Origin of Species Theory: Worksheet Wonders

Welcome to our journey into the Origin of Species Theory, one of the most profound concepts in the realm of evolutionary biology. Charles Darwin's revolutionary idea, presented in his landmark work "On the Origin of Species", has shaped our understanding of life's diversity and interconnectedness. Through this post, we'll explore various aspects of this theory using engaging worksheets, aiding in a deeper understanding of how species originate, adapt, and evolve over time.
Evolutionary Principles
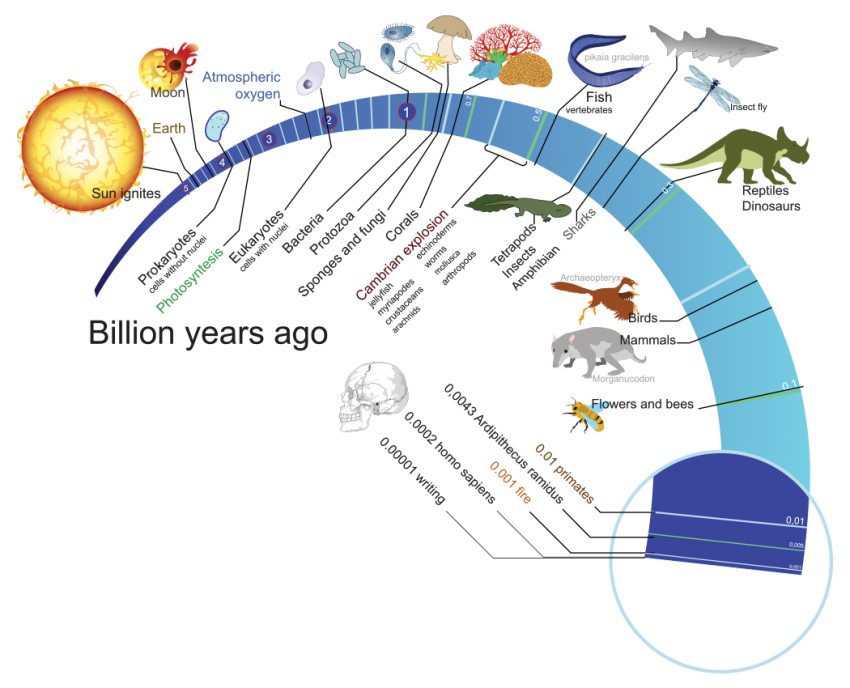
Before diving into Darwin’s specifics, let’s grasp the foundational principles of evolution:
- Natural Selection: The process where species with certain advantageous traits survive and reproduce at higher rates, passing on those traits to their offspring.
- Variation: Differences in species traits arise from mutations, gene flow, and sexual reproduction, providing raw material for natural selection.
- Isolation: When populations are separated, variations can accumulate, potentially leading to the formation of new species.
- Adaptation: Over time, species adapt to their environments, enhancing survival and reproductive success.
Natural Selection Worksheet Activity

Try this interactive worksheet to understand natural selection better:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify a hypothetical species in its natural habitat. |
| 2 | Introduce a sudden change in the environment (e.g., colder weather). |
| 3 | List three traits that would benefit survival in this new environment. |
| 4 | Draw a phylogenetic tree showing how these traits could lead to a new species over generations. |

💡 Note: This activity simulates a simplistic scenario. Real-world evolution involves complex interactions of multiple factors.
Darwin’s Voyage on the Beagle

Charles Darwin’s voyage on the HMS Beagle from 1831 to 1836 provided him with a wealth of observations that helped form his theory of evolution:
- Galapagos Islands: Darwin noted the variations in finch beaks, which later supported his ideas about adaptive radiation.
- Fossils: Discoveries of fossilized remains suggested species change over time.
- Geological observations: Observing geological phenomena gave him insights into Earth's age and changes over time.
Explore Darwin’s Beagle Route

Use this worksheet to trace Darwin’s journey and explore how his observations influenced his theory:
| Location | Observation/Discovery | Impact on Theory |
|---|---|---|
| South America | Fossil discoveries (e.g., glyptodon) | Indicated species change over time. |
| Galapagos Islands | Finch beak variations | Evidence of adaptive radiation. |
| St. Helena | Geological evidence of erosion | Suggested a long geological timescale for evolution. |
Survival of the Fittest

“Survival of the Fittest,” a phrase popularized by Herbert Spencer, encapsulates one of Darwin’s core ideas. Here’s how this concept unfolds:
- Species compete for limited resources.
- Individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
- These traits are passed to the next generation, shaping the species over time.
Survival of the Fittest Worksheet

Engage with this exercise to understand how ‘fitness’ influences evolution:
| Scenario | Survival Strategies |
|---|---|
| A predator hunting for prey | Speed, camouflage, agility |
| Plants competing for sunlight | Height, broad leaves, phototropism |
🌿 Note: 'Fitness' in evolutionary terms refers to reproductive success, not physical strength or endurance.
Speciation

The process of speciation, where new species arise, is central to Darwin’s theory. Here are key types:
- Allopatric Speciation: When populations are separated by physical barriers.
- Sympatric Speciation: Speciation occurs within the same geographic area.
- Parapatric Speciation: Populations are adjacent but with some gene flow.
Speciation Process Worksheet

Use this interactive chart to visualize how species diverge:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Isolation | Physical or ecological barriers prevent gene flow. |
| Genetic Drift | Random changes in allele frequency occur. |
| Mutation & Selection | Natural selection favors different traits in isolated populations. |
| Reproductive Isolation | Species become reproductively incompatible. |
Evolution and the Fossil Record

The fossil record provides evidence for evolutionary changes over geological time:
- Fossils show intermediate forms, indicating evolutionary transitions.
- The chronology of fossils aligns with the evolutionary timeline.
- Extinct species highlight evolutionary dead-ends.
Fossil Record Worksheet

Here’s an activity to explore the fossil record’s evidence for evolution:
| Layer | Geological Period | Species Found |
|---|---|---|
| Topmost | Holocene | Modern humans, large mammals |
| Middle | Pleistocene | Mammoth, saber-toothed cat |
| Lowermost | Cretaceous | Dinosaurs, ancient birds |
In our exploration of the Origin of Species Theory, we've ventured through the fundamental principles of evolution, Darwin's pivotal journey, the essence of natural selection, and the intricate processes of speciation. We've seen how the fossil record supports this theory, illustrating the past diversity of life and its progression over time.
What is the main idea behind Darwin’s Origin of Species?

+
The central idea is that species evolve over time through natural selection, where traits providing a survival advantage are more likely to be passed on, leading to species change and divergence.
Can evolution explain the development of complex organs like the eye?

+
Yes, evolution suggests complex structures develop through numerous small, incremental changes that each offer a survival advantage at the time, such as sensitivity to light leading to the development of the eye.
What are the key differences between Darwinism and Lamarckism?

+
Darwin’s theory focuses on natural selection and random variation, whereas Lamarckism suggests acquired traits during an organism’s lifetime can be inherited, an idea now considered flawed by modern genetics.
How does genetic drift influence evolution?

+
Genetic drift is the random fluctuation of allele frequencies in a population. It can lead to the loss or fixation of alleles, thereby playing a role in evolution, especially in smaller populations where chance events can have more impact.
Why is the theory of evolution considered controversial?

+
The controversy often stems from misunderstandings or ideological conflicts, particularly with creationist views, rather than with the scientific evidence itself, which overwhelmingly supports evolution as the explanation for the diversity of life.



