UK Defence Spending Trends Since 1945
UK Defence Spending Trends Since 1945: A Historical Analysis

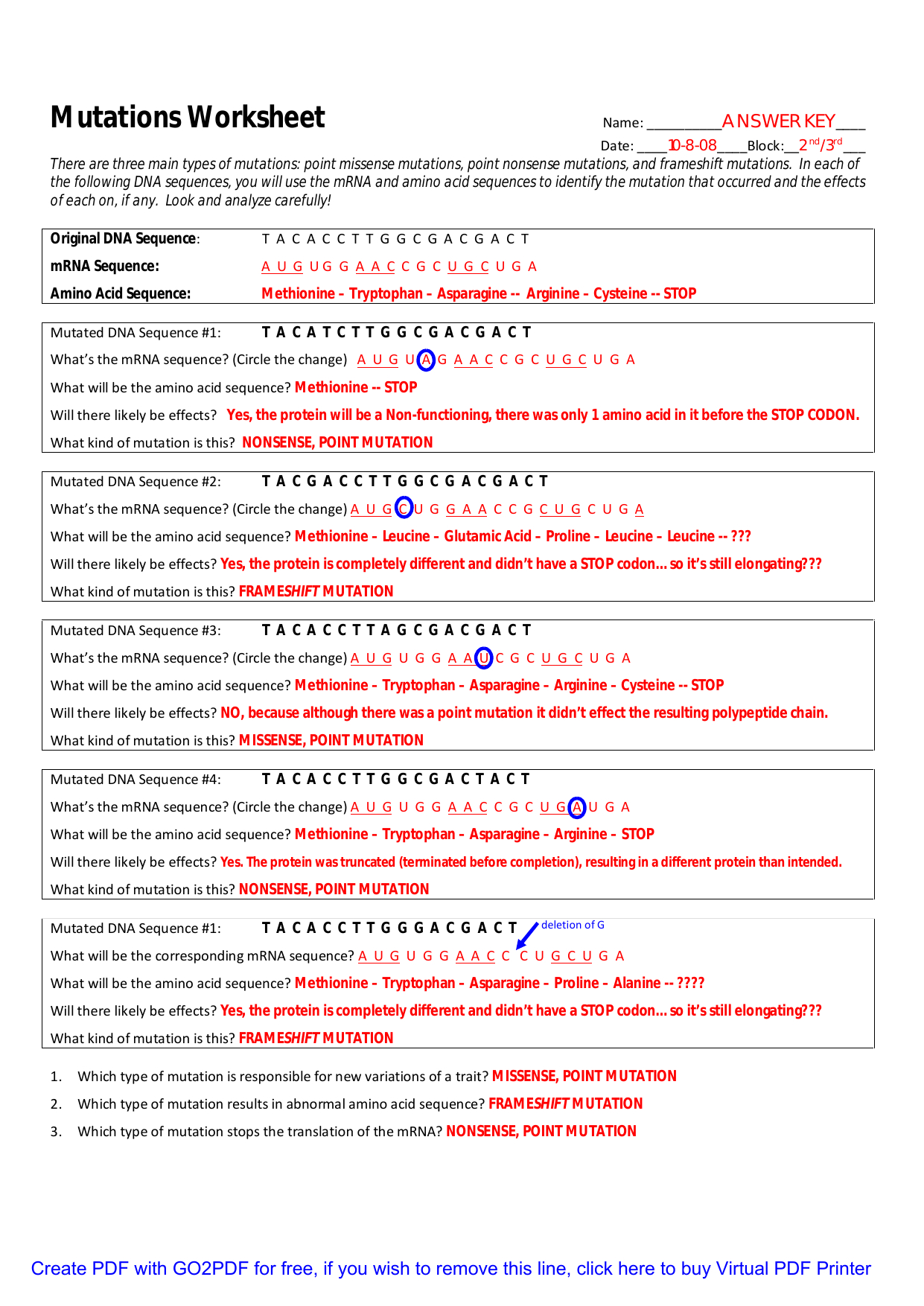
The United Kingdom’s defence spending has undergone significant changes since the end of World War II in 1945. This period has seen the country’s defence budget fluctuate in response to various global events, technological advancements, and shifting national priorities. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the UK’s defence spending trends since 1945, highlighting key events, policies, and their impact on the country’s military expenditure.
Post-War Period (1945-1960)
In the immediate aftermath of World War II, the UK’s defence spending remained high, with the country still maintaining a significant military presence around the world. The UK’s defence budget peaked in 1946, accounting for approximately 12% of the country’s GDP. However, as the Cold War intensified, the UK began to reduce its defence spending, with the budget decreasing to around 8% of GDP by the late 1950s.
📊 Note: The UK's defence spending during this period was heavily influenced by the country's commitment to NATO and the Korean War.
Cold War Era (1960-1990)

