Military
Veterans Copay Based on Income
Veterans Copay Based on Income: Understanding the System
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) offers healthcare services to eligible veterans, and the cost of these services can vary depending on the veteran’s income level. The VA uses a system to determine the copay amount for each veteran based on their income, which is designed to ensure that those who need care the most can access it at an affordable cost. In this article, we will delve into the details of the veterans copay system based on income, including how it works, the different copay tiers, and what factors affect the copay amount.
How the Veterans Copay System Works

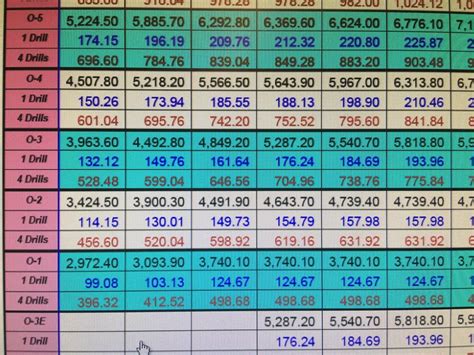
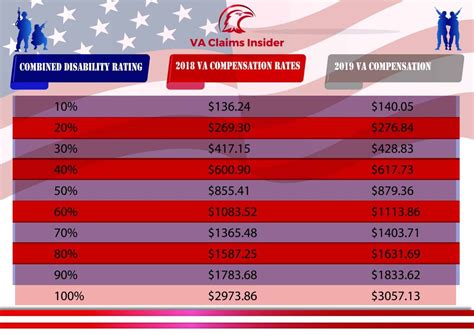
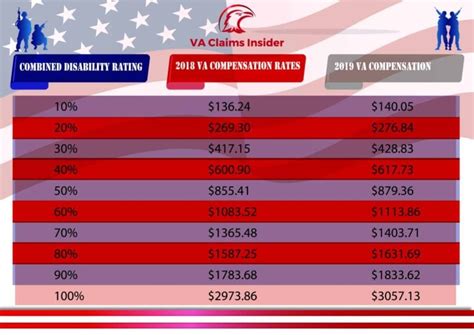
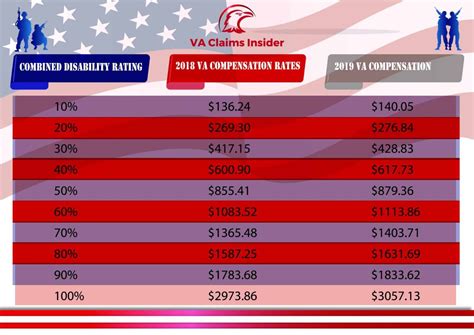
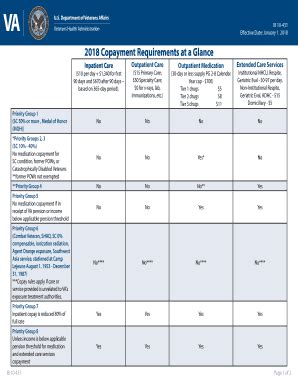
The VA uses a means-test to determine the copay amount for each veteran. This test takes into account the veteran’s income, as well as their family size, to determine their copay tier. The copay tiers are divided into eight categories, with Tier 1 being the lowest income level and Tier 8 being the highest. The copay amount increases as the veteran’s income level increases. The VA also considers other factors, such as the veteran’s disability rating, when determining their copay amount.
Copay Tiers and Income Levels

The following table shows the copay tiers and the corresponding income levels for a single veteran:
| Copay Tier | Income Level |
|---|---|
| Tier 1 | 0 - 12,907 |
| Tier 2 | 12,908 - 17,024 |
| Tier 3 | 17,025 - 23,078 |
| Tier 4 | 23,079 - 30,276 |
| Tier 5 | 30,277 - 38,362 |
| Tier 6 | 38,363 - 47,622 |
| Tier 7 | 47,623 - 60,000 |
| Tier 8 | $60,001 and above |

Note that these income levels are subject to change, and the VA may adjust them annually to reflect changes in the cost of living.
Factors Affecting Copay Amount
Several factors can affect the copay amount for veterans, including: * Income level: As mentioned earlier, the copay amount increases as the veteran’s income level increases. * Family size: The VA considers the veteran’s family size when determining their copay tier. * Disability rating: Veterans with a service-connected disability rating of 50% or higher may be eligible for a reduced copay amount. * Other health insurance: Veterans who have other health insurance coverage may be required to pay a higher copay amount. * Prescription medication: The copay amount for prescription medication may vary depending on the type of medication and the veteran’s copay tier.
📝 Note: Veterans should keep in mind that the copay system is subject to change, and they should check with the VA regularly to ensure they have the most up-to-date information.
How to Apply for a Copay Reduction

Veterans who are experiencing financial hardship may be eligible for a copay reduction. To apply for a copay reduction, veterans should: * Contact their local VA medical center to request a copay reduction application. * Provide documentation of their income and family size. * Submit the application to the VA for review. * Wait for a decision from the VA regarding their copay reduction application.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, the veterans copay system based on income is designed to ensure that eligible veterans can access the healthcare services they need at an affordable cost. By understanding how the system works and what factors affect the copay amount, veterans can make informed decisions about their healthcare. It is essential for veterans to stay informed about the copay system and to seek assistance if they are experiencing financial hardship.
What is the purpose of the veterans copay system?

+
The purpose of the veterans copay system is to ensure that eligible veterans can access the healthcare services they need at an affordable cost, based on their income level and other factors.
How do I apply for a copay reduction?
+
To apply for a copay reduction, contact your local VA medical center to request a copay reduction application, provide documentation of your income and family size, and submit the application to the VA for review.
What factors affect the copay amount?
+
Several factors can affect the copay amount, including income level, family size, disability rating, other health insurance, and prescription medication.