Triangle Congruence Theorems Made Easy

Triangle Congruence Theorems Made Easy
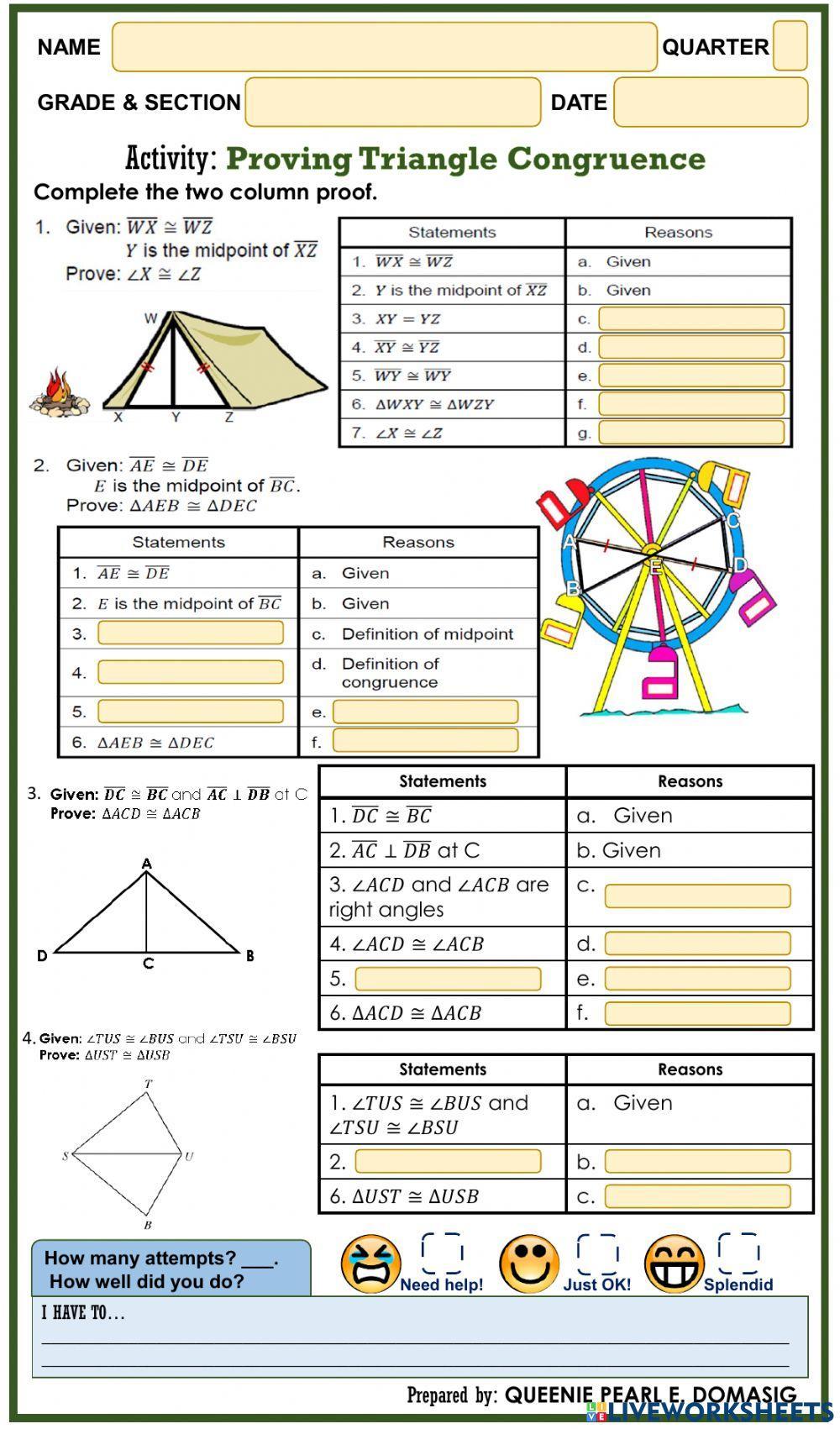
Triangle congruence theorems are fundamental concepts in geometry that help us determine whether two triangles are identical or not. In this article, we will explore the different types of triangle congruence theorems, their definitions, and examples. We will also discuss the significance of these theorems in various fields of mathematics and real-life applications.
What are Triangle Congruence Theorems?
Triangle congruence theorems are statements that define the conditions under which two triangles are said to be congruent. Two triangles are congruent if their corresponding sides and angles are equal. In other words, if two triangles have the same size and shape, they are congruent.
Types of Triangle Congruence Theorems
There are five main types of triangle congruence theorems:
- Side-Side-Side (SSS) Theorem: If three sides of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
- Side-Angle-Side (SAS) Theorem: If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides and angle of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
- Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) Theorem: If two angles and the included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding angles and side of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
- Angle-Angle-Side (AAS) Theorem: If two angles and a non-included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding angles and side of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
- Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) Theorem: If the hypotenuse and a leg of a right triangle are equal to the corresponding hypotenuse and leg of another right triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
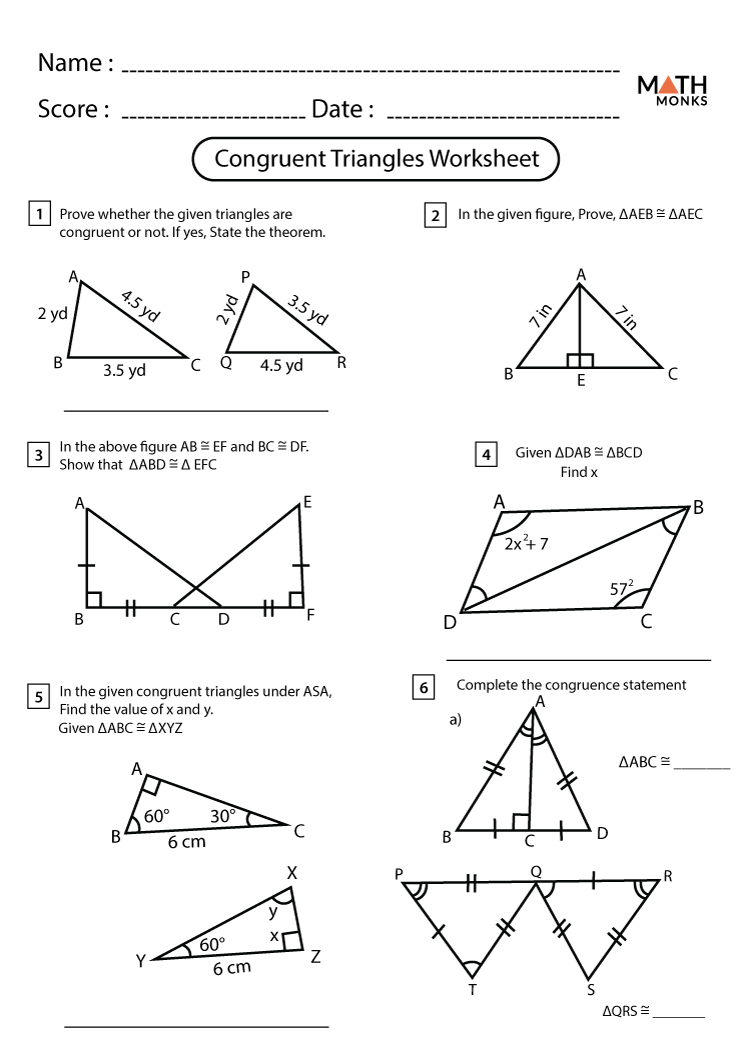
Examples of Triangle Congruence Theorems

