Master Wave Interactions with Our Engaging Worksheet
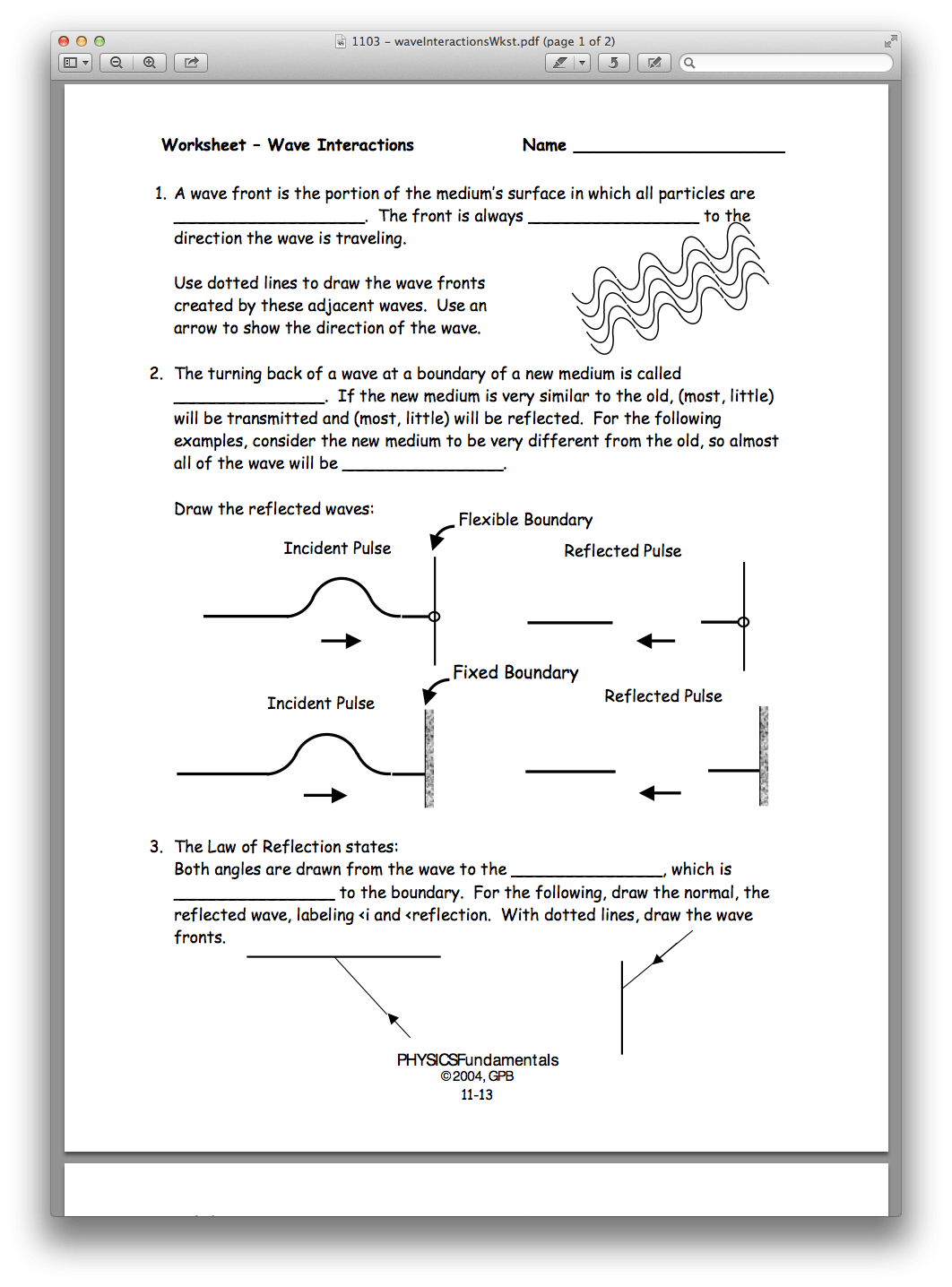
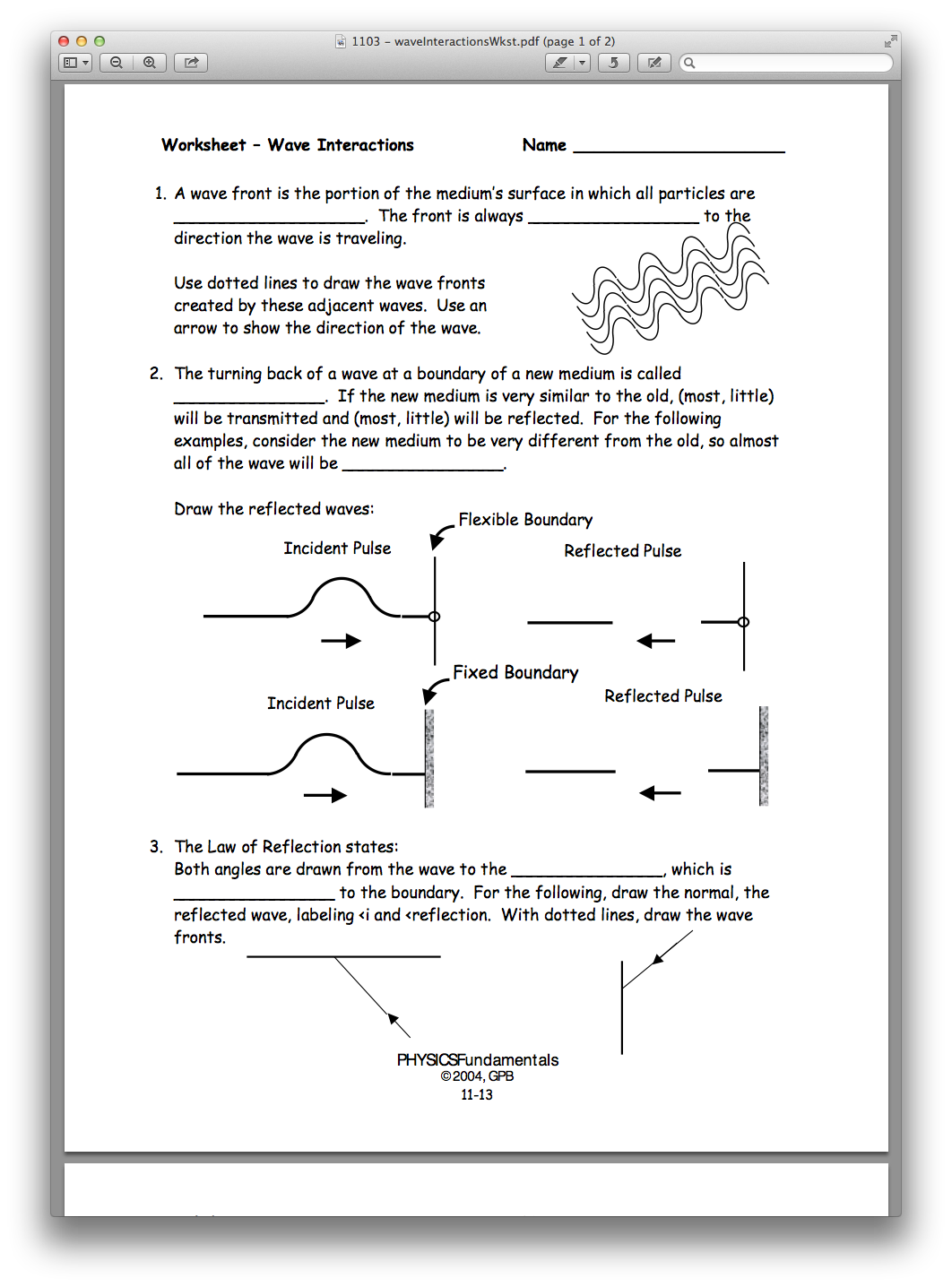
Wave interactions are fundamental phenomena that govern much of the natural world, from the ocean's ripples to the subtle vibrations that carry our favorite music through the air. Mastering the way waves interact with each other, with boundaries, and with various media, is crucial not just for theoretical physics but also for practical applications in engineering, oceanography, acoustics, and many more fields. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of wave interactions through an engaging worksheet designed to bolster your understanding and hands-on experience with these dynamic forces.
Understanding Wave Interactions


