5 Essential Types of Forces You Should Know

In our everyday lives, we interact with various forces that shape our world, from the subtle to the dramatic. Understanding these forces not only enriches our knowledge but also enhances our ability to appreciate the complexities of the physical world. Here are five essential types of forces you should know:
1. Gravity

Gravity, often referred to as the force of attraction, is perhaps the most universally experienced force. It is the reason why objects fall to the ground, why planets orbit around stars, and why we have weight. Here are key points about gravity:
- Gravity is an attractive force that acts between all masses.
- It follows the inverse square law, meaning the strength of gravity decreases as the distance between two masses increases.
- The universal gravitational constant, G, was calculated by Sir Isaac Newton and refined by subsequent scientists.
🌌 Note: While gravity seems omnipresent, its effects can be counteracted or influenced by other forces, such as lift in aerodynamics.
2. Electromagnetic Force
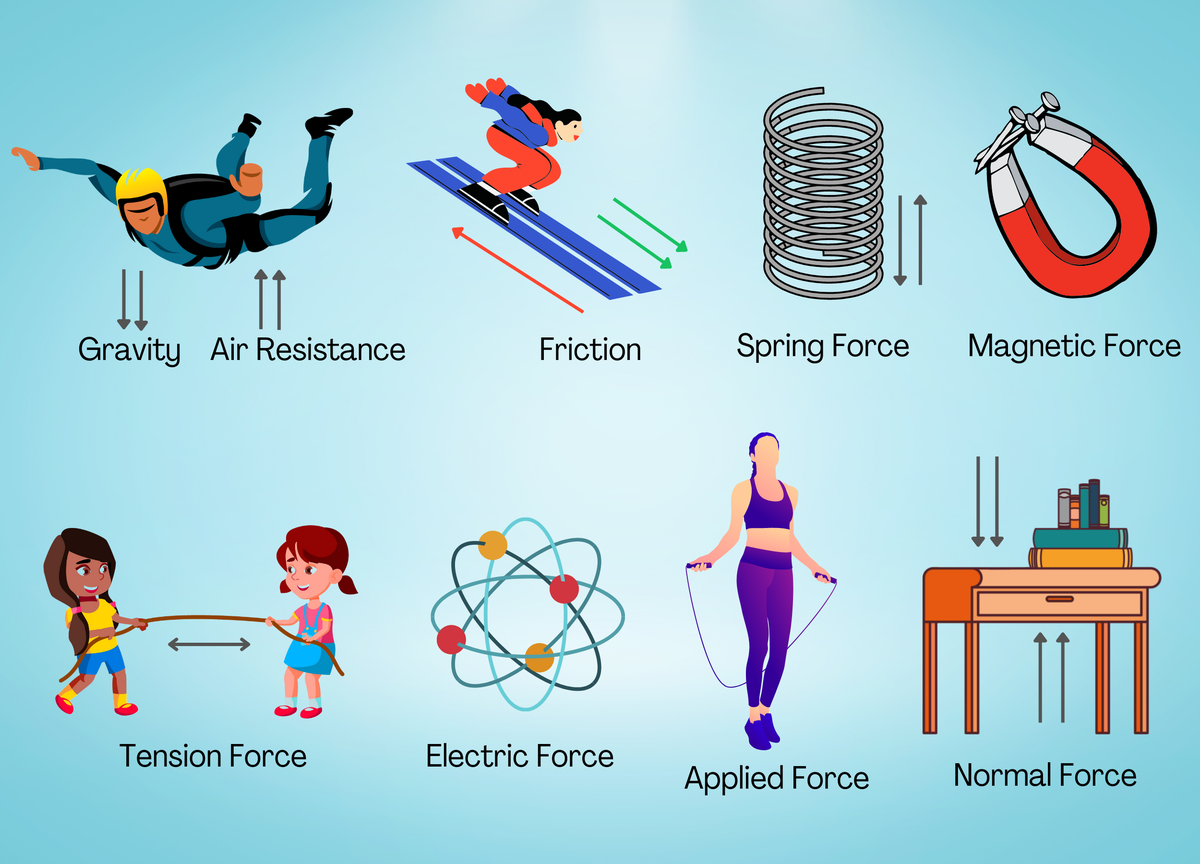
Electromagnetism is a fundamental force that includes both electrical and magnetic effects. Here’s what you need to know:
- It’s responsible for light, electricity, magnetism, and is essential for life itself as it holds atoms together.
- The force can both attract and repel, depending on the charge or polarity of the objects involved.
- It’s mediated by the exchange of photons.
3. Strong Nuclear Force

