Explore Different Soil Types in Our Fun Worksheet

In the realm of gardening, understanding the variety of soil types is fundamental for any enthusiast or professional. Soil is not just dirt; it is a complex, living medium that plants call home. This article dives deep into the different soil types and how they affect plant growth, offering you an educational and engaging worksheet to deepen your knowledge. Whether you're planning to improve your garden or are simply curious about the ground beneath your feet, this exploration into soil science is for you.
Understanding the Basics of Soil
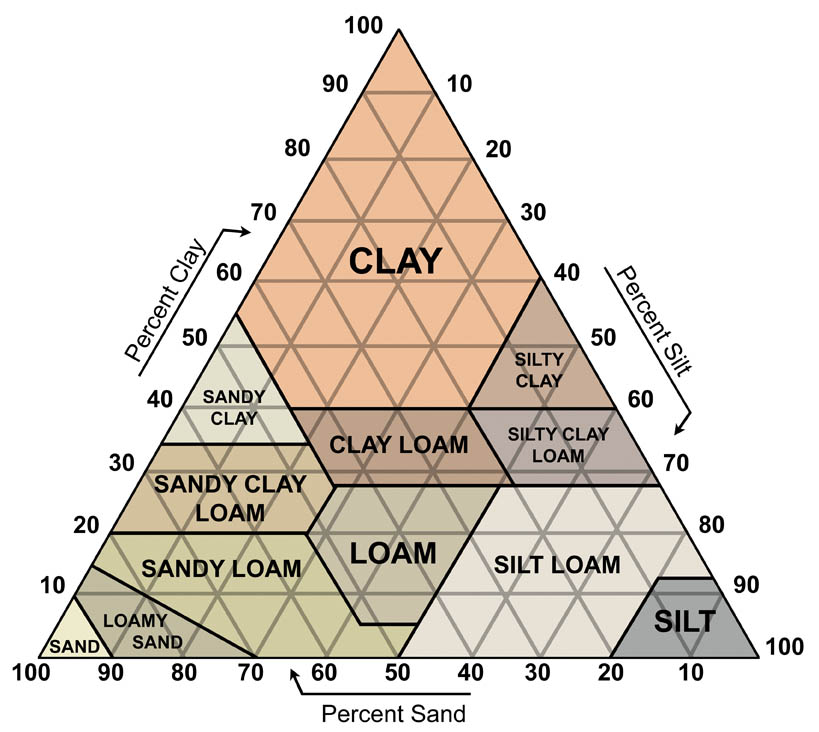
Soil isn’t merely earth; it’s an intricate ecosystem teeming with life and essential for the growth of all terrestrial plants. Here’s what you need to know:
- Soil Composition: Soil is made up of minerals, organic matter, water, air, and microorganisms. The mineral content varies greatly from one location to another, impacting soil texture and fertility.
- Soil Structure: This refers to how soil particles are grouped together and the pore space between them. It influences water infiltration, drainage, root penetration, and air movement in soil.
- Soil Texture: The proportion of sand, silt, and clay in soil determines its texture. Texture affects everything from soil drainage to nutrient retention.
🌱 Note: Different plants require different soil conditions. Understanding soil basics helps in creating an optimal growing environment.
Soil Classification by Texture

| Soil Type | Characteristics | Ideal for |
|---|---|---|
| Sandy Soil | Larger particles, fast drainage, poor nutrient retention | Plants that like dry conditions, like succulents |
| Loamy Soil | Balanced mix of sand, silt, and clay, excellent fertility | Most vegetable crops, flowers, and grasses |
| Clayey Soil | Small particles, heavy, slow drainage, good nutrient retention | Plants that require more moisture, like rice |
| Peaty Soil | High organic content, moisture retention, low nutrient content | Acid-loving plants like azaleas and blueberries |
| Chalky Soil | Limestone-rich, alkaline, poor for most plants but suitable for those that thrive in such conditions | Lavender, rosemary, and other Mediterranean plants |

