5 Key Differences: Warrant Officer vs Commissioned Officer

Understanding the Distinctions: Warrant Officer vs Commissioned Officer

The military is a hierarchical organization with a clear chain of command, and within this structure, there are various types of officers who play crucial roles. Two such categories are Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers. While both are essential to the functioning of the military, they have distinct responsibilities, requirements, and career paths. In this article, we’ll delve into the 5 key differences between Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers to provide a clearer understanding of these two vital components of the military.
Difference 1: Role and Responsibilities
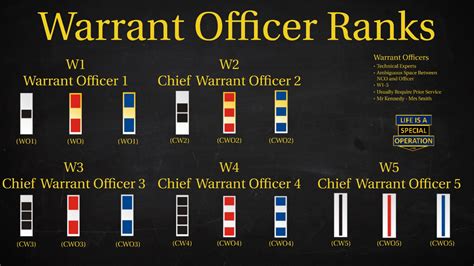
One of the primary differences between Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers lies in their roles and responsibilities. Warrant Officers are technical experts in their field and serve as advisors, instructors, and leaders in specific areas such as aviation, intelligence, communications, or maintenance. They are responsible for ensuring that their units are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their duties effectively.
Commissioned Officers, on the other hand, are leaders who hold positions of authority and responsibility. They can serve in a variety of roles, including command positions, staff roles, and as instructors. Commissioned Officers are responsible for making strategic decisions, leading troops, and overseeing the operations of their units.
📝 Note: Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers often work together, with Warrant Officers providing technical expertise and Commissioned Officers providing leadership and strategic direction.
Difference 2: Requirements and Qualifications

Another significant difference between Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers is the requirements and qualifications needed to become one. Warrant Officers typically begin their careers as enlisted personnel and then apply for Warrant Officer Candidate School (WOCS) after gaining significant experience in their field. To be eligible, they must meet specific requirements, such as time in service, rank, and performance.
Commissioned Officers, by contrast, typically enter the military through a service academy, Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (ROTC), or Officer Candidate School (OCS). They must meet specific requirements, such as education level, age, and physical fitness standards.
| Requirements | Warrant Officer | Commissioned Officer |
|---|---|---|
| Time in Service | Typically 8-12 years | Varies |
| Rank | Typically E-5 or higher | Varies |
| Education | Varies | Bachelor’s degree or higher |
| Physical Fitness | Meets military standards | Meets military standards |

Difference 3: Rank Structure and Promotion

The rank structure and promotion process also differ between Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers. Warrant Officers hold a unique rank structure that is separate from the enlisted and officer ranks. They are classified as W-1 to W-5, with W-5 being the highest rank.
Commissioned Officers, on the other hand, hold ranks from O-1 to O-10, with O-10 being the highest rank. The promotion process for Commissioned Officers is based on time in service, performance, and completion of professional military education (PME) courses.
Difference 4: Career Path and Advancement
The career path and advancement opportunities for Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers also differ. Warrant Officers typically specialize in a specific field and remain in that field throughout their careers. They may have opportunities to advance to higher ranks, but their career path is generally more narrow.
Commissioned Officers, by contrast, have a broader range of career opportunities. They can move between different branches, transition to civilian careers, or pursue advanced degrees. Commissioned Officers also have more opportunities for advancement, as they can be promoted to higher ranks and take on more senior leadership roles.
Difference 5: Pay and Benefits
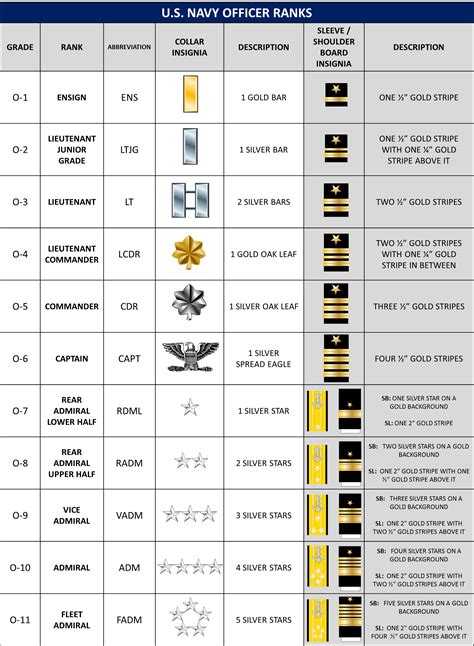
Finally, the pay and benefits for Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers differ. Warrant Officers are paid according to their rank and time in service, but their pay is generally lower than that of Commissioned Officers. Commissioned Officers, on the other hand, are paid according to their rank and time in service, and their pay is generally higher than that of Warrant Officers.
In addition to pay, both Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers receive a range of benefits, including access to military healthcare, education assistance, and veterans’ benefits.
In summary, while both Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers are essential to the military, they have distinct roles, responsibilities, and career paths. Understanding these differences is crucial for those considering a career in the military, as well as for those who want to appreciate the diverse range of contributions made by military personnel.
The military is a complex organization with many different roles and responsibilities. By understanding the differences between Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the sacrifices and contributions made by military personnel.
What is the primary difference between Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers?

+
The primary difference between Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers lies in their roles and responsibilities. Warrant Officers are technical experts who serve as advisors, instructors, and leaders in specific areas, while Commissioned Officers are leaders who hold positions of authority and responsibility.
How do Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers advance in their careers?

+
Warrant Officers typically specialize in a specific field and remain in that field throughout their careers, with opportunities to advance to higher ranks. Commissioned Officers, on the other hand, have a broader range of career opportunities and can move between different branches, transition to civilian careers, or pursue advanced degrees.
What are the pay and benefits for Warrant Officers and Commissioned Officers?

+
Warrant Officers are paid according to their rank and time in service, with pay generally lower than that of Commissioned Officers. Commissioned Officers are also paid according to their rank and time in service, with pay generally higher than that of Warrant Officers. Both receive a range of benefits, including access to military healthcare, education assistance, and veterans’ benefits.