Time Zones Worksheet: Simplify Your Global Timekeeping

Understanding time zones is more than just a practical skill; it's an essential aspect of our increasingly interconnected world. Whether you're planning international business meetings, coordinating travel, or simply keeping in touch with friends and family across the globe, having a solid grasp of how time zones work can simplify your life immensely. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of time zones, explore why they exist, how they are organized, and provide you with practical tips on managing time zone differences effectively.
What Are Time Zones?
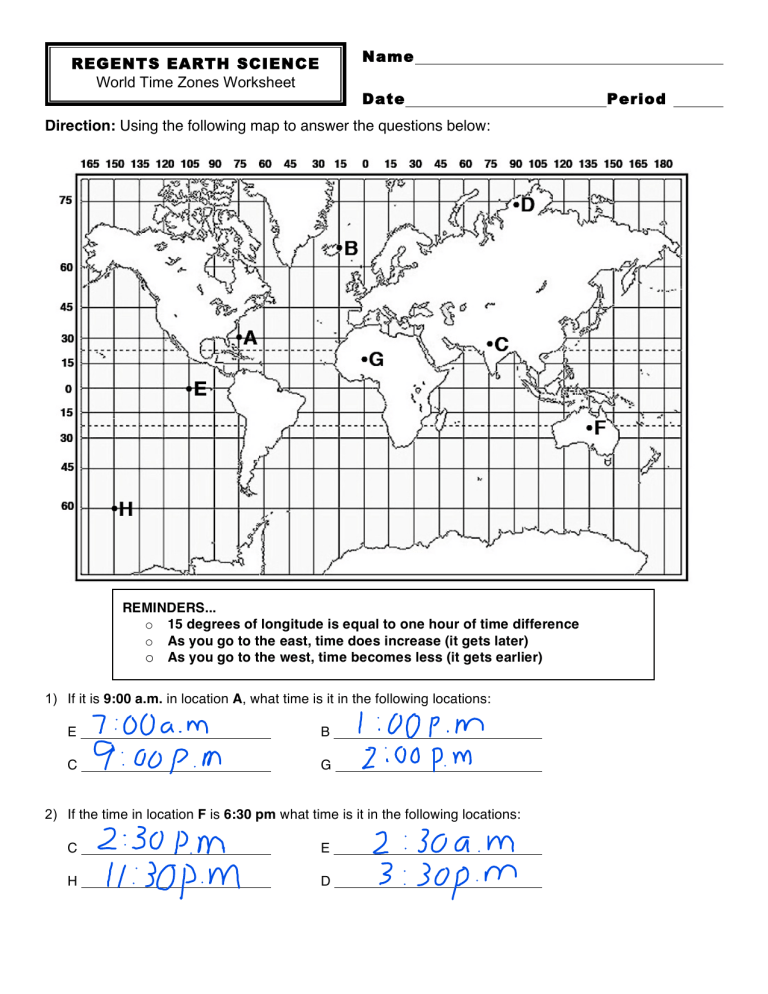
Time zones are regions of the Earth that have the same standard time. They were devised to make a common sense approach to timekeeping, despite the Earth’s rotation. Here’s why they are necessary:
- Uniformity in Timekeeping: Without time zones, it would be chaotic to schedule global activities as each location would have its own local solar time.
- Coordination: Time zones facilitate international coordination in travel, telecommunications, broadcasting, and many other fields.
- Economic and Political Considerations: Countries sometimes adjust their time zones for reasons of economic efficiency or national identity.
The History of Time Zones

Before diving deeper into the technical details, let’s explore the historical context:
- 19th Century: With the expansion of railways and telegraph systems, a need for standardized time across vast regions became evident.
- 1883: U.S. and Canadian railroads agreed to create four time zones. This was later followed by other countries.
- 1884: The International Meridian Conference was held, which established the Prime Meridian, or the zero longitude line, in Greenwich, England. This led to the creation of 24 time zones, one for each hour of the day.
How Time Zones Work

Each time zone represents a one-hour difference from the next zone, aligned with the Earth’s 24-hour rotation. Here’s how they are organized:
- Standard Time: Each time zone has a standard time based on the time at its central meridian, which is an imaginary line running north-south through the zone.
- Coordinated Universal Time (UTC): This is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. UTC is not subject to Daylight Saving Time (DST) changes.
- Daylight Saving Time: Some zones adjust their clocks forward or backward by one hour during certain times of the year, commonly to extend daylight hours in the evening.
Here's how you can visualize a simple version of time zones:
| Time Zone | UTC Offset |
|---|---|
| Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) | UTC±0 |
| Eastern Time (ET) | UTC−05:00 |
| Central Time (CT) | UTC−06:00 |
| Mountain Time (MT) | UTC−07:00 |
| Pacific Time (PT) | UTC−08:00 |

Practical Tips for Managing Time Zones

When you're dealing with time zone differences, here are some strategies to keep in mind:
- Use Online Tools: Websites or mobile apps like World Time Buddy or Timeanddate can help you easily convert times across different zones.
- Set up Multiple Clocks: If you frequently communicate with people in different time zones, setting up multiple time zone clocks on your computer or smartphone can be very handy.
- Understand DST Implications: Be aware that not all countries or regions observe DST, which can shift meeting times unexpectedly.
- Plan Meetings: Use tools like Google Calendar that automatically convert time zones when scheduling meetings or events.
- Use UTC: For international business, using UTC as a standard reference point can avoid confusion, especially when dealing with locations that might be in or out of DST.
⏱️ Note: Always double-check time zone conversions, especially around DST changes to avoid scheduling errors.
By embracing these tips, you'll find managing time zones less of a hassle and more of an organized part of your daily life. From understanding why we have time zones, learning their history, to practical application, you now have the tools to navigate this global aspect of timekeeping with ease.
Let's wrap up by considering that time zones, though initially complex, are a testament to human ingenuity in coordinating activities across our diverse planet. By mastering the understanding and management of time zones, we can enhance our communication, travel experiences, and business operations across the globe. Remember, the time in different parts of the world is not just a number; it's a bridge connecting us all.
Why do some countries change their time zones?

+
Countries might adjust their time zones due to political, economic, or cultural reasons. For example, changing time zones can help synchronize a country’s work hours with neighboring countries, or it can be a show of alignment with other nations. Economic benefits like increased daylight hours for shopping or tourism might also influence such decisions.
What is Daylight Saving Time (DST)?
+
Daylight Saving Time (DST) is the practice of advancing clocks during warmer months so that darkness falls later each day according to the standard time. It’s meant to make better use of natural daylight, saving energy and giving people more daylight for leisure after work.
How can I remember which direction to turn the clock for DST?
+
A popular mnemonic is “Spring forward, Fall back.” In spring, you move the clock forward one hour (losing an hour), and in the fall, you move it back (gaining an hour).



