Translation Shapes Worksheet: 5 Answer Key Tips

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on using translation shapes worksheets effectively! In mathematics, understanding geometric transformations is fundamental, and one of the key transformations is translation. Worksheets dedicated to translation shapes are invaluable tools for educators and learners alike, providing practical exercises that reinforce concepts learned in class. Here, we provide five key tips to ensure you make the most out of your answer key when using these worksheets.
Tip 1: Understand the Purpose of Translation
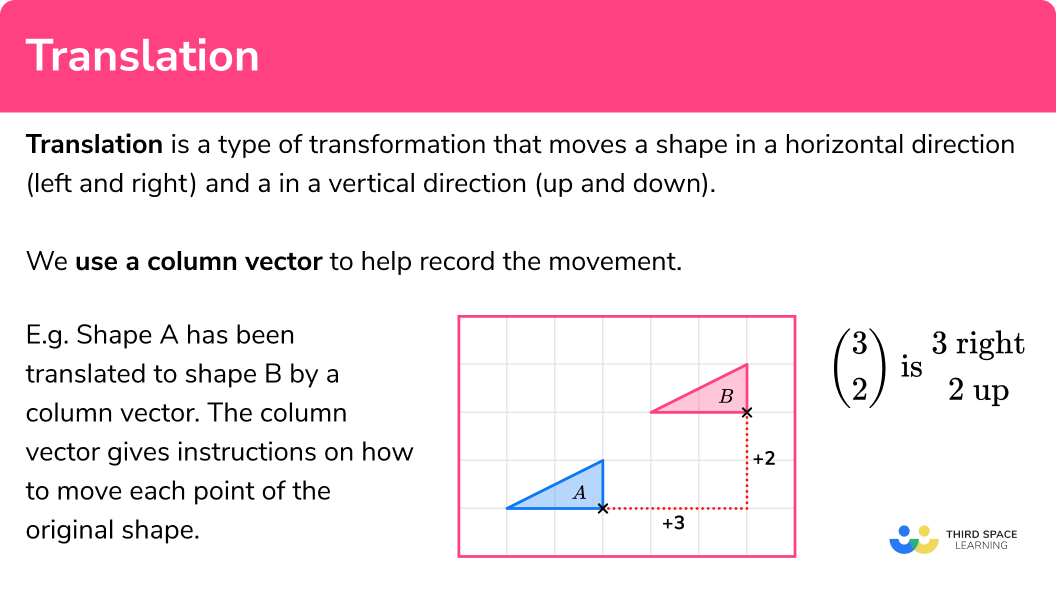
Before diving into the exercises, it’s crucial to grasp what translation means in geometry. Translation is a transformation that moves every point of a figure the same distance in the same direction. Here are some ways to utilize this knowledge:
- Identify Initial Position: Understand where each shape starts from. This will help in tracking the translation path.
- Vector Understanding: Each translation can be represented as a vector. Learn to read and interpret vectors to predict the new position of the shape.

Tip 2: Check for Accuracy
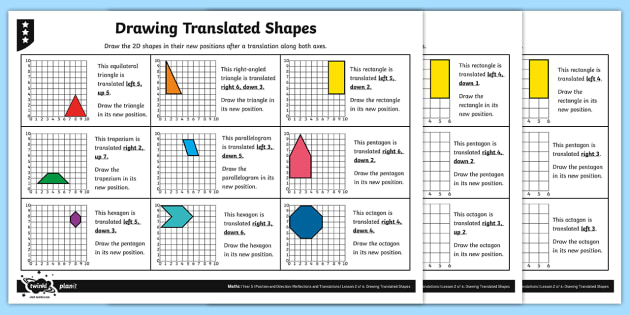
When reviewing answers or marking worksheets, accuracy is paramount. Here’s how to ensure the translations are correct:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Check Initial Coordinates | Confirm the original coordinates of the shape match with the given reference point. |
| 2. Verify Vector Application | Ensure the vector is correctly applied to each point of the shape. |
| 3. Confirm Resulting Coordinates | After translation, the new coordinates should reflect the exact movement specified by the vector. |

💡 Note: It's common to see students make mistakes in coordinate adjustments due to confusion between positive and negative movements. Double-check these details!
Tip 3: Utilize Visual Cues

Visual understanding greatly aids in learning geometry:
- Draw Grid Lines: If the worksheet doesn’t have grid lines, sketch them to help visualize the translation path.
- Use Arrows: Draw arrows representing the vector to guide students in tracking the shape’s new position.
Tip 4: Encourage Verbalization

Encouraging students to verbalize the process of translation can deepen their understanding:
- Have them describe the movement in terms of direction and distance.
- Ask questions like “What happens to the shape if we move it 3 units to the left?”
🌟 Note: This method not only helps in cementing the concept but also in assessing their grasp of the subject.
Tip 5: Foster Conceptual Learning

Beyond mere computation, conceptual understanding is vital:
- Relate to Real-life Examples: Show how translation applies in everyday life, like moving furniture around a room.
- Promote Problem Solving: Create scenarios where students need to figure out the translation needed to fit shapes into a puzzle.
In summary, translation shapes worksheets are more than just exercises; they’re a gateway to understanding geometric transformations. By focusing on the purpose, accuracy, visual cues, verbalization, and conceptual learning, educators can maximize the educational value of these resources. Remember, the key lies in not just finding the right answer but in understanding the process behind the transformation.
What is the difference between translation and rotation?

+
Translation moves every point of a figure the same distance in the same direction, without changing the orientation or size of the shape. Rotation, on the other hand, turns the shape around a fixed point, changing its orientation but keeping its size and position constant relative to that point.
How do I know if I’ve translated a shape correctly?

+
Check if each point of the original shape moves exactly the same distance in the same direction as specified by the vector. Also, ensure that the shape retains its original orientation and size after the movement.
Can translation be applied in 3D space?

+
Yes, translation can be applied in 3D space just like in 2D, where each point of the shape moves along a specified vector that includes a movement in the Z-axis as well as X and Y axes.