Rock Cycle Diagram Worksheet: Your Ultimate Guide
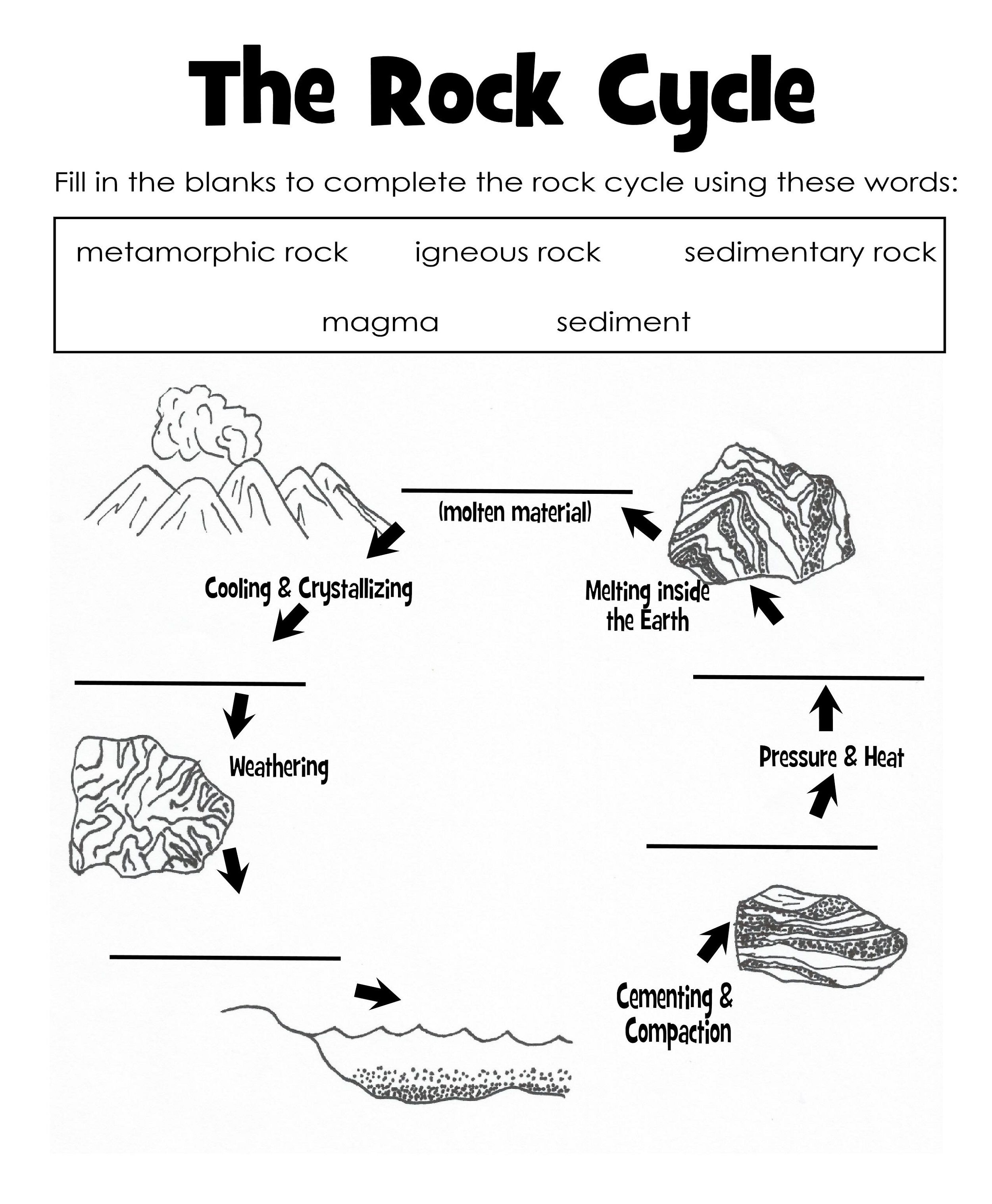
The rock cycle is a fundamental concept in geology, illustrating how rocks transform from one type to another under the influence of various geological processes. This journey through different rock forms is fascinating, not only for geologists but for students, educators, and science enthusiasts alike. A Rock Cycle Diagram Worksheet can serve as an excellent educational tool, helping learners visualize and understand these transformations. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore how to craft an engaging worksheet that both teaches and entertains.
Understanding the Rock Cycle

