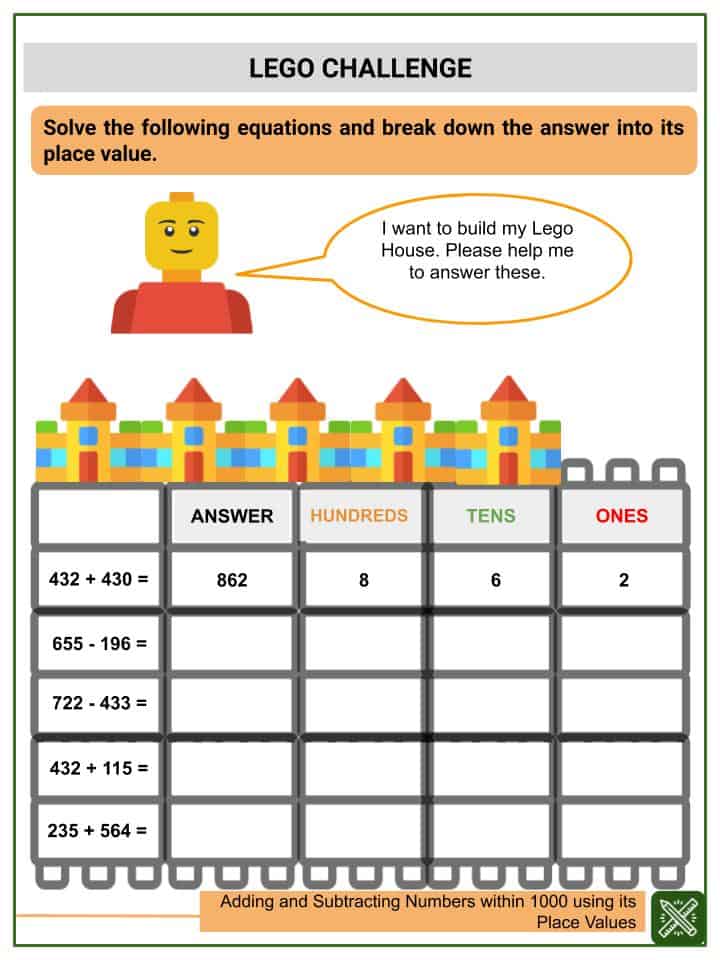
5 Essential Answers to Market Economy Questions

The market economy is a complex system that involves a myriad of interactions between buyers, sellers, producers, and consumers, all orchestrated through the forces of supply and demand. Understanding this system is crucial not only for economists but for anyone engaged in business, finance, or even everyday consumer activities. Here, we will delve into five essential questions about market economies, providing comprehensive answers to help demystify this dynamic and influential economic structure.
What is a Market Economy?

A market economy is an economic system in which the production, distribution, and pricing of goods and services are determined by the interactions of consumers and producers in markets. Here are some key characteristics:
- Voluntary Exchange: Individuals and organizations engage in transactions where both parties benefit.
- Private Ownership: Property rights are crucial, as individuals and companies own resources, capital, and goods.
- Competition: Multiple suppliers exist for most goods, promoting innovation and efficiency.
- Price Mechanism: Prices serve as signals for resource allocation, adjusting based on supply and demand.
💡 Note: In a pure market economy, government intervention is minimal, but in reality, most market economies operate with some degree of government oversight and regulation to prevent market failures.
How Does Supply and Demand Work in a Market Economy?

Supply and demand are fundamental forces in a market economy:
Supply

Supply refers to the amount of a good or service producers are willing and able to offer at various prices. When the price rises:
- Producers have an incentive to increase production.
- New producers might enter the market, leading to an increase in supply.
Demand

Demand relates to the quantity of goods or services consumers desire at different prices. When the price decreases:
- Consumers tend to buy more.
- There might be an expansion in the market or demand for substitutes.
| Price | Quantity Supplied | Quantity Demanded | Market Situation |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | Increase | Decrease | Surplus |
| Low | Decrease | Increase | Shortage |
| Equilibrium | Stays the Same | Stays the Same | Balanced |

The equilibrium price is where the quantity consumers want to buy equals the quantity producers want to sell. This dynamic interaction between supply and demand leads to price adjustments, which in turn affect production decisions and consumer behavior.
Why is Competition Important?
Competition is often referred to as the "lifeblood" of a market economy for several reasons:
- Innovation: Companies compete to offer better products, leading to technological advancements and improvements in quality.
- Efficiency: Competitive markets pressure companies to reduce costs, leading to more efficient production processes.
- Consumer Welfare: Consumers benefit from lower prices, better quality, and a wider variety of choices.
- Resource Allocation: Competition ensures resources are directed towards the most profitable uses, which should also align with societal needs.
- Barrier Reduction: It can lower the barriers for new entrants, fostering entrepreneurial activities.
⚠️ Note: While competition is beneficial, lack of regulation can lead to monopolistic practices, where one or few companies dominate the market, potentially harming consumer interests.
What Role Does Government Play?