Soil Worksheet
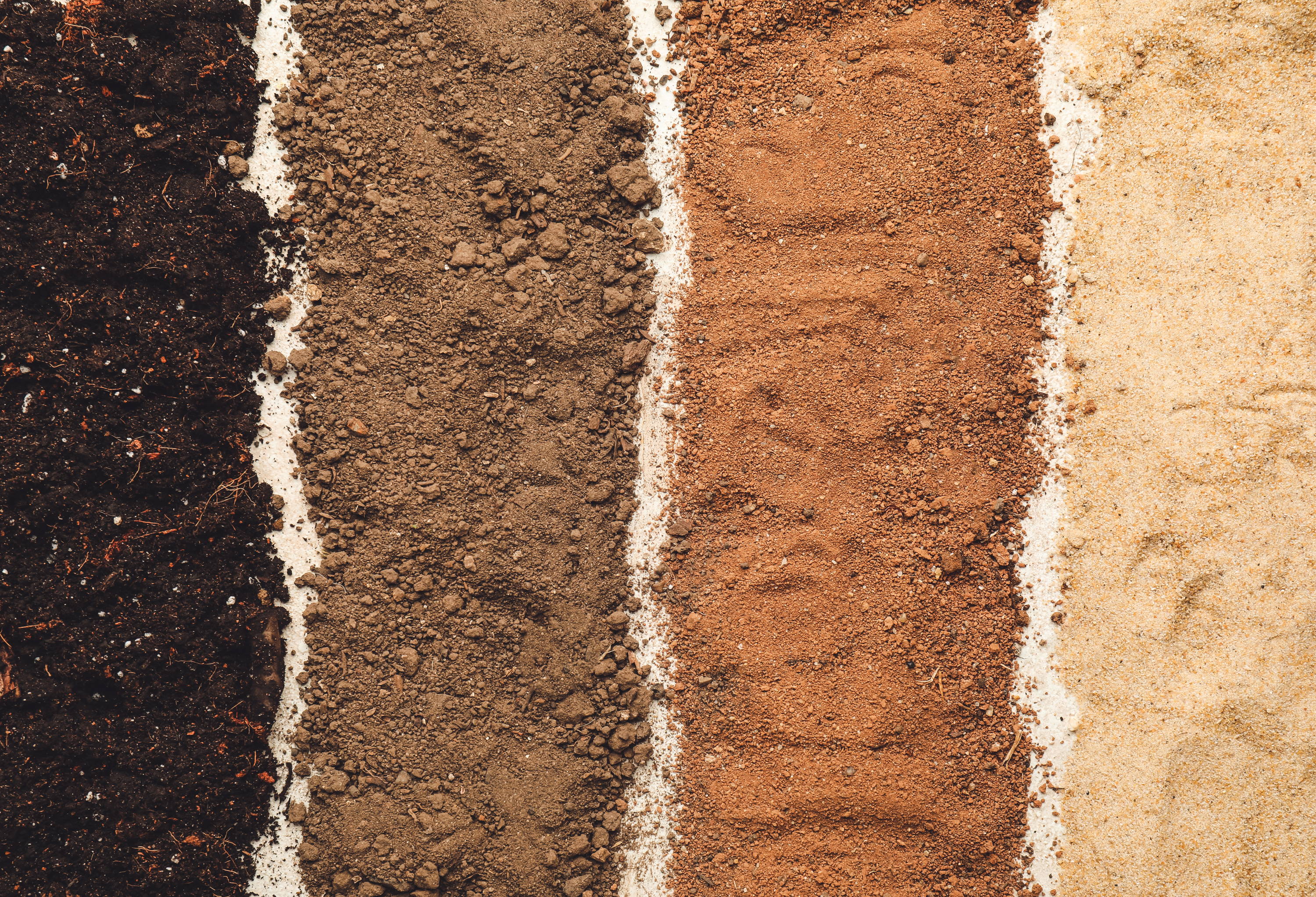

Let’s make learning interactive with a worksheet that helps you understand soil types:
- Soil Identification: Collect soil samples from your garden or nearby areas. Describe each soil type using the characteristics outlined above.
- Soil Texture by Feel: Feel the soil in your hand. Sandy soils feel gritty, silt soils feel smooth, and clay soils feel sticky when wet.
- Water Infiltration Test: Pour water on different soil samples and observe how quickly it drains. This helps to understand soil structure and drainage.
- pH Testing: Use a soil pH test kit or litmus paper to determine the acidity or alkalinity of the soil. This information is crucial for plant selection and soil amendment.
- Plant-Suitability Matrix: Create a table or list to match common garden plants with suitable soil types based on your findings.
Improving Soil Health

Once you’ve identified your soil type, here are some strategies to enhance its quality:
- Add Organic Matter: Compost, manure, and other organic materials enrich soil with nutrients and improve its structure.
- Mulching: This conserves moisture, reduces weed growth, and as organic mulch decomposes, it enriches the soil.
- Soil Testing: Regularly test your soil to adjust pH levels or nutrient deficiencies.
- Crop Rotation: Changing what you grow in a given area reduces nutrient depletion and soil-borne diseases.
- Minimizing Soil Disturbance: Avoid over-tilling as it can disrupt soil structure and microbial life.
🍃 Note: Remember, improving soil health is an ongoing process that benefits not just your plants, but the entire garden ecosystem.
Soil’s Role in Sustainability

The quality of soil directly impacts sustainability in gardening and agriculture:
- Erosion Control: Healthy soils with good structure reduce erosion, preserving the land’s fertility for future use.
- Water Conservation: Soil with good moisture retention reduces water wastage through runoff, promoting efficient use of water resources.
- Carbon Sequestration: Plants and soil microorganisms store carbon, helping mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Biodiversity: Soil health supports a diverse community of microbes, insects, and other organisms, contributing to ecosystem resilience.
Understanding and working with your soil type not only benefits your garden's productivity but also plays a significant role in environmental sustainability. In this journey of exploring soil types, you've learned how to identify and work with different soils, making informed choices that benefit your plants and the environment. Gardening isn't just about growing plants; it's about nurturing a dynamic, living ecosystem that starts with the soil. As you continue to cultivate your garden, remember that every decision from soil testing to plant selection contributes to a sustainable future.
What are the benefits of knowing your soil type?

+
Knowing your soil type allows for better plant selection, improved soil management practices, and ultimately leads to healthier, more productive gardens. It also aids in water conservation and reduces the need for fertilizers, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Can you grow anything in chalky soil?

+
While chalky soils are less versatile, certain plants like lavender and some grasses thrive in these conditions due to their well-drained nature and pH requirements.
How often should I test my garden soil?

+
Soil testing should be done every 2-3 years to monitor changes in pH and nutrient levels. However, if you notice poor plant growth or suspect a soil issue, test more frequently.



