Mastering Volume Calculations: Rectangular Prism Worksheet

Understanding volume is a fundamental concept in geometry that plays a pivotal role in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and manufacturing. Today, we're going to dive into the specifics of calculating the volume of a rectangular prism, one of the most common shapes you'll encounter. We'll provide a comprehensive walkthrough complete with examples, problems, and even a worksheet to help you cement your knowledge. Whether you're a student, teacher, or just someone intrigued by the intricacies of geometry, this post will enhance your understanding of volume in a clear, step-by-step manner.
Understanding Rectangular Prisms

A rectangular prism is a three-dimensional shape where all internal angles are right angles (90 degrees). It’s also known as a cuboid. Here’s what makes it unique:
- It has six rectangular faces.
- Its sides are pairwise perpendicular to each other.
- The volume can be calculated using the formula V = l * w * h where l is the length, w is the width, and h is the height of the prism.
Volume Calculation Steps
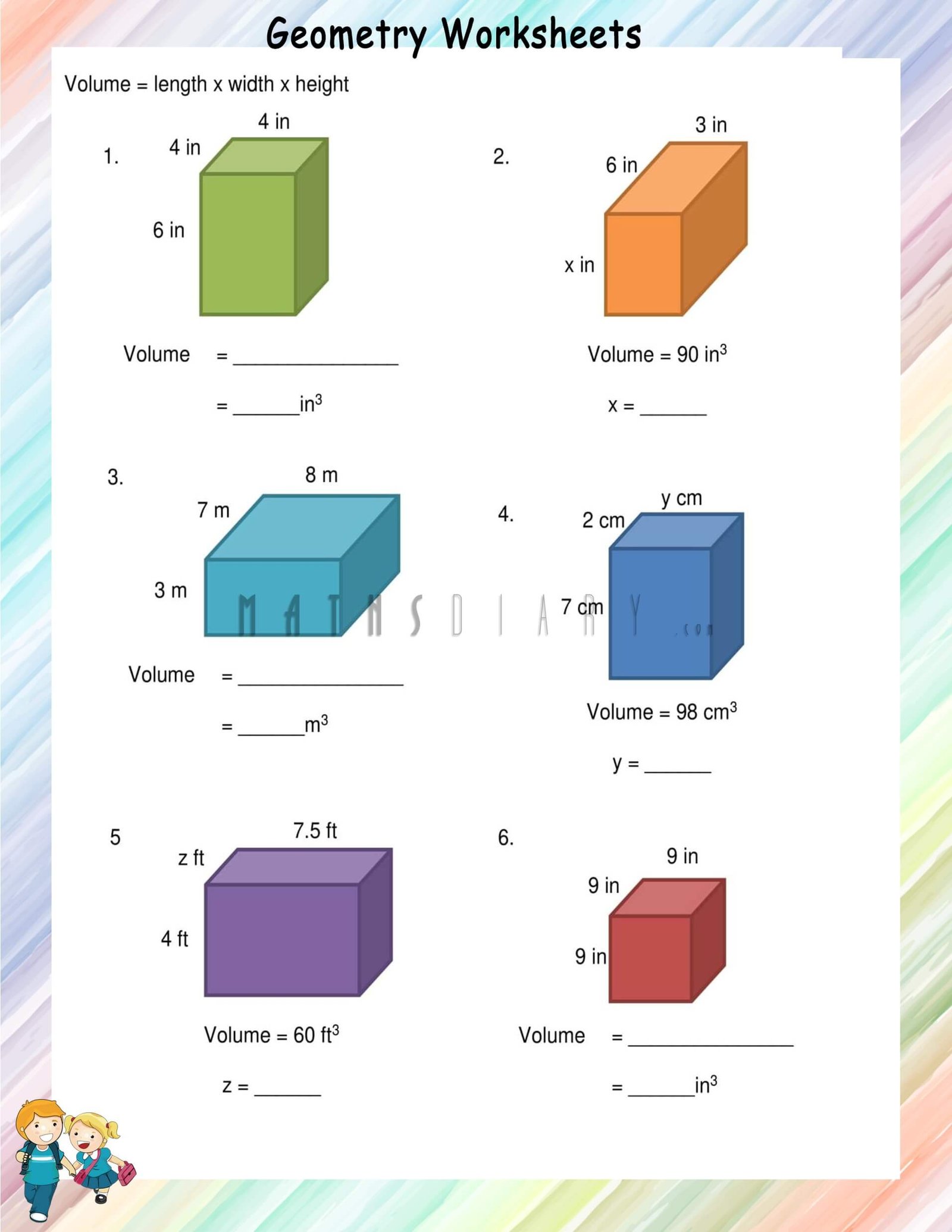
Let’s go through the process of calculating the volume of a rectangular prism step-by-step:
- Measure the Length (l): Identify the longest side of the base of the prism.
- Measure the Width (w): Measure along one of the sides of the base that’s not the length.
- Measure the Height (h): Measure the perpendicular height from the base to the top.
- Multiply the Measurements: Use the formula V = l * w * h to find the volume.
Example Calculation
Suppose you have a rectangular prism with the following dimensions:
| Dimension | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Length | 5 cm |
| Width | 4 cm |
| Height | 3 cm |

