Mole Concept & Avogadro's Number: Easy Answers

The concept of moles and Avogadro's Number are fundamental for understanding chemical reactions and quantities in chemistry. Whether you're a student or a professional chemist, these principles help in quantifying matter at the atomic and molecular level, thus making chemistry a measurable science.
What is a Mole?

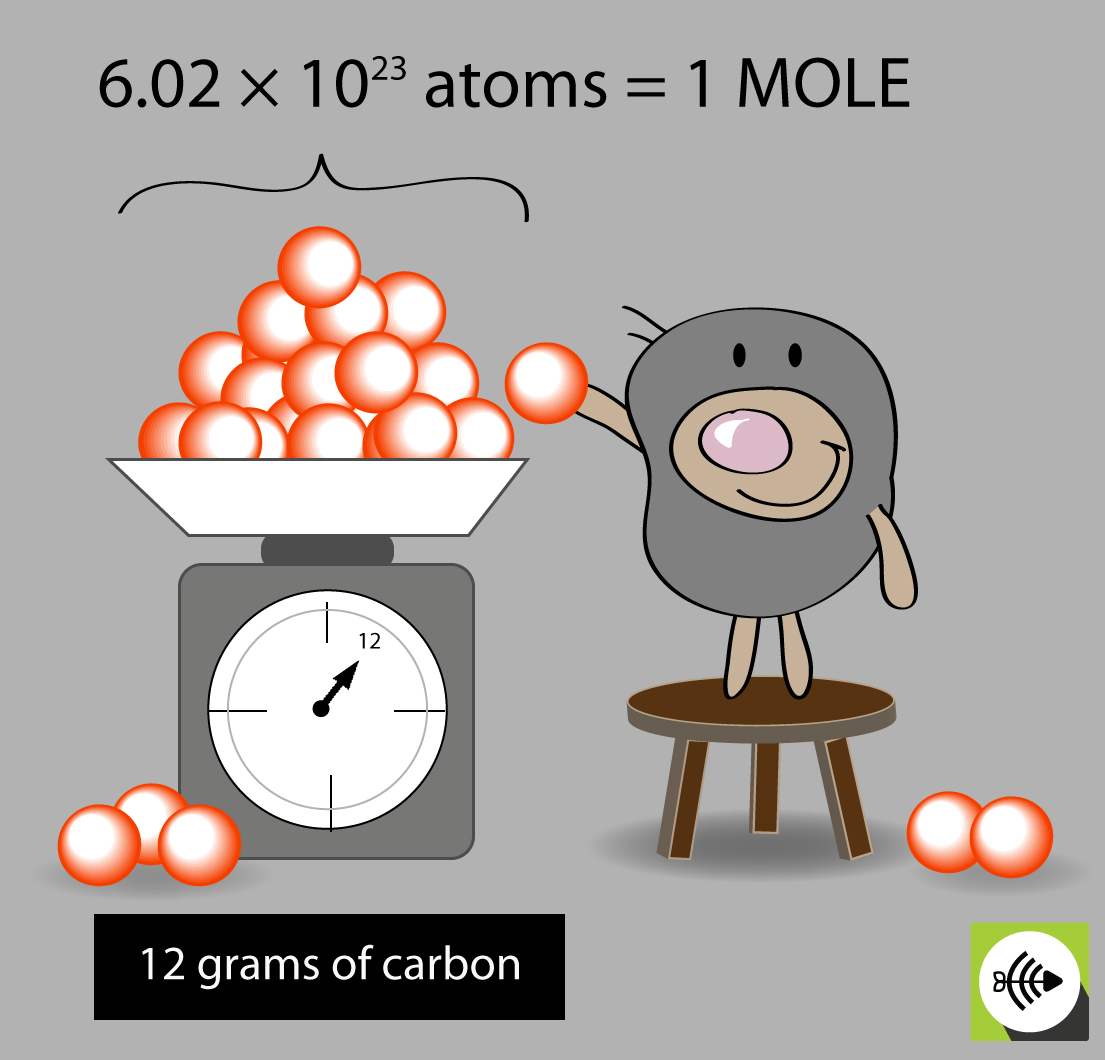
The mole is a unit of measurement in chemistry that acts like a bridge between the atomic world and the observable macroscopic world. It’s defined as the amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.) as there are atoms in exactly 12 grams of the isotope carbon-12.
- Definition: A mole represents 6.022 x 1023 entities.
- Symbol: The symbol for mole is "mol."
- Conversions: To convert from grams to moles, divide the mass by the molar mass. Conversely, to convert from moles to grams, multiply the moles by the molar mass.
Avogadro’s Number

Avogadro’s Number, 6.022 x 1023, is the magic number of entities in one mole of any substance. Named after Amedeo Avogadro, this number is the link between the mass of an element or compound and the number of atoms or molecules it contains.
- Representation: It's also known as Avogadro's constant (NA).
- Usage: It's crucial for calculating quantities in chemical reactions, stoichiometry, and understanding gas laws.
💡 Note: Avogadro's Number is a constant, meaning it does not vary with the size, mass, or shape of the substance but refers to the fundamental relationship between the amount of substance and its countable entities.
Why Moles Matter
The mole concept is essential because it:
- Allows for a consistent and universal way to count and talk about atoms, molecules, and ions.
- Bridges the gap between microscopic particles and macroscopic measurements.
- Facilitates stoichiometric calculations, helping chemists predict the outcomes of reactions.
It's the key to understanding how reactions work on a quantitative level.
Calculations and Examples

