Cell Cycle Coloring Worksheet: Answers and Insights
If you've ever tried to grasp the complexities of the cell cycle, you know it can feel like you're navigating through a maze of biological terminology and processes. However, understanding this fundamental concept is crucial for anyone studying life sciences. Today, we delve into the cell cycle with a fun twist—using a coloring worksheet as a learning tool.
The Importance of the Cell Cycle

Before diving into the worksheet, let’s consider why the cell cycle is essential:
- Growth and Development: Cells must multiply for growth, repair, and the development of complex organisms.
- Cell Replacement: The cycle ensures that cells worn out or damaged are replaced in a controlled manner.
- Disease Prevention: Errors in cell division can lead to cancers, highlighting the necessity of understanding and regulating this process.
📘 Note: The cell cycle is a highly controlled series of events that ensures cells divide correctly. Any disruption can have significant implications.
Phases of the Cell Cycle

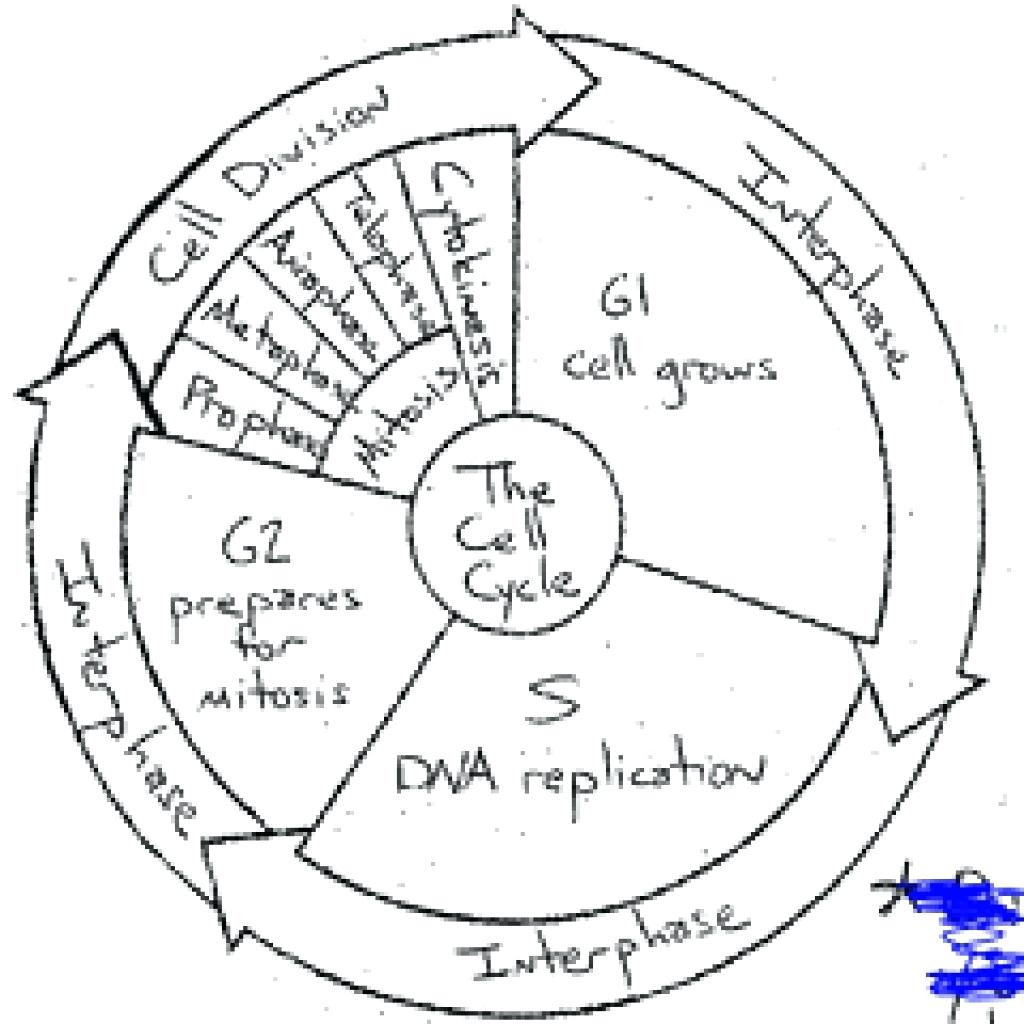
The cell cycle consists of several distinct phases, each critical to the process of cell division. Here’s a look at these phases through the lens of a coloring worksheet:
1. Interphase


Interphase is where the cell prepares for division:
- G1 Phase: Cells grow, perform functions, and prepare for DNA synthesis. Color this phase in blue.
- S Phase: DNA replication occurs. Choose green to color this phase.
- G2 Phase: The cell prepares for division; final preparations are made. Use purple here.
2. Mitotic Phase (M Phase)


This phase is where cell division takes place, further divided into:
- Prophase: Chromosomes condense, the mitotic spindle forms. Color this in red.
- Prometaphase: The nuclear envelope breaks down, allowing the spindle to capture chromosomes. This can be colored orange.
- Metaphase: Chromosomes align at the cell’s equator. Use yellow for this phase.
- Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate, moving to opposite poles. Here, color it brown.
- Telophase: New nuclear envelopes form around the chromosome sets. Color this phase in teal.
- Cytokinesis: The final division of the cytoplasm. Represent this with pink.
🎨 Note: Coloring these phases not only makes learning visual but also engages different parts of the brain, aiding in memory retention.
Regulation of the Cell Cycle

To ensure the orderly progression through these phases, the cell cycle is tightly regulated:
- Checkpoints: These are quality control points where the cell stops to check if conditions are right to proceed.
- Cyclins and Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs): These proteins regulate the cell’s progression through the cycle.
- External Signals: Growth factors, nutrient levels, and cell-cell interactions can influence cell cycle regulation.
Insights from the Cell Cycle Coloring Worksheet

Using a coloring worksheet to study the cell cycle offers several insights:
- Visual Learning: Seeing the sequence of events in color helps conceptualize the process.
- Retention: Engaging multiple senses can improve information retention significantly.
- Engagement: It makes the study of complex biology more interactive and less daunting.
In summary, understanding the cell cycle through a coloring worksheet provides a dynamic way to learn. The worksheet not only aids in visualizing the phases but also deepens understanding of cellular regulation, emphasizing the importance of each step for maintaining life's continuity and health. By associating colors with phases, students can better remember the intricate dance of cell division, ensuring that learning remains both informative and engaging.
Why is it important to understand the cell cycle?

+
Understanding the cell cycle is fundamental for studying growth, development, cancer, and aging processes. It helps in recognizing how cells control their division and what can go wrong, potentially leading to diseases.
How can coloring worksheets aid in learning biology?
+
Coloring worksheets engage visual and kinesthetic learning styles, making complex biological processes more memorable. They also cater to different learning preferences, enhancing overall retention of information.
What happens if the cell cycle goes wrong?

+
Errors in the cell cycle can lead to uncontrolled cell division, resulting in tumors or cancer. Proper regulation is crucial for preventing these conditions.
Can you study the cell cycle in other organisms?

+
Yes, the basic principles of the cell cycle are conserved across eukaryotic organisms, though there can be variations in specific checkpoints or regulatory mechanisms.
How are DNA checkpoints involved in the cell cycle?

+
DNA checkpoints ensure that the cell cycle proceeds only if DNA replication has occurred correctly. If DNA damage is detected, cells can halt progression, allowing for repair or triggering apoptosis to prevent the spread of damaged DNA.