Let’s consider a few examples to illustrate the use of triangle congruence theorems:
- Example 1: In the diagram below, we have two triangles, ΔABC and ΔDEF. We are given that AB = DE = 5 cm, BC = EF = 7 cm, and AC = DF = 3 cm. Using the SSS theorem, we can conclude that ΔABC ≅ ΔDEF.
| Side | ΔABC | ΔDEF | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AB | 5 cm | DE | 5 cm |
| BC | 7 cm | EF | 7 cm |
| AC | 3 cm | DF | 3 cm |

- Example 2: In the diagram below, we have two triangles, ΔPQR and ΔSTU. We are given that PQ = ST = 6 cm, QR = TU = 8 cm, and ∠PQR = ∠STU = 60°. Using the SAS theorem, we can conclude that ΔPQR ≅ ΔSTU.
Significance of Triangle Congruence Theorems

Triangle congruence theorems have numerous applications in various fields of mathematics and real-life scenarios:
- Geometry: Triangle congruence theorems are used to prove theorems and solve problems in geometry, such as finding the length of unknown sides and angles in triangles.
- Trigonometry: Triangle congruence theorems are used to solve problems involving right triangles, such as finding the length of the hypotenuse and the other sides.
- Physics: Triangle congruence theorems are used to solve problems involving force, velocity, and acceleration, such as finding the resultant force in a system of forces.
- Engineering: Triangle congruence theorems are used to design and analyze structures, such as bridges and buildings, to ensure stability and safety.
💡 Note: Triangle congruence theorems are also used in computer-aided design (CAD) software to create and manipulate 3D models.
Conclusion

Triangle congruence theorems are powerful tools in geometry that help us determine whether two triangles are identical or not. By understanding the different types of triangle congruence theorems and their applications, we can solve problems and prove theorems in various fields of mathematics and real-life scenarios.
What is the difference between the SSS and SAS theorems?

+
The SSS theorem states that if three sides of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. The SAS theorem states that if two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides and angle of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
Can you use the AAS theorem to prove that two triangles are congruent?

+
No, the AAS theorem is not a valid triangle congruence theorem. The AAS theorem is actually a statement of the ASA theorem, which states that if two angles and the included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding angles and side of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
What is the significance of the HL theorem in right triangles?
+
The HL theorem states that if the hypotenuse and a leg of a right triangle are equal to the corresponding hypotenuse and leg of another right triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. This theorem is significant in right triangles because it allows us to prove that two right triangles are congruent without having to show that all three sides are equal.
Related Terms:
- Triangle congruence theorems worksheet answers
- Triangle congruence theorems worksheet pdf
- proving triangles congruent worksheet kuta
- right triangle congruence worksheet pdf
- triangle congruence worksheet with answers
- triangle congruence postulate worksheet pdf