While market economies are characterized by minimal government intervention, the government does play several essential roles:
- Establishing and Enforcing Property Rights: Essential for transactions and investment.
- Providing Public Goods: Goods and services not provided by the market due to the free-rider problem (e.g., national defense, public infrastructure).
- Externalities Management: Addressing positive and negative externalities (costs or benefits not reflected in market prices).
- Regulation: To ensure fair competition, protect consumers, and maintain market stability.
- Social Safety Nets: Providing basic security for citizens, reducing the negative impacts of economic fluctuations.
How Does a Market Economy Differ from Other Systems?

Here are the primary distinctions between a market economy and other systems:
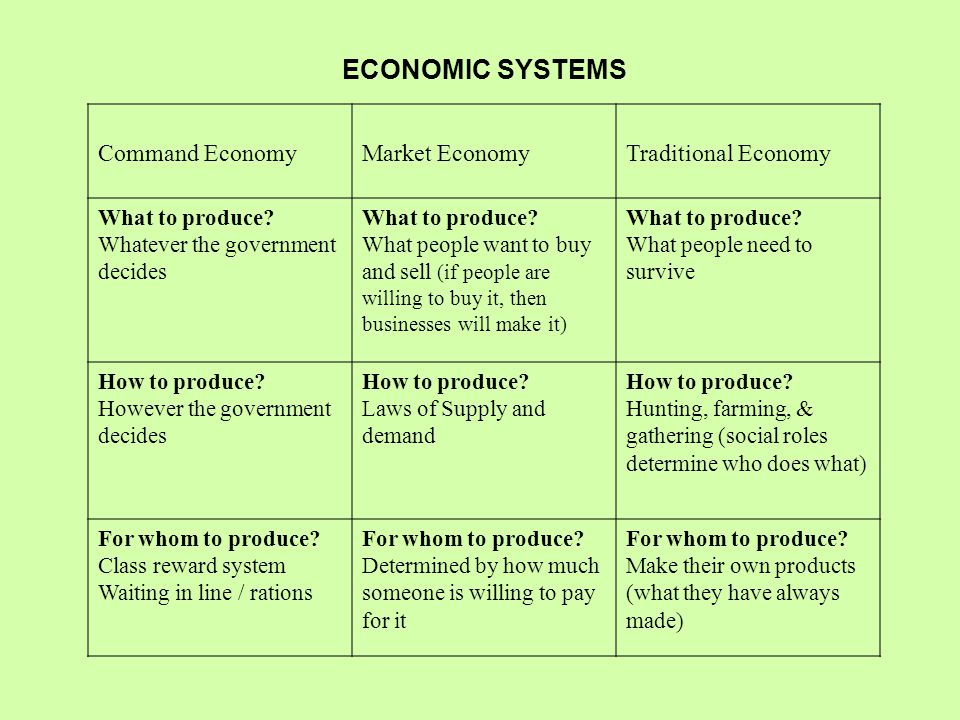
Planned Economy (Command Economy)
- Government owns and controls all means of production.
- Resource allocation is decided by central planning, not market mechanisms.
Mixed Economy

- Combines elements of market and planned economies.
- Markets operate with significant government oversight or intervention.
Traditional Economy
- Economic decisions are based on customs, history, and time-honored practices rather than market forces.
In summary, understanding these five essential questions provides a broad perspective on how market economies function, their benefits, their limitations, and their interactions with government. These insights are not only theoretical but have practical implications for business strategies, policy-making, and everyday economic decisions.
By exploring the intricacies of supply and demand, the importance of competition, the role of government, and the differences between economic systems, we've shed light on how a market economy operates. This understanding is key for navigating the complexities of modern economic life and participating effectively in this dynamic system.
What Are the Advantages of a Market Economy?

+
Market economies offer advantages like innovation, efficiency, and consumer choice, as businesses strive to meet demand and outperform competitors.
How Can Market Economies Fail?

+
Market economies can fail due to externalities, income inequality, monopolies, or lack of regulation, leading to market inefficiencies or economic crises.
What Happens When Supply and Demand Are Out of Balance?
+
If supply exceeds demand, prices decrease, potentially leading to overproduction and surpluses. If demand outpaces supply, prices increase, which can cause shortages and inflationary pressures.
Can a Market Economy Exist Without Any Government Regulation?

+
Pure market economies with zero government intervention are theoretically possible but practically unsustainable due to the need for laws, public goods, and externalities management.
What’s the Impact of Technological Change on Market Economies?

+
Technology can disrupt traditional markets by introducing new products, reducing costs, changing labor requirements, and altering competitive dynamics, often leading to economic shifts and innovations.