The Double Helix: DNA Worksheet Essentials

Understanding the basics of DNA is crucial for any student in the field of biology or related sciences. The concept of the double helix, first described by Watson and Crick in 1953, revolutionized our understanding of genetics. This blog post will dive deep into DNA worksheet essentials, providing you with a comprehensive guide to understanding the structure, function, and significance of DNA in cellular biology.
The Structure of DNA


The DNA molecule, or deoxyribonucleic acid, has a unique and elegant structure:
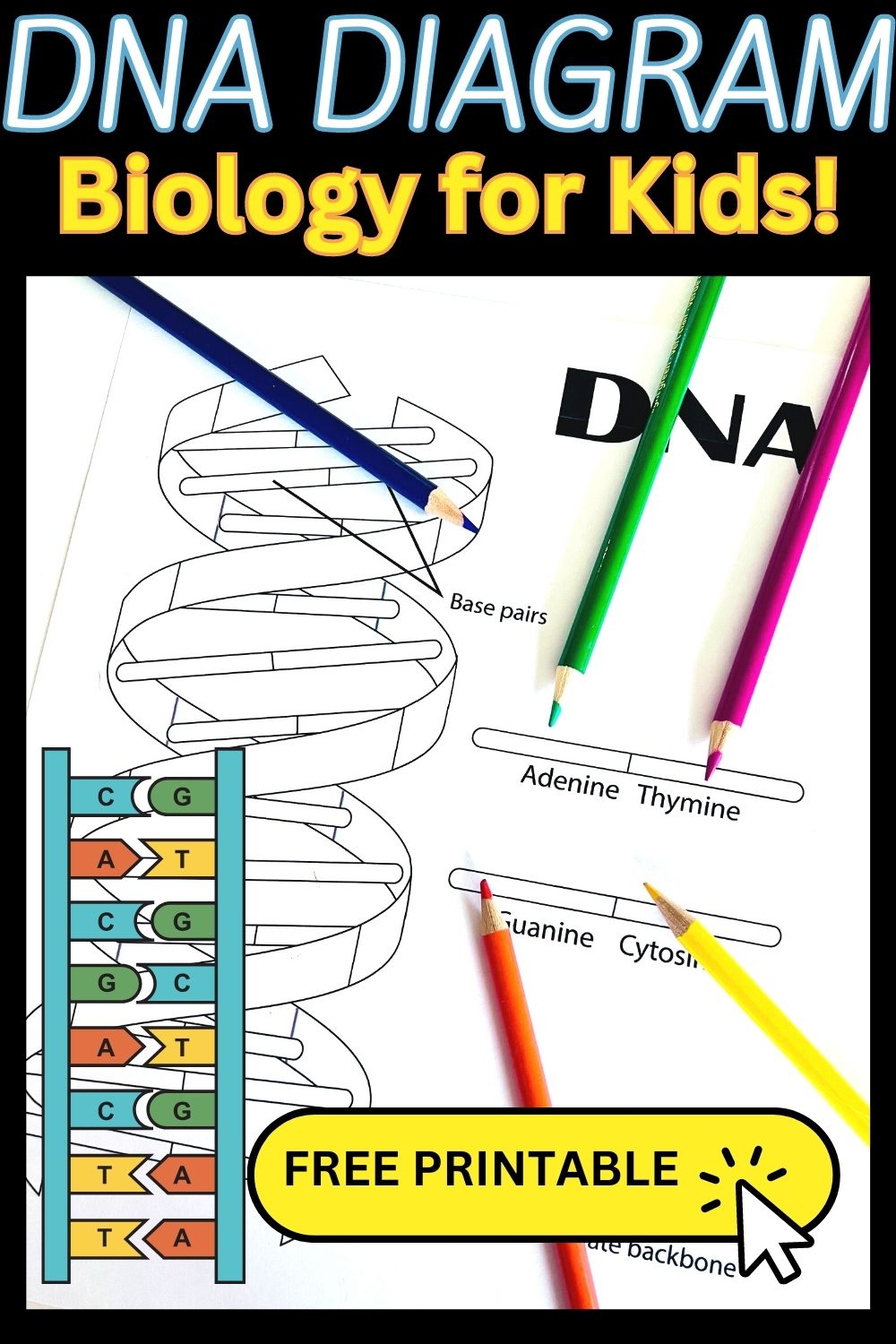
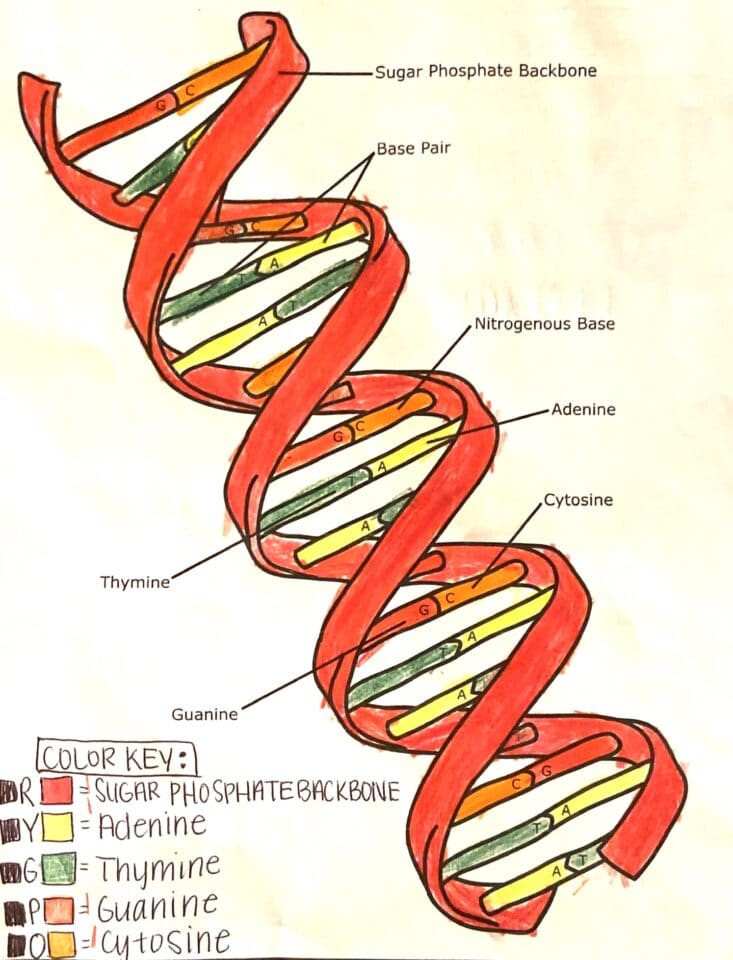
- Double Helix: DNA is composed of two long chains that coil around each other, forming the iconic double helix shape.
- Nucleotide Components: Each chain is made up of nucleotides, consisting of:
- A nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine).
- A sugar molecule (deoxyribose).
- A phosphate group.
- Base Pairing: Adenine pairs with thymine, while cytosine pairs with guanine. These pairings are held by hydrogen bonds.
- Sugar-Phosphate Backbone: The outside of the helix is formed by the sugar-phosphate backbones, which provide stability to the structure.
Why is the Double Helix Important?

