Transcription and Translation Coloring Worksheet Answer Key
Understanding the intricacies of transcription and translation in molecular biology can be a daunting task, especially for students who are new to this fascinating yet complex field. Transcription and translation are fundamental processes by which the genetic information encoded in DNA is used to produce proteins, the workhorses of the cell. To aid in learning these processes, educators often use worksheets, and having an answer key can be an invaluable resource for both teaching and self-study. In this blog post, we will explore how to navigate transcription and translation coloring worksheets, offering a detailed explanation and the answer key.
The Basics of Transcription and Translation
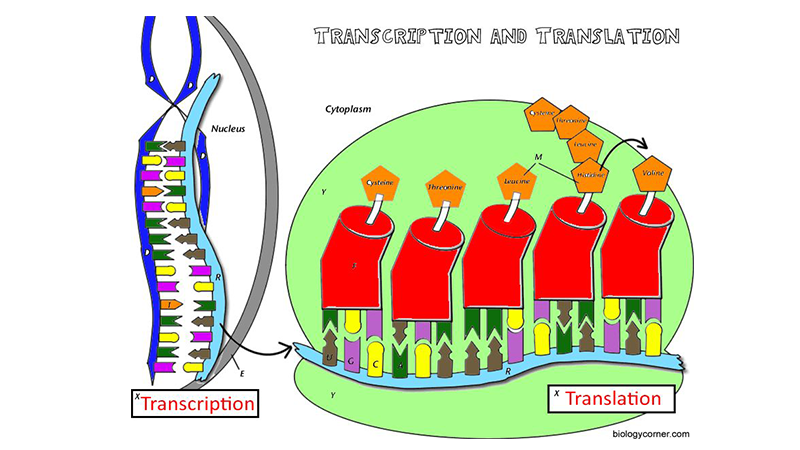
Before diving into the worksheet, let's briefly review what transcription and translation entail:
- Transcription: This is the first step in gene expression where the DNA sequence of a gene is copied into mRNA. It occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
- Translation: Following transcription, the mRNA moves to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm where it is read and translated into a sequence of amino acids, forming proteins.
Using the Coloring Worksheet

Coloring worksheets are designed to make learning more interactive and engaging. Here's how to approach one:
- Read the Instructions: Always start by thoroughly reading the instructions. Understanding what each color signifies is crucial for completing the worksheet correctly.
- Identify Key Components: Look for DNA, mRNA, ribosomes, tRNA, and amino acids as these will be the main elements you'll color.
- Coloring the Steps:
- Begin with DNA replication or unwinding, often marked by a specific color.
- Continue with mRNA synthesis, where different colors might represent different bases or the mRNA strand itself.
- Move to ribosomal stages, where translation begins, using colors to differentiate between ribosomal subunits, tRNA, and the growing polypeptide chain.
Answer Key: A Step-by-Step Guide

| Step | Process | Color Coding |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Unwinding of DNA | Use blue to highlight the regions where the DNA is unwinding. |
| 2 | Transcription | RNA polymerase should be colored orange, and the mRNA can be red as it is synthesized from the DNA template strand (blue). |
| 3 | Translation Initiation | Ribosomal subunits: Large (yellow) and Small (green). The start codon (AUG) can be colored purple. |
| 4 | Elongation | tRNA (with specific anticodons) to be colored in various colors corresponding to their amino acids. For instance, Methionine (AUG) could be light blue. |
| 5 | Termination | Stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) can be colored grey. |

🏫 Note: The colors used are just examples; different educational materials might use different color schemes.
Why Coloring Helps in Learning

- Visual Learning: It leverages the brain’s ability to process visual information quickly.
- Engagement: Making notes or worksheets interactive can boost interest and retention.
- Memory Reinforcement: Color-coding reinforces memory by creating associations between concepts and colors.
As we wrap up this guide on transcription and translation coloring worksheets, it's evident that these activities offer a hands-on approach to grasping the core concepts of molecular biology. From the unwinding of DNA to the final stages of translation, each step can be highlighted and remembered through the use of colors. This method not only aids in understanding but also makes the learning experience more enjoyable. Whether you're a student striving to master these processes or a teacher looking for engaging educational tools, coloring worksheets provide a practical and visually stimulating way to learn. Their utility goes beyond just coloring; they serve as an interactive bridge between the abstract world of genetics and tangible classroom activities, fostering a deeper understanding of life at its most basic level.
Why are transcription and translation important in biology?

+
Transcription and translation are fundamental because they dictate how genetic information is converted into functional proteins, which are essential for various cellular processes, organism growth, and function.
Can transcription and translation occur simultaneously in prokaryotes?

+
Yes, in prokaryotes, transcription and translation can happen at the same time since there is no nuclear envelope to separate DNA from the cytoplasm where translation occurs.
How does color-coding enhance learning in science?

+
Color-coding helps by associating visual cues with complex information, making it easier for the brain to categorize, remember, and recall scientific concepts.
What happens if there is an error in transcription or translation?

+
Errors can lead to mutations, potentially altering protein function. However, cells have mechanisms like proofreading during DNA replication and mRNA surveillance to minimize errors.
Are coloring worksheets beneficial for all age groups?

+
While coloring is traditionally associated with younger learners, it can also help older students by providing a fun, stress-relieving way to engage with complex material.



