Plate Tectonics Worksheet Answers: 5 Key Insights

The movement and dynamics of our planet's lithospheric plates give us a fascinating glimpse into the geological processes that have shaped Earth's surface throughout history. Understanding plate tectonics is crucial for explaining many natural phenomena, including earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the creation of mountain ranges. Here are 5 key insights into plate tectonics:
1. Fundamental Components of Plate Tectonics

At the core of plate tectonics are several fundamental components:
- Lithosphere: The Earth's crust and the upper part of the mantle, which is fragmented into about 15 major plates.
- Plate Boundaries: Where two plates meet, there are typically three types of interactions:
- Convergent boundaries: One plate is forced under another, leading to subduction zones, mountain formation, and often, volcanic activity.
- Divergent boundaries: Plates move apart, allowing new crust to form from magma rising from the mantle.
- Transform boundaries: Plates slide past each other, often resulting in earthquakes.
- Hotspots: Fixed locations of volcanism deep within the mantle, where magma burns through a plate to create volcanism away from plate boundaries.
🧐 Note: When referencing earthquakes, it's important to note that their locations are highly correlated with plate boundaries due to the friction and pressure that accumulate there.
2. Evidence Supporting Plate Tectonics

Modern science has found substantial evidence to support the theory of plate tectonics:
- Fossil Evidence: Fossils of the same species are found on separate continents, suggesting these landmasses were once joined.
- Geological Age and Structure: Rock layers of similar ages, types, and structures align across continents, indicating they were once part of a larger whole.
- Paleomagnetism: The orientation of magnetic particles in rocks changes over time, and their alignment across continents indicates movement.
- Seafloor Spreading: Evidence from the ocean floor supports the idea of new crust forming at divergent boundaries.
3. Types of Plate Movements
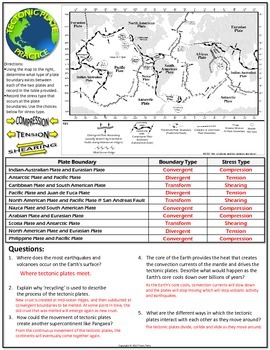
Understanding the types of plate movements helps clarify many geological phenomena:
| Movement | Description | Geological Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Convergence | Plates move towards each other. | Mountain building, trenches, and subduction zones |
| Divergence | Plates move apart from each other. | New oceanic crust formation, rift valleys |
| Transform | Plates slide past each other horizontally. | Faults, earthquakes |

4. Impact of Plate Tectonics on Earth's Geography

The movements of tectonic plates have profound effects on Earth's geography:
- Mountain Ranges: Collision of plates results in the uplift of mountain ranges like the Himalayas, Andes, and Alps.
- Continental Drift: The gradual drifting of continents has led to today's configuration of landmasses, which continues to evolve.
- Ocean Basins: Expansion and contraction of ocean floors through seafloor spreading and subduction contribute to the dynamic nature of ocean basins.
- Earthquakes and Volcanism: The vast majority of earthquakes and volcanic activity occur at or near plate boundaries.
5. Technological Advancements in Plate Tectonics Research

Technological innovations have greatly enhanced our understanding of plate tectonics:
- Seismic Imaging: Techniques like seismic tomography have provided detailed views of Earth's interior, revealing plate boundaries and mantle dynamics.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and GPS technology have helped track minute changes in the Earth's surface, providing real-time data on plate movements.
- Underwater Exploration: Advances in deep-sea exploration have uncovered hidden geological features like undersea volcanoes, trenches, and rifts.
In closing, the theory of plate tectonics serves as a foundational concept in geology, explaining many of Earth's most dynamic processes. It not only accounts for past geological events but also predicts future changes to Earth's geography. With continuous advancements in technology, our understanding of how plates interact and evolve will only deepen, offering us both practical insights for living on an active planet and a sense of awe at the complex and relentless movements shaping our world.
What is the lithosphere?

+
The lithosphere includes the Earth’s crust and the uppermost part of the mantle, forming the rigid layer that is fragmented into tectonic plates.
How do earthquakes relate to plate tectonics?

+
Earthquakes are largely the result of tectonic plate movements at boundaries where plates collide, slide past each other, or diverge.
Can we predict when the continents will look significantly different due to plate tectonics?
+
Geologists can project future continental positions based on current movement rates. However, due to the long timescales involved and the complexity of tectonic interactions, exact predictions are challenging.