Aging in the Ranks: US Military Soldier Health Concerns
Aging in the Ranks: US Military Soldier Health Concerns

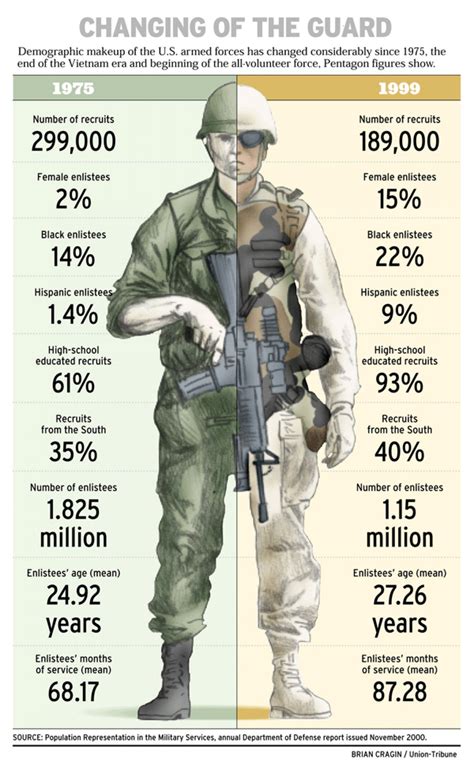
The US military is composed of individuals from diverse backgrounds, ages, and experiences. However, one factor that affects every soldier is the natural process of aging. As soldiers progress through their careers, they face unique health challenges that can impact their performance, deployment readiness, and overall quality of life. In this article, we will explore the health concerns associated with aging in the US military and discuss potential solutions to mitigate these issues.
Physical Demands of Military Service

Military service is physically demanding, requiring soldiers to perform tasks that push their bodies to the limit. The physical demands of military service can lead to various health problems, including musculoskeletal injuries, cardiovascular disease, and mental health issues. As soldiers age, their bodies may not be able to recover as quickly from these physical demands, leading to increased risk of chronic health problems.
Health Concerns Associated with Aging in the Military

Aging soldiers face a range of health concerns, including:
- Musculoskeletal injuries: Older soldiers are more prone to musculoskeletal injuries, such as joint pain, tendonitis, and stress fractures.
- Cardiovascular disease: As soldiers age, they are at increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
- Mental health issues: Older soldiers may experience mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- Cognitive decline: Aging can affect cognitive function, including memory, attention, and decision-making abilities.
- Sleep disorders: Older soldiers may experience sleep disorders, such as insomnia and sleep apnea.
- Chronic diseases: Aging soldiers are at increased risk of developing chronic diseases, such as diabetes, arthritis, and certain types of cancer.
Factors Contributing to Health Concerns in Aging Soldiers
Several factors contribute to the health concerns associated with aging in the military, including:
- Cumulative wear and tear: The physical demands of military service can lead to cumulative wear and tear on the body, increasing the risk of chronic health problems.
- Lack of physical activity: Older soldiers may experience a decline in physical activity, leading to a range of health problems.
- Poor nutrition: A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats can contribute to chronic health problems.
- Sleep deprivation: Military service often requires soldiers to work irregular schedules, leading to sleep deprivation and related health problems.
- Stress and trauma: Military service can be traumatic, leading to mental health issues and stress-related health problems.
Potential Solutions to Mitigate Health Concerns

To mitigate the health concerns associated with aging in the military, the following potential solutions can be implemented:
- Fitness programs: The military can implement fitness programs specifically designed for older soldiers, focusing on low-impact exercises and flexibility training.
- Nutrition education: Providing nutrition education and promoting healthy eating habits can help older soldiers maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Sleep management: Implementing sleep management strategies, such as establishing regular sleep schedules and creating sleep-conducive environments, can help older soldiers get adequate rest.
- Mental health support: Providing mental health support and resources can help older soldiers manage stress and trauma-related health problems.
- Health screenings: Regular health screenings can help identify health problems early, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of chronic diseases.
Implementation of Solutions

Implementing solutions to mitigate health concerns in aging soldiers requires a multi-faceted approach, involving:
- Leadership support: Military leaders must prioritize the health and well-being of older soldiers, providing resources and support for fitness programs, nutrition education, and mental health support.
- Healthcare provider engagement: Healthcare providers must be engaged in the process, providing regular health screenings and treatment for chronic health problems.
- Soldier education: Soldiers must be educated on the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, healthy eating, and stress management.
- Family support: Family members can play a critical role in supporting older soldiers, providing emotional support and helping to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
👥 Note: The military can also consider offering incentives for older soldiers to participate in fitness programs and nutrition education, such as reduced healthcare costs or increased leave time.
Conclusion

Aging in the military is a complex issue, requiring a comprehensive approach to mitigate health concerns. By implementing fitness programs, nutrition education, sleep management strategies, mental health support, and health screenings, the military can help older soldiers maintain their health and well-being. Leadership support, healthcare provider engagement, soldier education, and family support are critical components of a successful approach to addressing the health concerns associated with aging in the military.
What are the most common health concerns for aging soldiers in the military?

+
The most common health concerns for aging soldiers include musculoskeletal injuries, cardiovascular disease, mental health issues, cognitive decline, sleep disorders, and chronic diseases such as diabetes and arthritis.
What can the military do to support the health and well-being of older soldiers?
+
The military can implement fitness programs, provide nutrition education, offer sleep management strategies, provide mental health support, and conduct regular health screenings to support the health and well-being of older soldiers.
What role can family members play in supporting the health and well-being of older soldiers?

+
Family members can play a critical role in supporting the health and well-being of older soldiers by providing emotional support, helping to maintain a healthy lifestyle, and encouraging participation in fitness programs and nutrition education.



