Testing a Points Condenser Made Easy
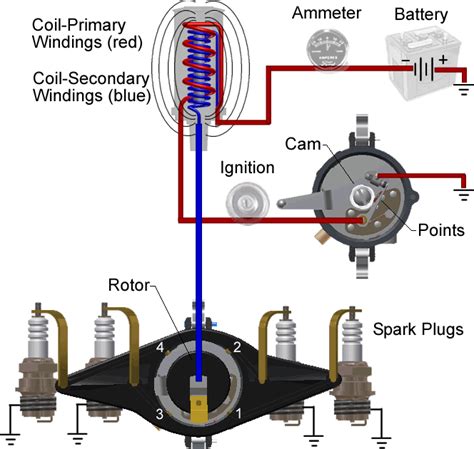
Understanding the Basics of a Points Condenser

A points condenser is a crucial component in various industrial and commercial applications, including refrigeration, air conditioning, and heat pumps. It plays a vital role in the condensation process, allowing the system to operate efficiently and effectively. In this article, we will explore the concept of a points condenser, its functions, and how to test it with ease.
What is a Points Condenser?

A points condenser is an electrical component that consists of two metal points separated by a small gap. When a voltage is applied across the points, it creates an electric field that attracts moisture from the surrounding air. As the moisture accumulates, it condenses into droplets, which are then collected and removed from the system.
Functions of a Points Condenser

The primary functions of a points condenser are:
- Moisture removal: The condenser removes excess moisture from the system, preventing damage to the equipment and ensuring optimal performance.
- Pressure regulation: By controlling the amount of moisture in the system, the condenser helps regulate pressure and maintain a stable operating environment.
- Efficiency improvement: By removing excess moisture, the condenser improves the overall efficiency of the system, reducing energy consumption and increasing productivity.
Testing a Points Condenser

Testing a points condenser can be a straightforward process if you follow the correct steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you test a points condenser:
Step 1: Visual Inspection
Begin by visually inspecting the condenser for any signs of damage, corrosion, or wear. Check for any blockages or debris that may be obstructing the airflow or electrical connections.
Step 2: Electrical Testing
Use a multimeter to test the electrical connections and voltage across the points. Ensure that the voltage is within the specified range and that there are no signs of electrical noise or interference.
Step 3: Condensation Testing
To test the condensation function, apply a small amount of moisture to the points using a spray bottle or a wet cloth. Observe the points for any signs of condensation, such as droplets forming or water vapor accumulating.
Step 4: Pressure Testing
Use a pressure gauge to test the pressure regulation function. Apply a small amount of pressure to the system and observe the condenser’s response. The pressure should be regulated within the specified range.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Here are some common issues that may arise during testing:
- Insufficient condensation: Check for blockages or debris obstructing the airflow or electrical connections.
- Electrical noise or interference: Inspect the electrical connections and ensure that they are secure and free from corrosion.
- Pressure regulation issues: Check the pressure gauge and ensure that it is calibrated correctly.
🔍 Note: When testing a points condenser, ensure that the system is turned off and the power is disconnected to avoid any electrical shock or injury.
Best Practices for Maintenance and Repair

To ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of your points condenser, follow these best practices:
- Regular cleaning: Regularly clean the condenser to prevent blockages and debris accumulation.
- Electrical maintenance: Inspect and maintain the electrical connections to prevent corrosion and electrical noise.
- Pressure regulation: Regularly check and adjust the pressure regulation to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion

Testing a points condenser can be a straightforward process if you follow the correct steps and best practices. By understanding the functions and testing procedures, you can ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of your points condenser.
What is the primary function of a points condenser?

+
The primary function of a points condenser is to remove excess moisture from the system, preventing damage to the equipment and ensuring optimal performance.
How do I test a points condenser?

+
To test a points condenser, follow the steps outlined in this article, including visual inspection, electrical testing, condensation testing, and pressure testing.
What are common issues that may arise during testing?

+
Common issues that may arise during testing include insufficient condensation, electrical noise or interference, and pressure regulation issues.