Korean War Worksheet Answers: Essential Guide for Students

The Korean War, a pivotal moment in modern history, still echoes in the collective memory of nations, marking a significant division on the Korean Peninsula. This guide offers an in-depth look into essential worksheet answers for students studying this period, making complex historical events more accessible and understandable.
Understanding the Causes of the Korean War

At the heart of the Korean War was the ideological conflict between communism and democracy, intensified by global tensions following World War II. Here are key factors that led to the conflict:
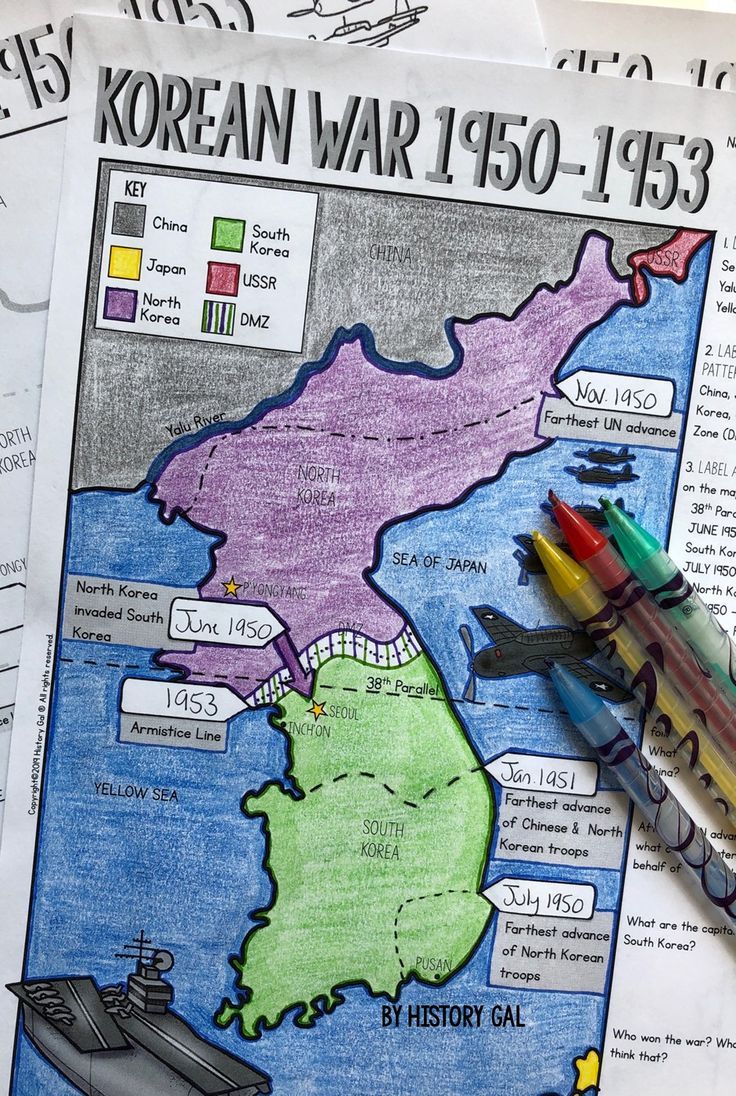
- Division of Korea: After the surrender of Japan in 1945, Korea was divided at the 38th Parallel. The Soviet Union occupied the north, establishing a communist government, while the United States supported a democratic regime in the south.
- The Cold War Context: The Korean War was a proxy war within the larger framework of the Cold War, where superpowers supported opposing factions without engaging in direct combat.
- Kim Il-sung’s Ambitions: The North Korean leader sought reunification under communism, with his invasion in June 1950 marking the beginning of the war.
📝 Note: The term "proxy war" refers to a conflict where major powers exert influence indirectly by supporting smaller nations or factions. This was a prevalent strategy during the Cold War.
The Course of the War


The Korean War can be divided into several critical phases:
- Initial North Korean Invasion: North Korea, backed by Soviet equipment, invaded South Korea, quickly capturing Seoul.
- UN Intervention: The United Nations, predominantly the US, stepped in to repel the invasion. General Douglas MacArthur led the Incheon Landing, a pivotal moment that turned the tide.
- China’s Entry: Fearful of a US-led force at their border, China entered the war in support of North Korea.
- Stalemate and Armistice: The war stagnated along the 38th Parallel, leading to peace talks. An armistice was signed on July 27, 1953, but no peace treaty was established, leaving the peninsula divided.
Impact of the Korean War

The war left lasting impacts:
- Humanness: Millions of civilian casualties and displacement shaped Korea’s demographic landscape.
- Politics: It solidified the Cold War divide in Asia, influencing decades of international relations.
- Economy: South Korea’s devastation was followed by a surge in economic recovery, while North Korea, isolated, maintained a totalitarian regime.
Worksheet Answers
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What was the significance of the 38th Parallel? | It served as the pre-war and post-armistice boundary between North and South Korea. |
| Why did the US get involved in the Korean War? | To prevent the spread of communism, under the policy of containment, and due to South Korea’s appeal for assistance against the invasion. |
| What was the role of the United Nations in the Korean War? | The UN authorized an international military coalition to aid South Korea, marking one of the first collective security operations. |
| How did China’s entry change the course of the war? | It led to the war’s prolongation and a stalemate, preventing a complete US victory. |

In studying the Korean War, these answers provide students with a comprehensive overview. Understanding these facets allows for a deeper appreciation of not only the conflict itself but also its implications for global politics and human history.
Recapitulation

Exploring the Korean War through this guide highlights its complexities. The war resulted from ideological and geopolitical tensions, leaving a lasting mark on Korea and the world. From understanding its causes, to examining the war’s timeline, and analyzing its impacts, this guide delivers essential answers and insights for students diving into this era of history. By grasping these key elements, students gain a richer understanding of how events like the Korean War shape our current world order and continue to influence international relations.
What caused the Korean War?

+
The Korean War was primarily caused by the ideological split of Korea into a communist north supported by the USSR, and a capitalist south backed by the US. Tensions escalated after Japan’s defeat in WWII, leading to the 1945 division of Korea.
How did the Korean War end?

+
The Korean War ended with an armistice on July 27, 1953, which ceased hostilities but left the peninsula divided at roughly the same 38th Parallel as before the war started. No peace treaty was signed, and the division remains today.
Was the Korean War part of the Cold War?

+
Yes, the Korean War is considered one of the first significant conflicts of the Cold War. It was a manifestation of the ideological and geopolitical struggle between communism and democracy, where superpowers indirectly battled through smaller nations.
What was the impact of China’s involvement in the Korean War?

+
China’s entry into the war changed its course significantly, forcing the United Nations forces into a stalemate. This intervention prolonged the war and helped prevent a complete victory by UN forces, ultimately leading to the armistice.