This force is the glue that binds protons and neutrons in atomic nuclei:
- The strong nuclear force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature.
- It’s the strongest force known, but it operates at very short ranges, roughly the size of a nucleus.
- It overcomes the electric repulsion between protons to keep the nucleus stable.
Without the strong nuclear force, atoms as we know them would not exist.
4. Weak Nuclear Force

While weaker than the strong force, the weak nuclear force plays a crucial role in particle physics:
- It is responsible for processes like beta decay, where a neutron turns into a proton, an electron, and an anti-neutrino.
- It involves the exchange of W or Z bosons.
- Its influence is short-ranged like the strong force but is involved in radioactive decay.
5. Friction
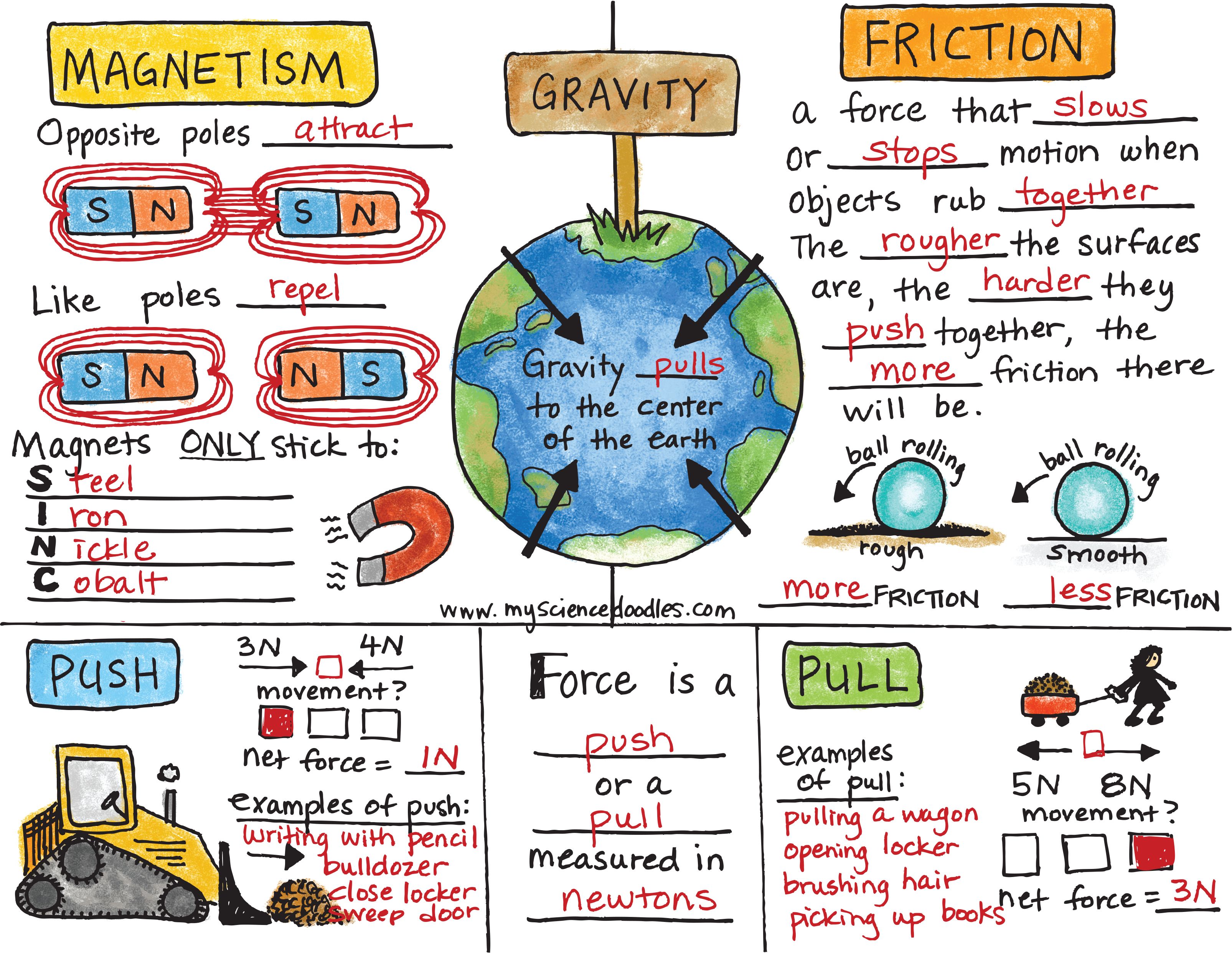
Friction might seem mundane, but its effects are pervasive in our daily interactions:
- There are several types of friction, including static, kinetic, and rolling friction.
- It opposes motion and is caused by the interaction between two surfaces in contact.
- Friction is essential for walking, driving, and even writing.