The Cold War marked a significant shift in the UK’s defence spending, with the country’s military budget fluctuating in response to the Soviet Union’s military expansion. The UK’s defence spending increased during the 1970s and 1980s, with the budget reaching around 5% of GDP. This period saw significant investments in nuclear deterrence, with the development of the Polaris and Trident missile systems.
💣 Note: The UK's nuclear deterrent was a key component of its defence strategy during the Cold War, with the country maintaining a nuclear arsenal to counter the Soviet Union's military might.
Post-Cold War Era (1990-2001)

The collapse of the Soviet Union marked a significant reduction in the UK’s defence spending, with the budget decreasing to around 3% of GDP by the late 1990s. This period saw a shift in the UK’s defence priorities, with the country focusing on peacekeeping and humanitarian interventions.
War on Terror and the Iraq War (2001-2010)

The 9⁄11 attacks and the subsequent War on Terror led to a significant increase in the UK’s defence spending, with the budget reaching around 4% of GDP by the mid-2000s. The UK’s involvement in the Iraq War also saw a significant increase in military expenditure, with the country committing troops and resources to the conflict.
🏆 Note: The UK's military involvement in the Iraq War was widely criticized, leading to a significant reduction in public support for the country's defence spending.
Austerity and the SDSR (2010-2015)
The 2010 Strategic Defence and Security Review (SDSR) marked a significant shift in the UK’s defence spending, with the country committing to reduce its military budget by 8% over four years. The SDSR also saw a reduction in the UK’s military personnel and the closure of several military bases.
💼 Note: The SDSR was widely criticized by the UK's military establishment, with many arguing that the reductions would compromise the country's national security.
Current Trends (2015-Present)
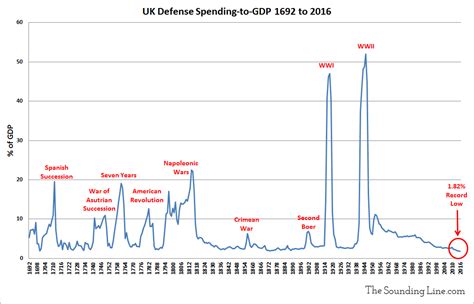
The UK’s defence spending has continued to fluctuate in recent years, with the country committing to increase its military budget by 0.5% above inflation until 2025. The UK’s defence priorities have also shifted, with the country focusing on cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and the development of a new generation of military equipment.
🤖 Note: The UK's investment in emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and cybersecurity, reflects the country's recognition of the changing nature of modern warfare.
| Year | Defence Spending ( £ billion) | % of GDP |
|---|---|---|
| 1946 | £3.4 billion | 12.1% |
| 1960 | £1.4 billion | 8.1% |
| 1980 | £10.3 billion | 5.3% |
| 1995 | £23.2 billion | 3.4% |
| 2005 | £31.3 billion | 4.1% |
| 2015 | £34.4 billion | 2.2% |
| 2020 | £43.1 billion | 2.5% |
The UK’s defence spending has undergone significant changes since 1945, reflecting the country’s response to global events, technological advancements, and shifting national priorities. While the country’s defence budget has fluctuated over the years, the UK remains committed to maintaining a capable and effective military, with a focus on emerging technologies and a continued commitment to NATO and international security.
In summary, the UK’s defence spending trends since 1945 reflect the country’s ongoing efforts to balance its military capabilities with the demands of a rapidly changing global security environment.
What was the UK’s defence spending like during the post-war period?
+
The UK’s defence spending remained high in the immediate aftermath of World War II, accounting for approximately 12% of the country’s GDP in 1946. However, as the Cold War intensified, the UK began to reduce its defence spending, with the budget decreasing to around 8% of GDP by the late 1950s.
How did the UK’s defence spending change during the Cold War era?
+
The UK’s defence spending increased during the 1970s and 1980s, with the budget reaching around 5% of GDP. This period saw significant investments in nuclear deterrence, with the development of the Polaris and Trident missile systems.
What was the impact of the War on Terror on the UK’s defence spending?
+
The War on Terror led to a significant increase in the UK’s defence spending, with the budget reaching around 4% of GDP by the mid-2000s. The UK’s involvement in the Iraq War also saw a significant increase in military expenditure.
Related Terms:
- uk defence spending since 1945
- UK military budget percentage
- UK defence spending 2024
- UK defence spending 1930s
- UK defence budget 2010
- UK defence spending increase