5 DNA Structure and Replication Tips

Delving into the intricacies of DNA structure and replication can be a fascinating journey for those keen on understanding the basic building blocks of life. Here are five tips that can help you grasp these complex scientific concepts with ease:
1. Understand the Double Helix Model
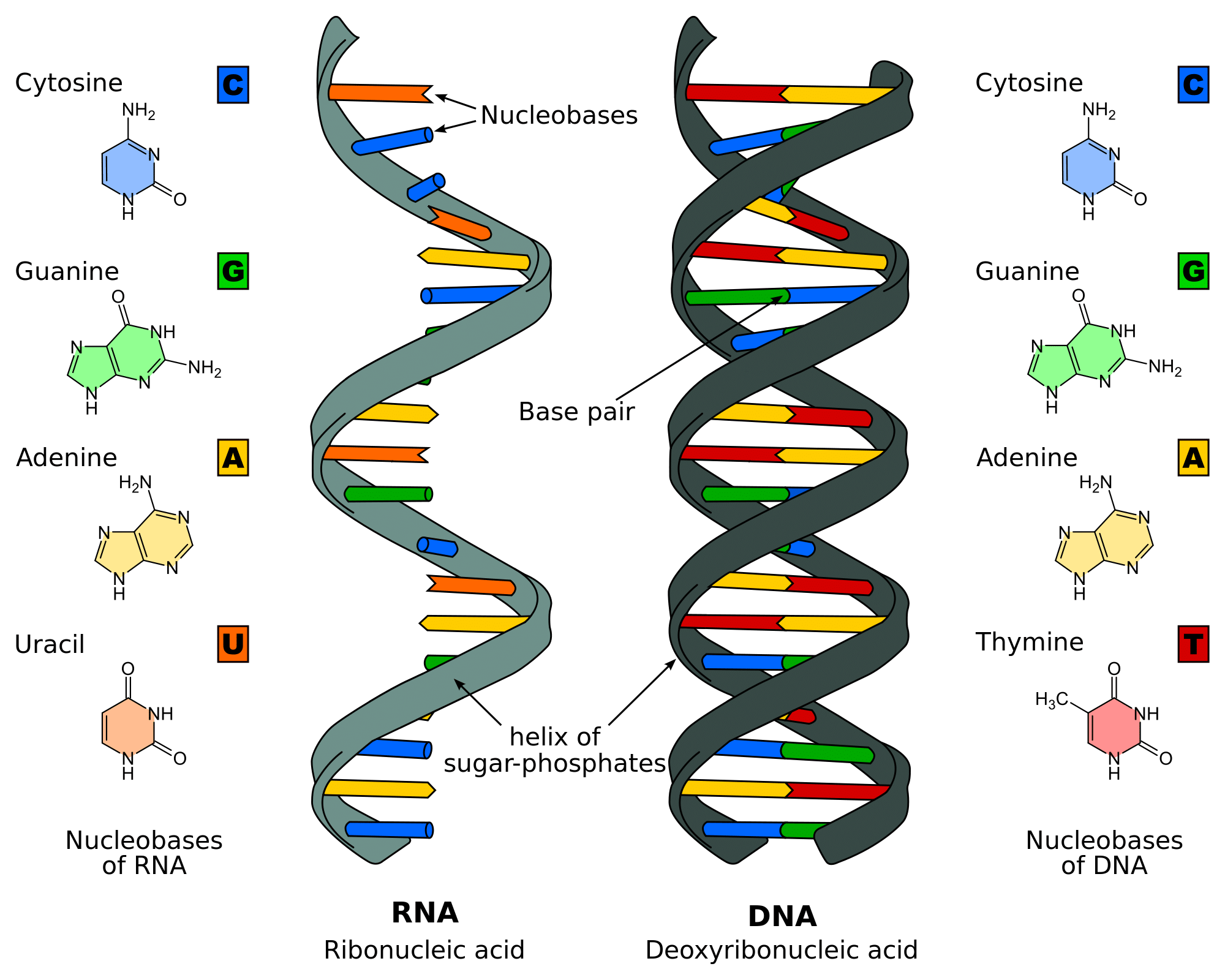
The structure of DNA is often described as a double helix, which might conjure images of a twisted ladder or a spiraling staircase. This model, developed by Watson and Crick in the 1950s, revolutionized the understanding of genetics:
- Sides of the Ladder: These are composed of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate molecules, forming the backbone of the DNA.
- Rungs of the Ladder: These are the base pairs, adenine (A) with thymine (T) and cytosine (C) with guanine (G). This pairing is not random but follows base-pairing rules.
- Key Concept: The bases are hydrogen bonded to each other, ensuring stability to the structure.
🔬 Note: The 3D structure of DNA allows for a stable storage of genetic information which is essential for the replication process.
2. Learn the Replication Process

DNA replication is a fundamental cellular process where one cell divides, and each daughter cell receives an identical copy of DNA:
- Initiation: This step occurs at specific points called origins of replication, where the DNA strands begin to separate.
- Elongation: New strands are synthesized using the original strand as a template. Each new strand forms along one of the original strands in a semi-conservative manner.
- Termination: Replication completes with the formation of two identical DNA molecules, ready for distribution among daughter cells.
📝 Note: The enzymes involved in replication, like DNA polymerase, ensure high accuracy, but errors can still occur leading to mutations.
3. Visualize the Process

Visual aids can significantly enhance the understanding of complex processes like DNA replication:
- Animated Diagrams: Videos showing how DNA unwinds, how nucleotides pair, and the role of various proteins.
- Interactive Models: Software or physical models where you can manipulate parts of DNA to see the impact on replication.

4. Familiarize with Key Enzymes

Understanding the roles of various enzymes in DNA replication can deepen your knowledge:
- Helicases: Unwind the double helix.
- Topoisomerases: Help prevent supercoiling.
- Primase: Synthesizes a short RNA primer.
- DNA Polymerases: Add nucleotides to the growing DNA strand.
- Ligases: Join Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
5. Master the Concept of Semi-Conservative Replication

The semi-conservative model of DNA replication explains how each daughter molecule contains one parental (old) and one new strand:
- Each replication event doubles the DNA content without losing any genetic information.
- This model was experimentally proven, which is critical for understanding genetic continuity.
These tips provide a comprehensive overview of DNA structure and its replication, covering the key scientific concepts necessary for anyone looking to delve into the fundamentals of genetics. The elegance and complexity of DNA make it one of nature's most awe-inspiring creations, enabling life's continuity and diversity.
Why is the double helix structure of DNA important?

+
The double helix allows for effective replication and storage of genetic information, maintaining the stability of the molecule while allowing for access to the information.
Can DNA replication occur without any enzymes?

+
Enzymes are crucial for DNA replication; without them, the process would be significantly slower and error-prone, if it occurred at all.
What is the significance of base pairing in DNA?

+
Base pairing ensures the accuracy of replication and allows for the formation of genes that are read by the cellular machinery to produce proteins.



