US Navy S-3 Viking: Maritime Patrol and Reconnaissance

Introduction to the US Navy S-3 Viking

The Lockheed S-3 Viking is a four-seat, twin-engine turbofan-powered jet aircraft that was used by the United States Navy for anti-submarine warfare, reconnaissance, and patrol missions. The S-3 Viking was designed to replace the piston-powered S-2 Tracker and first flew in 1972. It was a critical component of the US Navy’s anti-submarine warfare capabilities during the Cold War era.
Design and Development

The S-3 Viking was designed to meet the US Navy’s requirement for a high-performance, carrier-based anti-submarine warfare aircraft. The aircraft’s design featured a high-wing configuration, with two General Electric TF34 turbofan engines providing a combined 22,500 pounds of thrust. The S-3 Viking had a maximum speed of over 450 knots (833 km/h) and a range of over 2,000 nautical miles (3,704 km).
The aircraft was equipped with a range of sensors and avionics, including radar, sonobuoys, and magnetic anomaly detectors (MAD). The S-3 Viking’s airframe was also designed to be highly durable, with a strong emphasis on corrosion resistance and reduced maintenance requirements.
Operational History
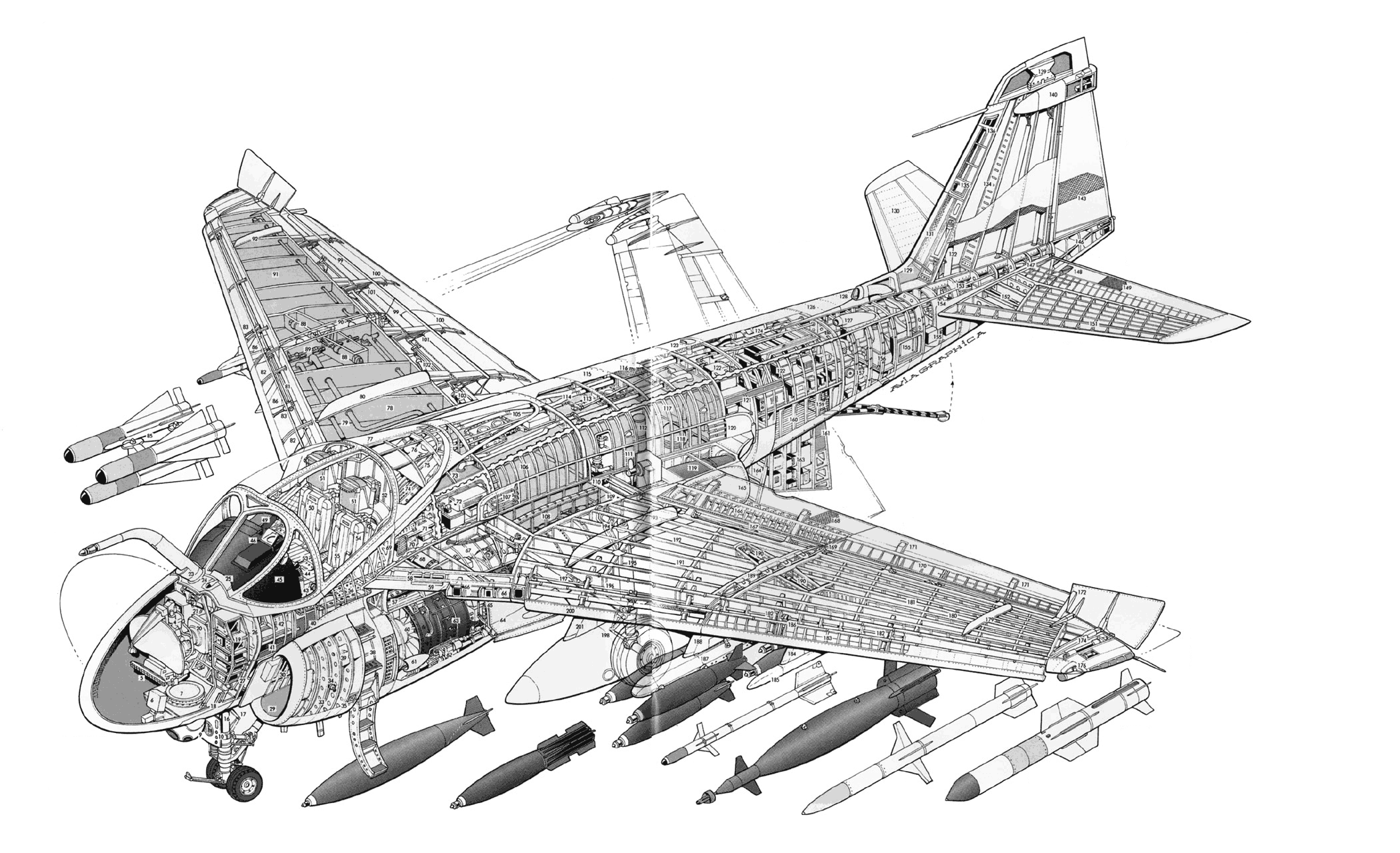
The S-3 Viking entered service with the US Navy in 1974 and quickly became a critical component of the Navy’s anti-submarine warfare capabilities. The aircraft was used for a range of missions, including:
- Anti-submarine warfare (ASW)
- Maritime patrol and reconnaissance
- Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR)
- Carrier-based reconnaissance
During its operational service, the S-3 Viking was used in a number of conflicts, including the Gulf War and the Yugoslav Wars. The aircraft’s versatility and range of capabilities made it an essential asset for the US Navy.
Key Features and Capabilities