Waves are rhythmic disturbances that transfer energy without transferring matter. They can interact in various ways:
- Reflection: Waves bounce back from a barrier.
- Refraction: Waves change direction due to a change in medium.
- Diffraction: Waves bend around obstacles or through apertures.
- Interference: Superposition of waves can result in constructive or destructive interference.
Before we dive into the worksheet, let's review these key concepts to ensure a solid foundation:
The Principle of Superposition

At the heart of wave interactions is the principle of superposition, stating that when two or more waves meet, the resulting wave function is the algebraic sum of the individual wave functions at each point.
| Wave Interaction | Description | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Superposition | Additive nature of wave amplitudes | \[Y = y_1 + y_2\] |

Constructive and Destructive Interference

When two waves meet, they can interact in two primary ways:
- Constructive Interference: When two waves are in phase, their amplitudes add up, resulting in a wave with greater amplitude.
- Destructive Interference: When waves are out of phase, their amplitudes cancel each other out, reducing or completely eliminating the wave’s presence.
🎶 Note: The interference patterns you see in acoustics, like the booming lows or sharp peaks in sound, are due to constructive and destructive interference.
Engaging Wave Interactions Worksheet

To master wave interactions, practical exercises are essential. Here’s an engaging worksheet to deepen your understanding:
Activity 1: Interference Patterns

Materials:
- A sheet of paper
- A pen or pencil
- A ruler or straightedge
Instructions:
- Draw two sets of waves on your paper. Make one set represent water waves, and the other represent sound waves.
- Sketch the interference patterns when these waves meet at various phases. Label where constructive and destructive interference would occur.
📚 Note: If the waves are perfectly in phase, you'll see complete constructive interference; if they are 180 degrees out of phase, complete destructive interference.
Activity 2: Reflection and Refraction

Materials:
- A wave tank (or shallow tray with water)
- A dropper or stick to create waves
- Obstacles like small blocks or barriers
Instructions:
- Fill the wave tank with water. Use the dropper or stick to create waves from one side.
- Observe how waves reflect off the sides of the tank or any obstacles you introduce.
- Now introduce a different medium by adding a layer of oil or another liquid that changes the wave's speed. Note how the waves refract as they move into this new medium.
Activity 3: Diffraction and Wave Bending
Materials:
- Wave tank from Activity 2
- A set of adjustable slits or barriers
Instructions:
- Create waves in the tank.
- Place a barrier with a small opening. Observe how the wave bends around the barrier.
- Adjust the size of the opening or place multiple slits to see different diffraction patterns.
Putting It All Together

These activities showcase the real-world effects of wave interactions. From controlling sound in an auditorium to understanding how radio signals can bend around buildings, mastering wave interactions has far-reaching implications.
The journey through this worksheet has not only allowed you to see these principles in action but also helped in strengthening your conceptual grasp on how waves behave in different scenarios.
What is the difference between reflection and refraction?

+
Reflection is when a wave bounces off a barrier without penetrating it, like sound off a wall. Refraction is when a wave changes direction as it enters a new medium due to a change in wave speed, like light bending through water.
Can you observe wave diffraction in everyday life?

+
Yes, diffraction can be observed in everyday situations. For example, when light passes through a narrow gap or around a small obstacle, it bends, spreading the light into regions of the shadow that would otherwise be dark.
Why is constructive and destructive interference important?

+
Understanding interference is crucial for applications in acoustics, where engineers use it to reduce noise (destructive) or enhance desired sounds (constructive), in optical engineering for creating anti-glare coatings, and in quantum mechanics for understanding wave-particle duality.