Let’s delve into some practical examples to illustrate how the mole concept is applied in real-world calculations:
Calculating Molar Mass

To find the molar mass of a compound, you add up the atomic masses of its constituent elements. Here’s how:
- For water (H2O):
- Hydrogen: 1.008 g/mol x 2 = 2.016 g/mol
- Oxygen: 16.00 g/mol x 1 = 16.00 g/mol
- Total Molar Mass: 2.016 + 16.00 = 18.016 g/mol
Converting Grams to Moles

If you have 36.04 grams of water:
- Formula: Moles = Mass / Molar Mass
- Calculation: Moles of Water = 36.04 g / 18.016 g/mol ≈ 2 mol
Determining Molecular Formula from Empirical Formula

If you know the empirical formula and need to find the molecular formula, you can use the molar mass:
- Empirical formula: CH₂O
- Molecular mass of CH₂O: 12.01 + 1.008 x 2 + 16.00 = 30.026 g/mol
- Given molecular mass: 60.052 g/mol
- Ratio: (60.052 g/mol) / (30.026 g/mol) = 2
- Therefore, molecular formula: C2H4O2
🔍 Note: The molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms in a molecule, while the empirical formula expresses the simplest ratio of atoms in the compound.
Practical Applications

The mole concept is not just a theoretical tool; it’s immensely practical:
- Stoichiometry: Understanding the moles helps predict the amounts of reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
- Industrial Chemistry: It allows for scaling up from lab experiments to industrial quantities, ensuring efficiency and reducing waste.
- Pharmacology: In drug development, knowing the molecular weights and mole ratios ensures the correct proportions of compounds are used to achieve desired effects.
In summary, the mole concept and Avogadro's Number provide chemists with a universal system to count atoms and molecules, helping to quantify, predict, and understand chemical reactions. By bridging the gap between the invisible atomic world and the tangible macroscopic scale, these concepts are the cornerstone of quantitative chemistry. They not only simplify calculations but also allow chemists to explore, innovate, and create in a more precise and consistent manner.
Why is the mole important in chemistry?

+
The mole is crucial in chemistry because it provides a consistent way to measure and count atoms, ions, and molecules, allowing chemists to work with precise quantities in chemical reactions.
What does Avogadro’s Number represent?

+
Avogadro’s Number represents the number of entities (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.) in one mole of any substance, which is approximately 6.022 x 1023.
How do you convert moles to grams?
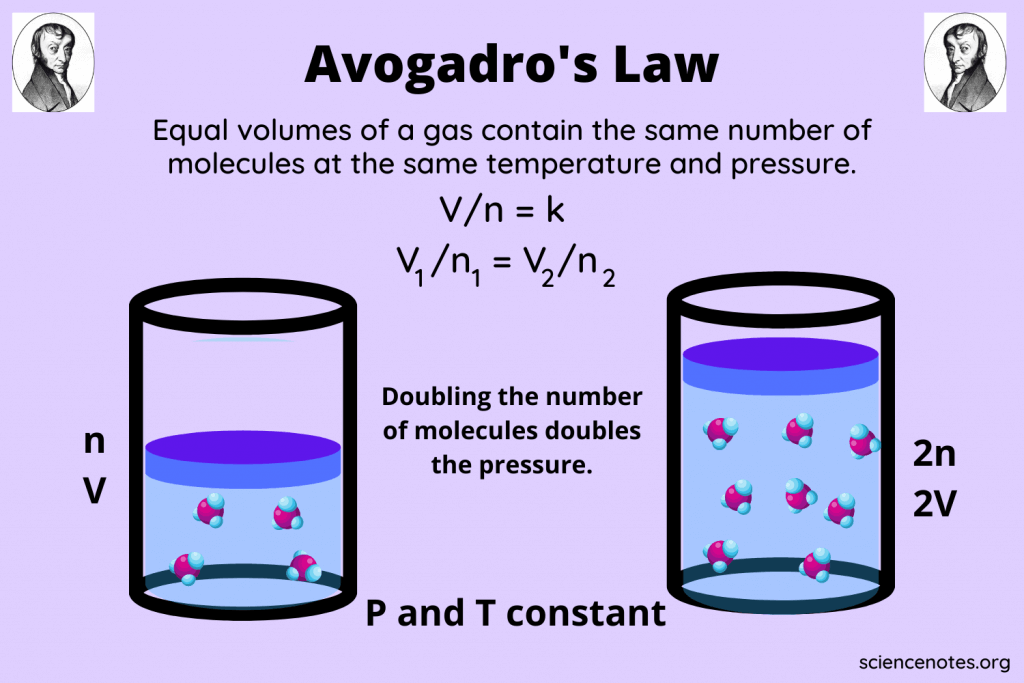
+
To convert moles to grams, you multiply the number of moles by the molar mass of the substance.
Can the mole concept be applied to gases?

+
Yes, the mole concept is particularly useful in gas laws, where Avogadro’s Law states that equal volumes of all gases at the same temperature and pressure contain an equal number of moles.
Why is the molar mass in grams per mole?

+
The molar mass is expressed in grams per mole because it’s derived from the mass of Avogadro’s number of atoms or molecules, providing a convenient way to link the number of entities to a measurable mass.