United States Air Force Intelligence

Overview of United States Air Force Intelligence

The United States Air Force Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) agency is a critical component of the US Air Force, responsible for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating vital information to support national security and defense strategies. The agency plays a crucial role in providing timely and accurate intelligence to commanders, policymakers, and warfighters, enabling them to make informed decisions and take effective actions.
History of Air Force Intelligence

The US Air Force Intelligence agency has its roots in the early days of military aviation. In 1917, the US Army Signal Corps established the first military intelligence unit, which focused on aerial reconnaissance and intelligence gathering. Over the years, the agency has evolved and expanded its mission to address emerging threats and technological advancements.
During World War II, the US Army Air Forces (USAAF) established the first centralized intelligence agency, which played a significant role in supporting Allied operations. In the post-war period, the US Air Force continued to develop its intelligence capabilities, with a focus on strategic reconnaissance and signals intelligence.
Organization and Structure

The US Air Force Intelligence agency is organized into several key components, each with distinct responsibilities:
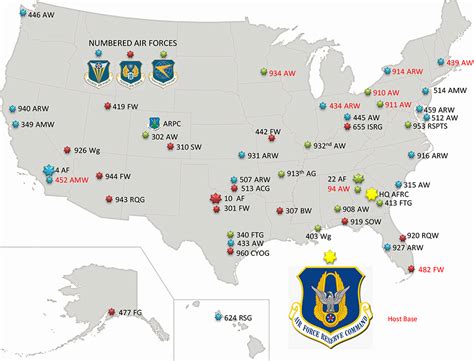
- Air Force Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance Agency (AFISRA): AFISRA is the primary intelligence agency of the US Air Force, responsible for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating intelligence to support national security and defense strategies.
- National Air and Space Intelligence Center (NASIC): NASIC is a critical component of AFISRA, providing strategic intelligence on foreign air and space capabilities, including ballistic missiles, space systems, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
- Air Force Cryptologic Office: The Air Force Cryptologic Office is responsible for providing cryptographic support to US Air Force units, including encryption, decryption, and signals intelligence.
Intelligence Collection and Analysis

The US Air Force Intelligence agency employs a range of methods to collect and analyze intelligence, including:
- Imagery Intelligence (IMINT): IMINT involves the collection and analysis of imagery from various sources, including satellites, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and manned aircraft.
- Signals Intelligence (SIGINT): SIGINT involves the collection and analysis of signals from various sources, including communications, radar, and other electronic systems.
- Human Intelligence (HUMINT): HUMINT involves the collection of intelligence from human sources, including interviews, interrogations, and other forms of human interaction.
- Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT): OSINT involves the collection and analysis of publicly available information, including social media, news reports, and other open-source materials.
🔍 Note: The US Air Force Intelligence agency also employs advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), to enhance its intelligence collection and analysis capabilities.
Intelligence Support to Operations

The US Air Force Intelligence agency provides critical intelligence support to a range of operations, including:
- Tactical Operations: Intelligence support to tactical operations involves providing real-time intelligence to warfighters, enabling them to make informed decisions and take effective actions.
- Strategic Operations: Intelligence support to strategic operations involves providing long-term intelligence to commanders and policymakers, enabling them to develop and implement effective national security and defense strategies.
- Special Operations: Intelligence support to special operations involves providing tailored intelligence to special operations forces, enabling them to conduct effective operations in a range of environments.
Challenges and Future Directions
The US Air Force Intelligence agency faces a range of challenges, including:
- Emerging Threats: The agency must address emerging threats, including cyber threats, terrorism, and the proliferation of advanced technologies.
- Technological Advancements: The agency must keep pace with technological advancements, including the development of new sensors, platforms, and analytical tools.
- Resource Constraints: The agency must operate within resource constraints, including budget and personnel limitations.
To address these challenges, the US Air Force Intelligence agency is investing in a range of initiatives, including:
- Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) Modernization: The agency is modernizing its ISR capabilities, including the development of new sensors, platforms, and analytical tools.
- Cybersecurity: The agency is enhancing its cybersecurity capabilities, including the development of new technologies and strategies to counter emerging cyber threats.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): The agency is leveraging AI and ML to enhance its intelligence collection and analysis capabilities.
In summary, the US Air Force Intelligence agency plays a critical role in supporting national security and defense strategies. The agency’s history, organization, and structure provide a foundation for understanding its intelligence collection and analysis capabilities. The agency’s support to operations and its efforts to address emerging challenges and future directions are critical to its success.
What is the primary mission of the US Air Force Intelligence agency?
+
The primary mission of the US Air Force Intelligence agency is to collect, analyze, and disseminate vital information to support national security and defense strategies.
What are the key components of the US Air Force Intelligence agency?

+
The key components of the US Air Force Intelligence agency include AFISRA, NASIC, and the Air Force Cryptologic Office.
What methods does the US Air Force Intelligence agency employ to collect and analyze intelligence?

+
The US Air Force Intelligence agency employs a range of methods, including IMINT, SIGINT, HUMINT, and OSINT.
Related Terms:
- Air Force Intelligence Officer salary
- Us air force intelligence
- Intelligence Analyst Air Force
- 16th Air Force
- Air Force Intelligence mos
- Intelligence website



