5 Types of Chemical Reactions Worksheet Answers

Understanding the fundamentals of chemistry not only paves the way for a better comprehension of the natural world but also aids in daily activities and industrial applications. Among these basics are the different types of chemical reactions, each characterized by how reactants transform into products. Today, we will delve into five common types of chemical reactions, providing clarity through examples, definitions, and a simple worksheet to test your understanding. Whether you're a student looking to deepen your grasp of chemistry or just a curious learner, this guide will serve as an essential resource.
1. Synthesis Reactions

Definition: A synthesis reaction occurs when two or more simple substances combine to form a more complex compound. The general formula for this reaction is:
A + B → AB
Example: Here is an everyday example of a synthesis reaction:
- 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
In this example, hydrogen and oxygen gases combine to form water, which is indeed a synthesis reaction.
2. Decomposition Reactions

Definition: Decomposition reactions are essentially the opposite of synthesis reactions. In these, a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. The general formula for decomposition reactions is:
AB → A + B
Example: A common decomposition reaction is:
- CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Here, calcium carbonate decomposes upon heating into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
3. Single Displacement Reactions
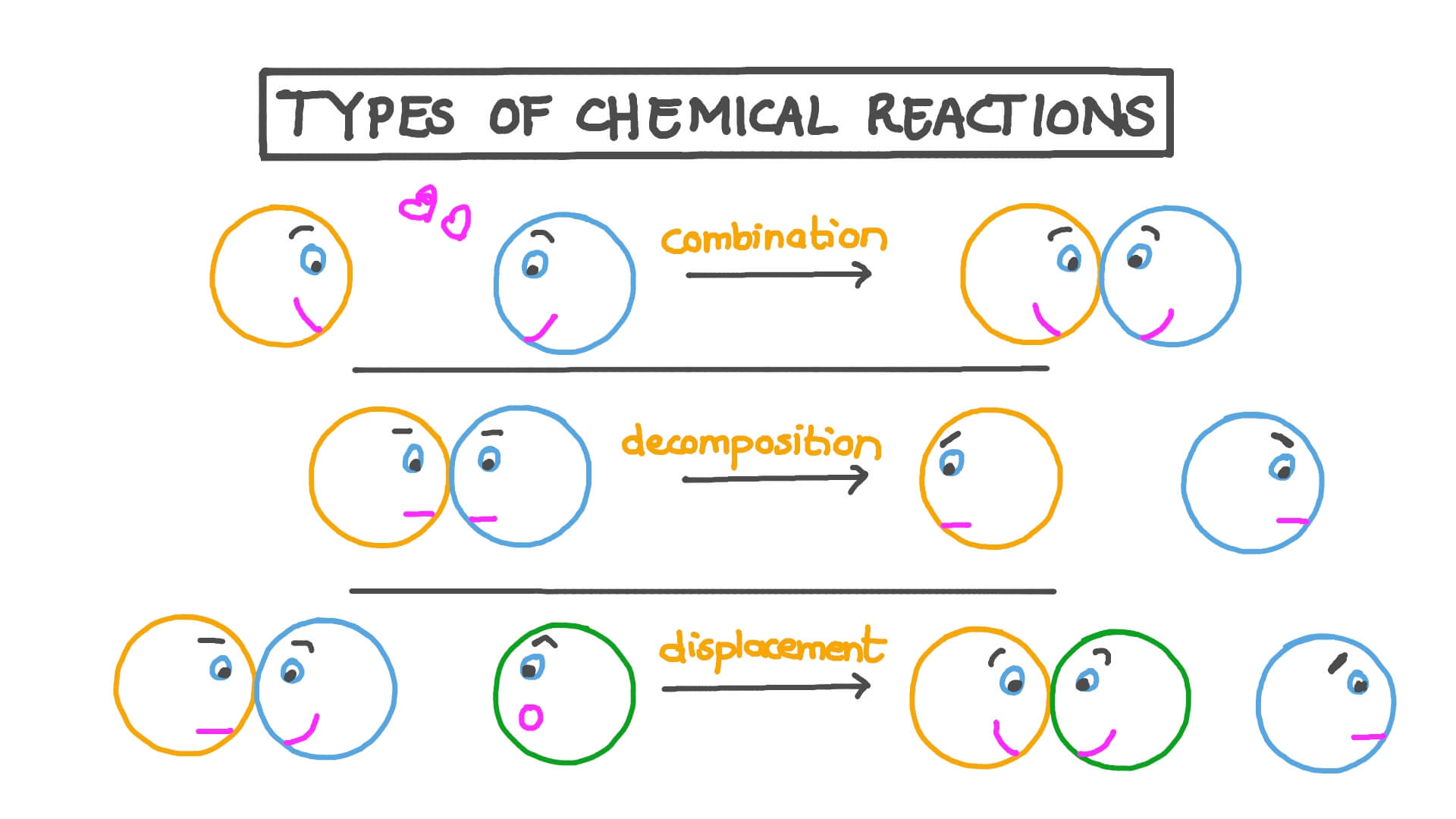
Definition: This type of reaction occurs when one element replaces another element in a compound. It typically follows this pattern:
A + BC → AC + B
Example: Here's an illustration:
- Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
In this reaction, zinc displaces copper in the copper sulfate solution, forming zinc sulfate and leaving copper behind as a solid.
4. Double Displacement Reactions

Definition: Double displacement reactions occur when the positive and negative ions of two ionic compounds exchange places, forming two new compounds. The general representation is:
AB + CD → AD + CB
Example: Consider the following reaction:
- NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
Sodium chloride reacts with silver nitrate, resulting in the formation of silver chloride, a precipitate, and sodium nitrate.
5. Combustion Reactions

Definition: Combustion is an exothermic reaction where a substance reacts with oxygen, often producing heat and light in the form of flames. The reactants are typically a hydrocarbon or an organic molecule with oxygen. The products are usually carbon dioxide and water, alongside other gases in some instances. The general form can be:
Fuel + O2 → CO2 + H2O + Heat
Example: The most widely recognized combustion reaction is the burning of methane:
- CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Methane, the primary component of natural gas, combusts in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and heat.
Worksheet

| Reaction Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Synthesis | 4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3 |
| Decomposition | 2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2 |
| Single Displacement | Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2 |
| Double Displacement | Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI → PbI2 + 2KNO3 |
| Combustion | C2H5OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O |

🔬 Note: Ensure you balance the chemical equations for accurate depiction of reactions. Also, remember that the context of a reaction might alter the type; for instance, combustion can involve synthesis if new compounds are formed.
Learning about these five types of chemical reactions is essential for a deeper understanding of chemistry, whether you're exploring the world of scientific research or simply engaging in everyday problem-solving. They represent foundational principles that govern how elements interact, compounds form, and materials change. Understanding these reactions enables us to predict outcomes of chemical processes, enhance safety, and drive innovation in numerous fields. From the creation of life-sustaining molecules to the control of potentially dangerous reactions, chemistry, and these reactions, play a critical role in our daily lives and the natural environment.
What is the difference between synthesis and decomposition reactions?

+
Synthesis reactions involve combining simpler substances to form a more complex compound, while decomposition reactions break down a single compound into simpler substances.
How do I know which element will displace another in a single displacement reaction?

+
The activity series of metals determines which element will displace another. The higher an element is in the series, the more likely it is to replace a lower element in a compound.
Can combustion reactions occur without oxygen?

+
Combustion typically requires oxygen, but under very high temperatures and pressures, other oxidizers like chlorine or fluorine can facilitate similar reactions.