🛠 Note: While friction can often be considered a 'nuisance' when it comes to energy efficiency, it's vital for many applications where control of motion is necessary.
To wrap up, understanding these five forces helps us comprehend how the universe functions on various scales, from the microscopic world of particles to the vast expanses of space. They are integral to our daily lives, shaping how we interact with the environment and with each other.
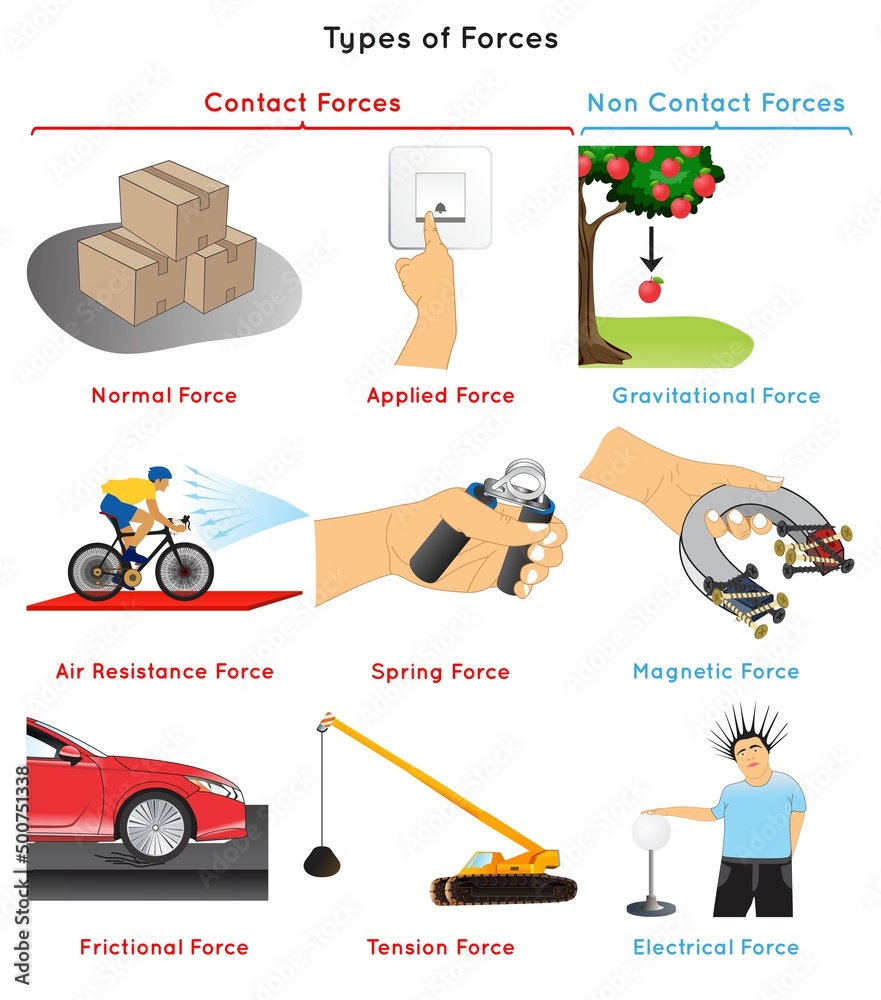
How does gravity affect Earth’s shape?
+
Gravity helps shape the Earth into an oblate spheroid, where it is slightly flattened at the poles and bulges at the equator due to the planet’s rotation.
Can we eliminate friction entirely?

+
Friction can be minimized but not entirely eliminated. In ideal conditions like in space or using special materials, friction can be significantly reduced, but some form of resistance always exists.
What would happen if the strong nuclear force didn’t exist?
+
Without the strong nuclear force, protons and neutrons could not form atomic nuclei, and thus, there would be no atoms or stable elements, essentially leading to a universe very different from the one we know.