The double helix structure of DNA is not just a visual marvel; it’s vital for several reasons:
- Replication Efficiency: The structure allows for semi-conservative replication, where each strand can serve as a template for new DNA synthesis.
- Stability and Protection: The helical structure protects the genetic code, keeping the sequence of nucleotides safe from damage.
- Accessibility for Proteins: Certain proteins can access specific parts of the DNA without unwinding the entire molecule, facilitating functions like transcription.
DNA Function and Role

Here’s how DNA functions within a cell:
- Genetic Information Storage: DNA contains the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses.
- Replication: Before cell division, DNA replicates itself, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material.
- Transcription and Translation: DNA is transcribed into RNA, which then translates into proteins. This process is fundamental for gene expression.
Importance in Biotechnology

The knowledge of DNA structure and its functions has paved the way for numerous biotechnology advancements:
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): Allows for the amplification of DNA segments for research, diagnostics, and forensic analysis.
- Genetic Engineering: The understanding of DNA has enabled the modification of organisms to produce desired traits or products like insulin or pest-resistant crops.
- Gene Therapy: Researchers can correct or replace mutated genes using vectors carrying the correct DNA sequence.
⚠️ Note: DNA, while stable, can be damaged by environmental factors, leading to mutations. Cells have repair mechanisms, but over time, these can fail, contributing to aging and diseases like cancer.
Practical Applications in Education
DNA worksheets often include practical exercises to enhance understanding:
- Model Building: Creating physical models of DNA helps students visualize the structure.
- Restriction Enzyme Digestion: Experimenting with enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences teaches students about gene manipulation techniques.
- Gel Electrophoresis: Visualizing how DNA fragments move through a gel under the influence of an electric field.
| Activity | Objective |
|---|---|
| Model Building | To understand DNA structure and base pairing. |
| Restriction Enzyme Digestion | To learn about DNA manipulation and cloning. |
| Gel Electrophoresis | To separate and analyze DNA fragments. |

Interdisciplinary Connections

Learning about DNA isn’t just for biology students:
- Chemistry: Understanding the chemical bonds that form the DNA structure.
- Physics: The physical properties of DNA, like how it coils, bends, and responds to forces.
- Computer Science: Algorithms for DNA sequence alignment and analysis.
Wrapping Up
Understanding the essentials of DNA through worksheets can transform the learning experience. By focusing on its structure, function, and significance, we gain insight into life at its most fundamental level. The double helix of DNA is not only a blueprint for life but also a key to unlocking some of the greatest scientific and medical mysteries of our time. Remember, each time you study DNA, you’re exploring the core of all living organisms, the very code of life itself.
What does DNA stand for?

+
DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid, which is the molecule that carries the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all known living organisms.
Why is the DNA structure called a double helix?
+
The DNA structure is called a double helix because it consists of two long chains of nucleotides that coil around each other in a helical pattern, resembling a twisted ladder or spiral staircase.
How can DNA worksheets help in understanding genetics?

+
DNA worksheets provide hands-on activities that simplify complex genetic concepts. They help students visualize DNA structure, understand how genes are copied, and how genetic information is stored and accessed, making genetics more accessible and tangible.