- Anti-submarine warfare (ASW): The S-3 Viking was equipped with a range of ASW sensors, including sonobuoys and MAD. The aircraft could also carry a range of ASW torpedoes and depth charges.
- Maritime patrol and reconnaissance: The S-3 Viking was used for maritime patrol and reconnaissance missions, providing critical information on enemy shipping and naval movements.
- Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR): The S-3 Viking’s advanced sensors and avionics made it an ideal platform for ISR missions, providing critical information on enemy military movements and installations.
- Carrier-based reconnaissance: The S-3 Viking’s ability to operate from aircraft carriers made it an essential asset for carrier-based reconnaissance missions.
Operators and Variants

The S-3 Viking was operated by the US Navy, with a total of 188 aircraft produced. The S-3 Viking was also exported to a number of countries, including Argentina, Brazil, and Japan.
There were several variants of the S-3 Viking, including:
- S-3A: The initial production variant, which entered service in 1974.
- S-3B: An upgraded variant, which featured improved avionics and sensors.
- S-3V: A dedicated reconnaissance variant, which featured advanced sensors and avionics.
Retirement and Legacy

The S-3 Viking was retired from US Navy service in 2009, after over 35 years of operational service. The aircraft’s legacy is that of a highly capable and versatile maritime patrol and reconnaissance platform, which played a critical role in the US Navy’s anti-submarine warfare capabilities during the Cold War era.
The S-3 Viking’s advanced sensors and avionics made it an ideal platform for a range of missions, from anti-submarine warfare to intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance. The aircraft’s durability and low maintenance requirements also made it a favorite among pilots and maintenance personnel.
Comparison to Other Aircraft

The S-3 Viking was a unique aircraft, with a range of capabilities that set it apart from other maritime patrol and reconnaissance platforms. Some of the key differences between the S-3 Viking and other aircraft include:
- Lockheed P-3 Orion: The P-3 Orion was a turboprop-powered maritime patrol aircraft, which was used by the US Navy and other countries. The P-3 Orion had a longer range and endurance than the S-3 Viking, but was less capable in terms of speed and maneuverability.
- Northrop Grumman E-2 Hawkeye: The E-2 Hawkeye was a carrier-based airborne early warning aircraft, which was used by the US Navy. The E-2 Hawkeye had a similar range and endurance to the S-3 Viking, but was less capable in terms of anti-submarine warfare and reconnaissance.
Conclusion

The US Navy S-3 Viking was a highly capable and versatile maritime patrol and reconnaissance aircraft, which played a critical role in the US Navy’s anti-submarine warfare capabilities during the Cold War era. The aircraft’s advanced sensors and avionics, combined with its durability and low maintenance requirements, made it an ideal platform for a range of missions.
As the S-3 Viking is retired from service, its legacy will be remembered as a highly effective and reliable aircraft, which served the US Navy and other countries for over 35 years.
What was the primary mission of the S-3 Viking?

+
The primary mission of the S-3 Viking was anti-submarine warfare (ASW), although it was also used for maritime patrol and reconnaissance, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR), and carrier-based reconnaissance.
What was the range and endurance of the S-3 Viking?

+
The S-3 Viking had a maximum range of over 2,000 nautical miles (3,704 km) and an endurance of up to 5 hours.
What was the top speed of the S-3 Viking?

+
The top speed of the S-3 Viking was over 450 knots (833 km/h).
Related Terms:
- Northrop Grumman E 2 Hawkeye
- A 6 Intruder
- McDonnell Douglas F A 18 Hornet
- Grumman F 14 Tomcat
- s 3 viking crew positions