5 Tips for Mastering Two Way Tables Easily
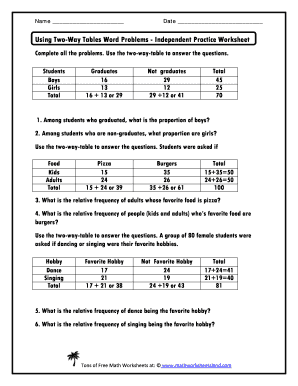
In the world of statistics and data analysis, two-way tables, also known as contingency tables, are invaluable tools. These tables provide a clear view of the relationship between two categorical variables, allowing for a better understanding of their joint distribution. If you're looking to master two-way tables and leverage their power in your data analysis tasks, here are five practical tips that can help.
Understanding Two-Way Tables

Before diving into the tips, let’s briefly understand what two-way tables are. A two-way table displays the frequency distribution of two variables simultaneously. Each row represents one variable, while each column represents another. Here’s a basic example:
| Category A | Category B | |
|---|---|---|
| Variable 1 | 10 | 20 |
| Variable 2 | 15 | 25 |
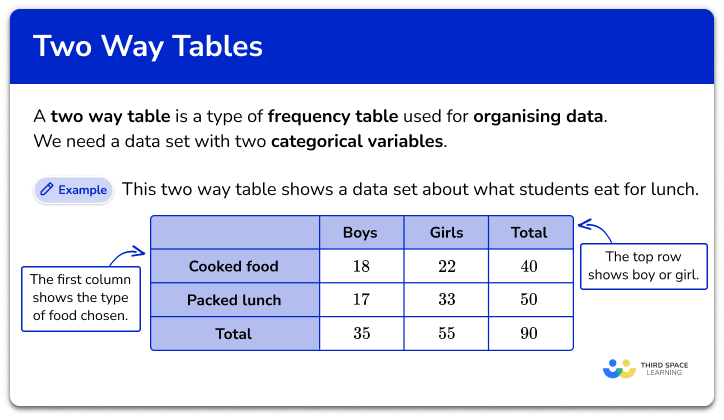
This table shows the frequency of occurrences for two variables across their respective categories. Understanding how to interpret this table is the first step toward mastering two-way tables.
Tip 1: Develop a Clear Objective
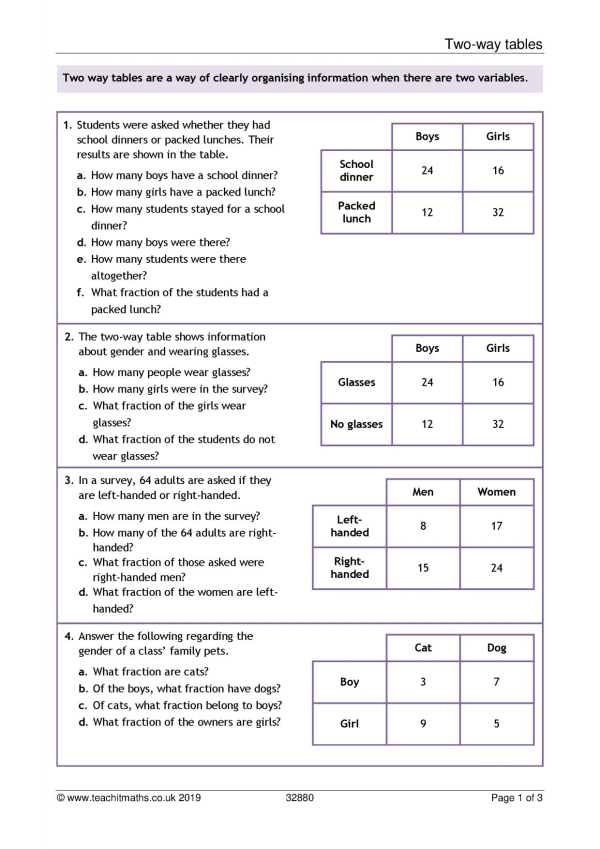
The foundation of effectively using two-way tables lies in defining what you aim to learn from your data. Ask yourself:
- What relationship between the variables are you exploring?
- Are you looking for independence or dependence between the variables?
- What specific hypotheses or questions do you have?
Setting a clear objective helps tailor your analysis, ensuring that the data collection and interpretation are aligned with your goals.
Tip 2: Organize Your Data Properly

