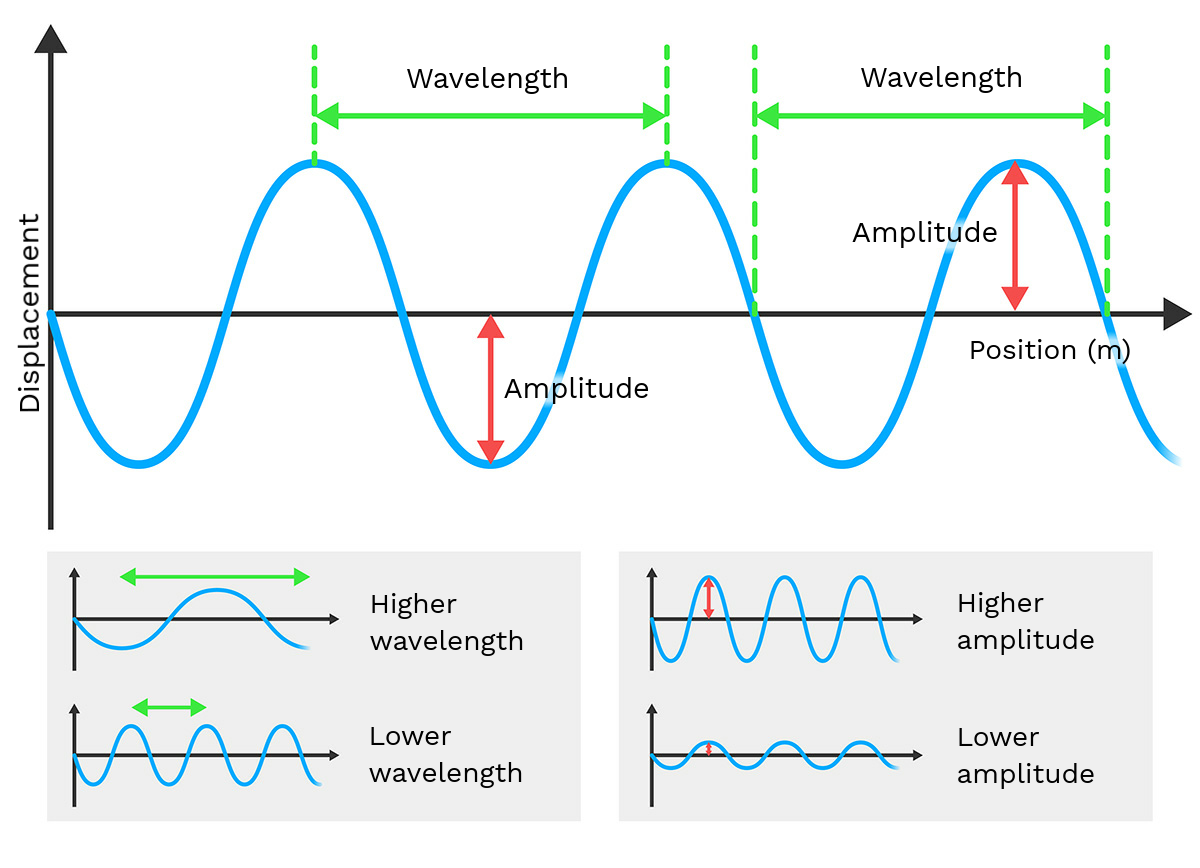
- Wave Properties: Wavelength, amplitude, frequency, and speed.
- Types of Interference: Constructive (addition of waves) and Destructive (subtraction).
Constructive Interference

When two waves of the same frequency and wavelength meet in phase, meaning their crests and troughs align, they add together to increase the amplitude:
- The resultant wave amplitude is the sum of the individual wave amplitudes.
- This principle is at play in phenomena like the loud spots created by speakers in a room.
Destructive Interference

In contrast, when two waves meet out of phase, their amplitudes cancel out:
- The resultant amplitude is reduced or nullified depending on how out of phase the waves are.
- Noise-canceling headphones use this principle to filter out unwanted sounds.
Worksheet Exercises on Wave Interference

💡 Note: For each exercise, consider the medium (air, water, etc.), wave properties, and conditions for interference.
Exercise 1: Constructive Interference

Imagine two identical waves with amplitude 2 cm traveling towards each other in the same medium:
- What would be the amplitude of the resultant wave when they meet?
- How would you describe this type of interference?
Exercise 2: Destructive Interference

Consider two identical waves with amplitude 3 cm traveling towards each other, but now they are out of phase by 180 degrees:
- What will the amplitude of the resultant wave be?
- Can this type of interference occur in real-world scenarios? Provide examples.
Exercise 3: Phase Shift Analysis

Given two waves with amplitudes 4 cm, one traveling towards the right with no phase shift and another traveling towards the left with a phase shift of π/2:
- What would be the net amplitude at various points along the medium?
- Sketch the resultant wave pattern.
Applications of Wave Interference

Acoustics

The principles of wave interference govern sound engineering, both in enhancing and controlling audio:
- Acoustic Resonance: Musical instruments are designed to enhance constructive interference for louder notes.
- Noise Control: Interference patterns can be used to reduce unwanted noise in environments.
Optics

In optics, wave interference plays a pivotal role:
- Thin-Film Interference: The colorful patterns on soap bubbles or oil slicks.
- Diffraction Gratings: Creating multiple images of a light source through constructive interference.
Creating Your Own Interference Patterns
For a practical approach, let’s consider how to visualize interference patterns:
- Setup a ripple tank with a shallow layer of water.
- Generate waves using a vibrator connected to two oscillating points.
- Observe and record how the waves interact.
💡 Note: Adjusting the frequency of the waves can change the interference pattern.
Final Thoughts

Mastering wave interference not only deepens our understanding of wave behavior but also equips us with the tools to manipulate and control waves for practical purposes. Whether it’s improving the sound in a concert hall or designing efficient optical systems, the concepts discussed here are the building blocks. Engaging with these principles through worksheets and real-world applications ensures a comprehensive learning experience that transcends theoretical knowledge into practical use.
What is the difference between constructive and destructive interference?

+
Constructive interference occurs when waves add up to increase the amplitude, whereas destructive interference happens when waves cancel each other out.
Can we see wave interference?
+
Yes, wave interference can be visualized through patterns like those on oil slicks, soap bubbles, or in ripple tanks. Optical phenomena like diffraction and thin-film interference provide visible evidence of wave interference.
How does wave interference affect the quality of sound?

+
Wave interference influences how sound waves interact with each other and their surrounding environment, affecting acoustics. Through constructive interference, the sound can become louder, while destructive interference can create areas of silence or reduced volume, leading to variations in sound quality.