Mastering VBA to Select Worksheets Quickly
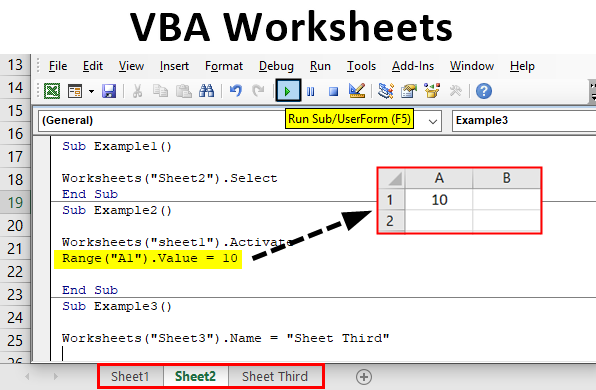
If you've ever found yourself sifting through numerous Excel worksheets to perform a task, you know how time-consuming and frustrating it can be. Whether you're an Excel user looking to streamline your workflow, a VBA programmer seeking to enhance your coding skills, or a manager overseeing data analysis in your organization, mastering VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) to select worksheets quickly can significantly improve your productivity. This comprehensive guide will delve into various techniques for managing worksheets with VBA, from selecting single or multiple sheets to employing advanced methodologies for enhanced functionality.
Understanding the Basics of VBA

Before we dive into the techniques for selecting worksheets, it's crucial to have a basic understanding of VBA. VBA, integrated into Microsoft Office applications like Excel, allows users to automate tasks, enhance functionality, and tailor Excel to meet their unique needs. Here's a quick primer:
- Macros: These are sets of instructions that automate repetitive tasks.
- VBA IDE: The Visual Basic Editor where you write, edit, and run your VBA code.
- Objects, Properties, and Methods: VBA deals with these components to interact with Excel elements.
Now, let's proceed to mastering worksheet selection with VBA.
Selecting a Single Worksheet


To select a worksheet using VBA, you can utilize the Worksheets collection or Sheets collection. Here are two common methods:
Using the Name

```vb Sub SelectSheetByName() Sheets("SheetName").Select End Sub ```
📝 Note: Replace "SheetName" with the actual name of your worksheet.
Using the Index

```vb Sub SelectSheetByIndex() Sheets(1).Select End Sub ```
📝 Note: The index number depends on the sheet's position in the workbook.
Selecting Multiple Worksheets

Selecting multiple worksheets can be handy when you need to format, delete, or perform actions across several sheets simultaneously. Here's how:
- Contiguous Sheets: To select a range of adjacent sheets: ```vb Sub SelectContiguousSheets() Sheets(Array("Sheet1", "Sheet2", "Sheet3")).Select End Sub ```
- Non-contiguous Sheets: For non-adjacent sheets: ```vb Sub SelectNonContiguousSheets() Sheets(Array("Sheet1", "Sheet3", "Sheet5")).Select End Sub ```
📝 Note: Ensure the sheet names in the array match exactly with those in your workbook.
Advanced Selection Techniques
VBA allows for more complex selections through various methods:
Using Sheet Names or Codename

If you prefer using codenames, which don't change when sheet names are modified:
```vb Sub SelectSheetByCodeName() Sheet1.Select End Sub ```Looping Through All Sheets

To perform an action on every sheet in the workbook:
```vb Sub LoopThroughSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets ws.Select ' Your code here Next ws End Sub ```📝 Note: This method might slow down execution if there are many sheets.
Error Handling and Best Practices

It's essential to handle errors gracefully when working with VBA to prevent your code from crashing:
Basic Error Handling

Sub ErrorHandlingExample()
On Error Resume Next
Sheets("InvalidSheetName").Select
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
MsgBox "Sheet not found. Please check the name."
Err.Clear
End If
End Sub
Turning Off Alerts

To avoid popup messages and improve performance:
Sub TurnOffAlerts()
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
' Your code here
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
End Sub
Table: VBA Methods for Selecting Sheets

| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Sheets(“SheetName”).Select | Selects a specific sheet by its name |
| Sheets(Index).Select | Selects a sheet by its position in the workbook |
| Sheets(Array(Sheet1, Sheet2)).Select | Selects multiple sheets by name |
| Sheet1.Select | Selects a sheet by its codename |
| For Each ws in ThisWorkbook.Worksheets | Loops through all worksheets |

In conclusion, mastering VBA to select worksheets quickly can drastically enhance your efficiency in Excel. By understanding how to select single and multiple sheets, employing advanced selection techniques, and applying best practices like error handling, you'll be able to automate and customize your work processes, saving time and reducing the potential for manual errors. Excel's capabilities, combined with VBA's flexibility, unlock a world of possibilities for data management and analysis.
Why should I use VBA for selecting worksheets?

+
VBA automates repetitive tasks, allowing you to perform actions on multiple sheets with a single command, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Can VBA select sheets from different workbooks?

+
Yes, you can select sheets from other workbooks by specifying the workbook first, like Workbooks("Book2.xlsx").Sheets("Sheet1").Select.
What happens if I select multiple sheets in VBA?

+
Selecting multiple sheets groups them together, allowing you to perform bulk operations like formatting or deleting.