Using the formula, the volume V = 5 cm * 4 cm * 3 cm = 60 cubic centimeters (cm³).
Practical Applications

Understanding volume calculations is not just theoretical; it’s incredibly practical:
- In manufacturing, knowing the volume can help determine material requirements for product design.
- Architects use volume to calculate space, which can affect everything from heating and cooling to design functionality.
- For shipping, volume calculations are crucial for logistics and packaging.
- In 3D printing, estimating the amount of filament needed for a print relies on volume calculations.
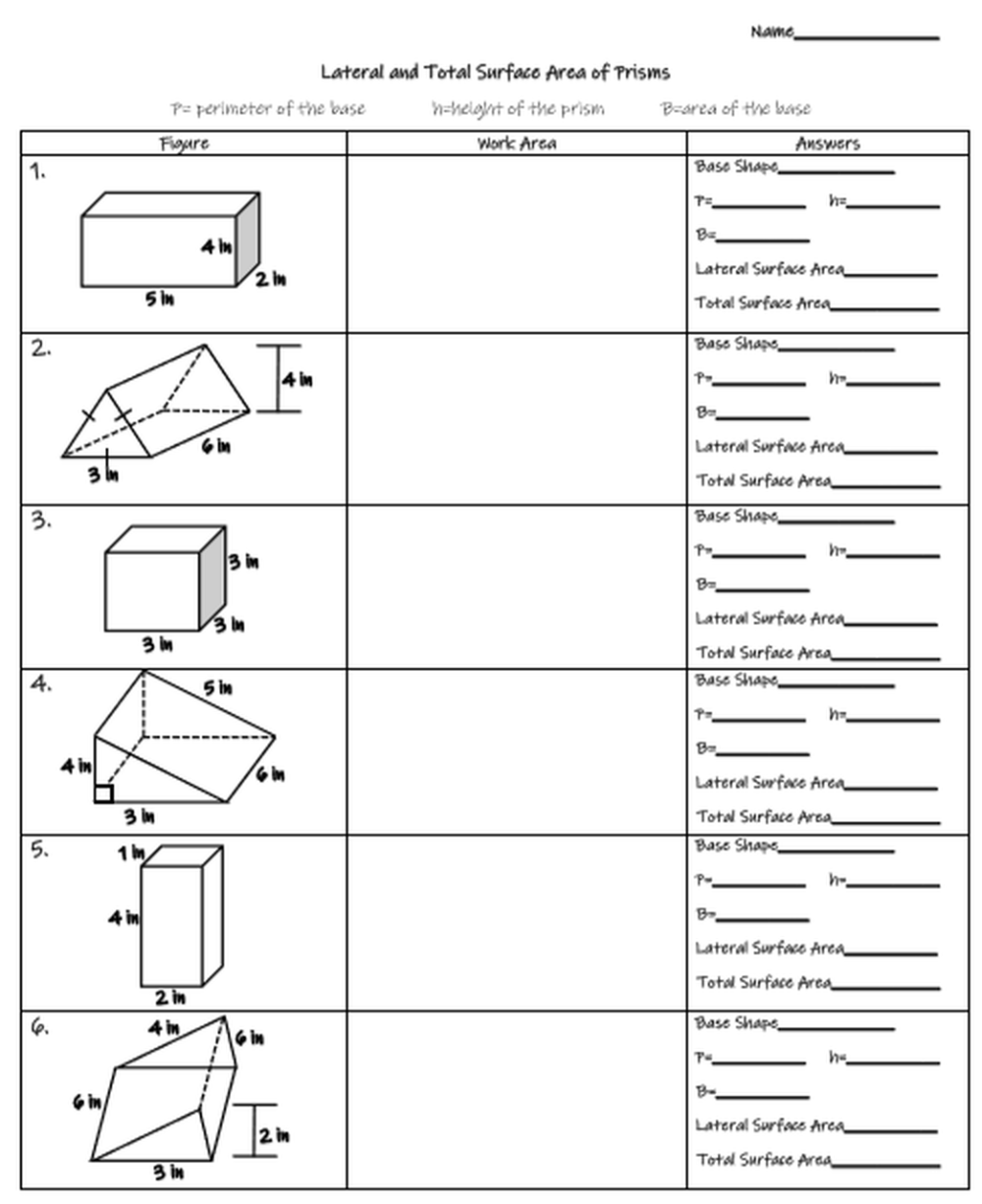
Worksheet Exercise
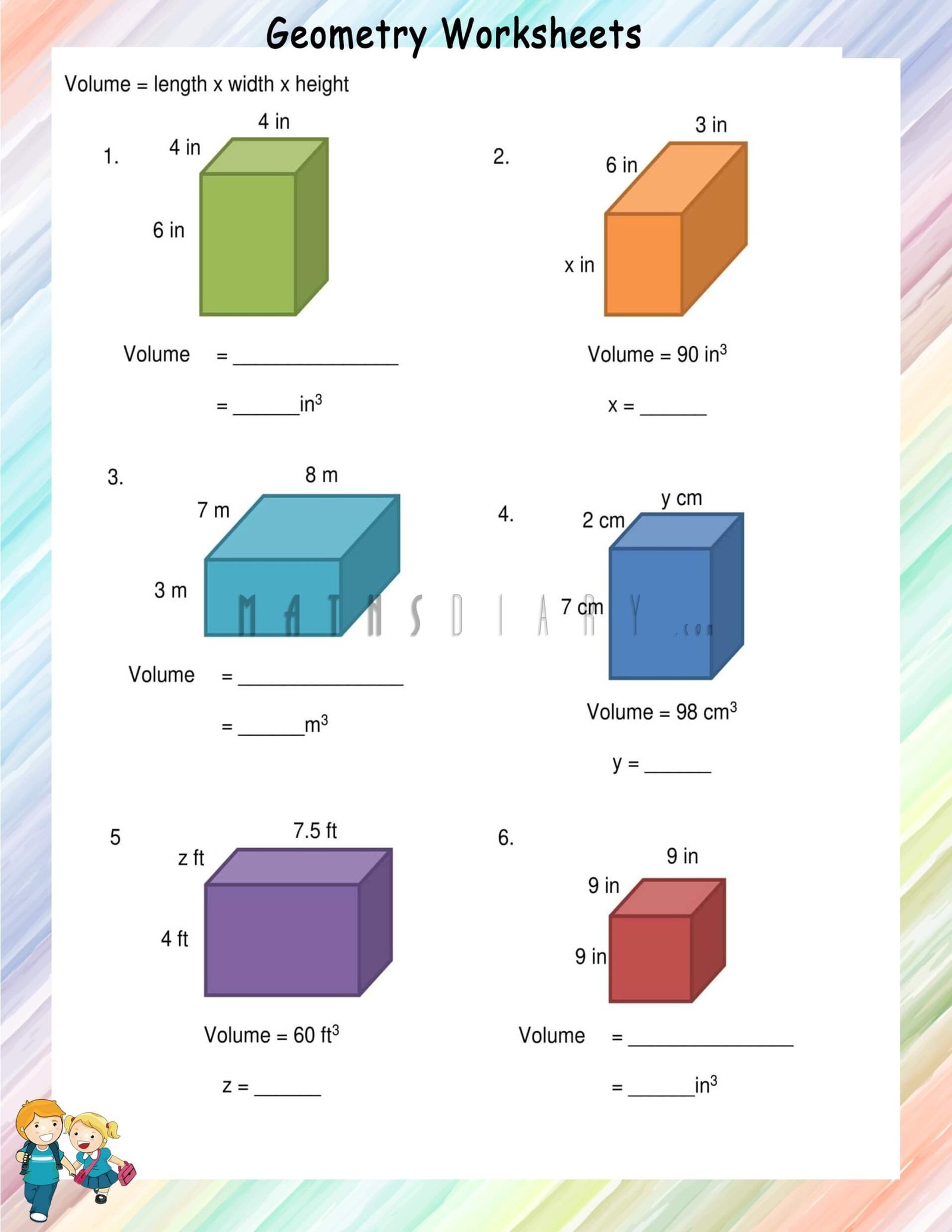
To practice, here are a few problems for you to solve:
- Calculate the volume of a rectangular prism with dimensions 7cm x 4cm x 10cm.
- A box has a base area of 48 square inches, and a height of 12 inches. What is its volume?
- Find the volume of a prism where the length is 6 feet, the width is 2 feet, and the height is 8 feet.
📝 Note: Ensure all units are consistent when calculating volume. Mixing units like centimeters with inches will lead to incorrect results.
After calculating the volumes in the worksheet exercises, here's how we might approach the answers:
- Problem 1: Volume = 7 cm * 4 cm * 10 cm = 280 cm³
- Problem 2: First, find the base side lengths using the area. Assuming a square base, each side would be √48 ≈ 6.928 inches. Volume = 48 sq.in * 12 in = 576 cu.in
- Problem 3: Volume = 6 ft * 2 ft * 8 ft = 96 ft³
In conclusion, mastering the volume of rectangular prisms involves understanding the foundational principles of geometry. By practicing with examples and exercises, you can solidify your knowledge of how to measure, calculate, and apply volume in various practical scenarios. It's a skill that not only aids in academic pursuits but also offers insights into real-world applications where spatial awareness and calculation precision are key.
What’s the difference between volume and surface area?

+
Volume measures the amount of space inside a 3D object, while surface area measures the total area of all surfaces of that object.
Why is it important to know the volume of a rectangular prism?

+
Knowing the volume is essential for manufacturing, design, logistics, and in any scenario where understanding the capacity of space is required.
How do you find the dimensions of a rectangular prism when you only know the volume?

+
If you know the volume and have at least one other dimension (like the height), you can divide the volume by the known dimension to find the area of the base, then solve for the other dimensions. However, without additional information, the dimensions are not uniquely determined.