Before diving into the specifics of the worksheet, it’s crucial to have a firm grasp of what the rock cycle entails:
- Igneous Rocks: Formed from cooled and solidified magma or lava. Examples include granite and basalt.
- Sedimentary Rocks: These rocks result from the accumulation and cementation of sediments, like sandstone or limestone.
- Metamorphic Rocks: When existing rock types are altered by heat or pressure, metamorphic rocks like marble and schist are created.
The cycle involves processes like:
- Melting: Rocks melt to form magma.
- Cooling: Magma cools to form igneous rocks.
- Weathering and Erosion: Breaking down rocks into sediments.
- Compaction and Cementation: Transformation of sediments into sedimentary rocks.
- Metamorphism: Changing the structure of rocks through heat or pressure.
- Uplift and Erosion: Bringing rocks to the surface where they can erode and begin the cycle anew.
🔍 Note: Not all rocks go through all stages, and they can take different paths in the rock cycle.
Designing a Rock Cycle Diagram Worksheet

A well-designed worksheet can make learning about the rock cycle an interactive and memorable experience:
1. Layout and Structure

Structure your worksheet in a way that guides the student through the rock cycle:
- Begin with an overview of the cycle.
- Include clear, high-quality diagrams for each rock type.
- Use arrows or lines to illustrate transformations between rock types.
- Add a table or a section for definitions and key terms.
2. Activities and Exercises

Engage your audience with activities like:
- Color Coding: Have students color-code different rock types for easy identification.
- Matching: Provide names of rocks and their photos or descriptions for students to match.
- Labeling: Students can label different stages of the rock cycle in the diagram.
- Short Answer Questions: Pose questions that require understanding of the process rather than rote learning.
Here’s an example of how to structure a table for different rock types:
| Rock Type | Formation Process | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Igneous | Cooling and solidification of magma or lava | Granite, Basalt |
| Sedimentary | Deposition, compaction, and cementation of sediments | Sandstone, Limestone |
| Metamorphic | Heat or pressure altering existing rocks | Marble, Schist |

3. Adding Depth with Text

Support your visuals with explanatory text:
- Use italics to emphasize key terms or processes.
- Employ bold to highlight important points or headings.
- Include call-out boxes for interesting facts or tips.
4. Interactive Elements

To keep learners engaged:
- Scavenger Hunt: Include a task where students have to find real-world examples of rock cycle stages.
- Online Resources: Link or direct to websites where they can see interactive rock cycle diagrams.
💡 Note: Interactive elements can also be achieved through augmented reality (AR) apps that display 3D models of rock formations.
Incorporating Technology

Modern technology offers numerous ways to enhance the traditional worksheet:
- QR Codes: Insert QR codes that link to videos or simulations of rock cycle processes.
- AR Apps: Encourage the use of AR apps that can provide 3D visualizations of rocks and their formation.
- Interactive PDFs: Create PDFs with clickable elements for deeper exploration.
Assessment and Feedback

At the end of your worksheet:
- Quiz Section: Include a short quiz to gauge understanding.
- Feedback Forms: Use forms or spaces for students to provide feedback on the worksheet.
- Teacher’s Notes: Offer a section for teachers to add notes, providing context or additional questions.
In summary, creating a Rock Cycle Diagram Worksheet requires a blend of accurate scientific content, clear visualization, interactive elements, and an engaging layout. By focusing on the journey of rocks through the rock cycle, you can craft an educational tool that not only informs but also inspires curiosity about geology. Through thoughtful design and activities, students can explore the fascinating world of rocks and the natural processes that shape our planet, making learning about geology both fun and educational.
What are the three main types of rocks in the rock cycle?

+
The three main types are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooled magma or lava, sedimentary rocks from compressed sediments, and metamorphic rocks from existing rocks transformed by heat or pressure.
Can rocks revert from metamorphic back to sedimentary or igneous?

+
Rocks don’t revert but can continue through the cycle in various ways. For instance, a metamorphic rock can undergo weathering and erosion to become sediment, which can then be compacted into a new sedimentary rock. Or, if exposed to heat and pressure again, it might form another type of metamorphic rock.
Why are worksheets an effective tool for teaching the rock cycle?

+
Worksheets provide a structured format for learning, combining visual aids with activities that reinforce learning. They cater to different learning styles, offering diagrams for visual learners, hands-on activities for kinesthetic learners, and interactive questions for analytical thinkers.