Proper organization is key:
- Label Clearly: Ensure each category is labeled correctly to avoid confusion.
- Categorical Variables: Your variables should be categorical (nominal or ordinal). If not, they need to be converted or grouped.
- Ensure Completeness: Check if the data is complete and all possible combinations of categories are accounted for.
A well-organized table will facilitate easier interpretation and analysis.
Tip 3: Use the Chi-Square Test

To go beyond mere observation and assess the relationship:
- Understand the Chi-square test to determine if there’s a significant association between the variables.
- Learn how to calculate expected frequencies and compare them with observed frequencies.
- Interpret the p-value to understand if the observed distribution differs significantly from expected randomness.
✅ Note: The Chi-square test assumes that the samples are independent of each other.
Tip 4: Master Row and Column Proportions

Looking at row or column proportions gives you a different perspective:
- Row Proportions: Show the distribution within each category of the row variable. This can reveal how the column categories behave for different levels of the row variable.
- Column Proportions: Provide insights into the distribution within each column category, helping to understand the behavior of the row variable across column levels.
Here’s a simple example:
| Category A | Category B | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable 1 | 10 (50%) | 20 (50%) | 30 |
| Variable 2 | 15 (30%) | 35 (70%) | 50 |
Tip 5: Apply Visual Techniques

While tables are excellent for data analysis, visualizations can significantly enhance understanding:
- Use bar charts or heat maps to visually represent the distribution.
- Employ stacked or grouped bar charts to show proportions.
- Create mosaic plots for a graphical depiction of proportions and area representation.
In summary, mastering two-way tables is about understanding the relationships between categorical variables, setting clear objectives, organizing data correctly, applying statistical tests, analyzing proportions, and using visual aids to tell a data-driven story. By implementing these tips, you can gain deeper insights from your data, make informed decisions, and communicate findings effectively.
As you progress in your journey with two-way tables, remember that practice is key. Continuously working with different datasets and exploring various aspects of your data will refine your skills. Embrace the challenges, learn from your analysis, and let two-way tables be your tool to unlock the secrets within your data.
What are the benefits of using two-way tables in data analysis?

+
Two-way tables allow you to observe the relationship between two categorical variables simultaneously, making it easier to understand how these variables interact or depend on each other. They help in:
- Identifying patterns or associations in data.
- Assessing the independence or dependence between variables.
- Conducting hypothesis tests like the Chi-square test to validate or refute assumptions.
- Providing a visual summary for presentations and reports.
How do I know when to use the Chi-square test on a two-way table?

+
Use the Chi-square test when:
- You want to test if there’s a significant association between the two categorical variables.
- The sample size is large enough (as the test assumes large sample approximations).
- The expected frequencies in each cell of the two-way table are at least 5 for a reliable test result.
Can I create a two-way table with continuous data?
+
While two-way tables are typically used for categorical data, you can:
- Convert continuous data into categories or groups to form a contingency table. For instance, age can be grouped into categories like ‘18-25’, ‘26-35’, etc.
- Use scatter plots or other correlation techniques when dealing with continuous variables.
What software tools are best for creating and analyzing two-way tables?
+
Several tools are well-suited for this purpose:
- Excel: For basic two-way tables and simple analysis.
- R: Offers comprehensive packages like ‘ggplot2’ for visualizations and ‘stats’ for statistical tests.
- Python: With libraries like Pandas, Matplotlib, and SciPy for data manipulation and analysis.
- SPSS or SAS: Statistical software that provides advanced options for statistical analysis.