5 Key Taxonomy Worksheet Answers Revealed

The realm of education often involves sifting through extensive textbooks, papers, and various study materials in search of the best way to comprehend complex subjects. Taxonomy, the science of classification, is one such subject that can be quite intricate. It deals with the categorization of species, their hierarchies, and relationships—a foundational element in biological sciences. In this post, we'll delve into the essential "taxonomy worksheet answers" that can unlock a deeper understanding of this vast topic.
Understanding Taxonomy

Taxonomy, derived from the Greek word "taxis" (arrangement) and "nomos" (law), serves as the fundamental principle of arranging and identifying organisms. It's crucial for both academic understanding and practical applications like medical research or biodiversity preservation.
The key elements of taxonomy include:
- Identification: Determining what an organism is.
- Classification: Arranging organisms into taxa based on shared characteristics.
- Nomenclature: The naming of organisms using a two-part Latin binomial system.
- Systematics: Studying evolutionary relationships between organisms.
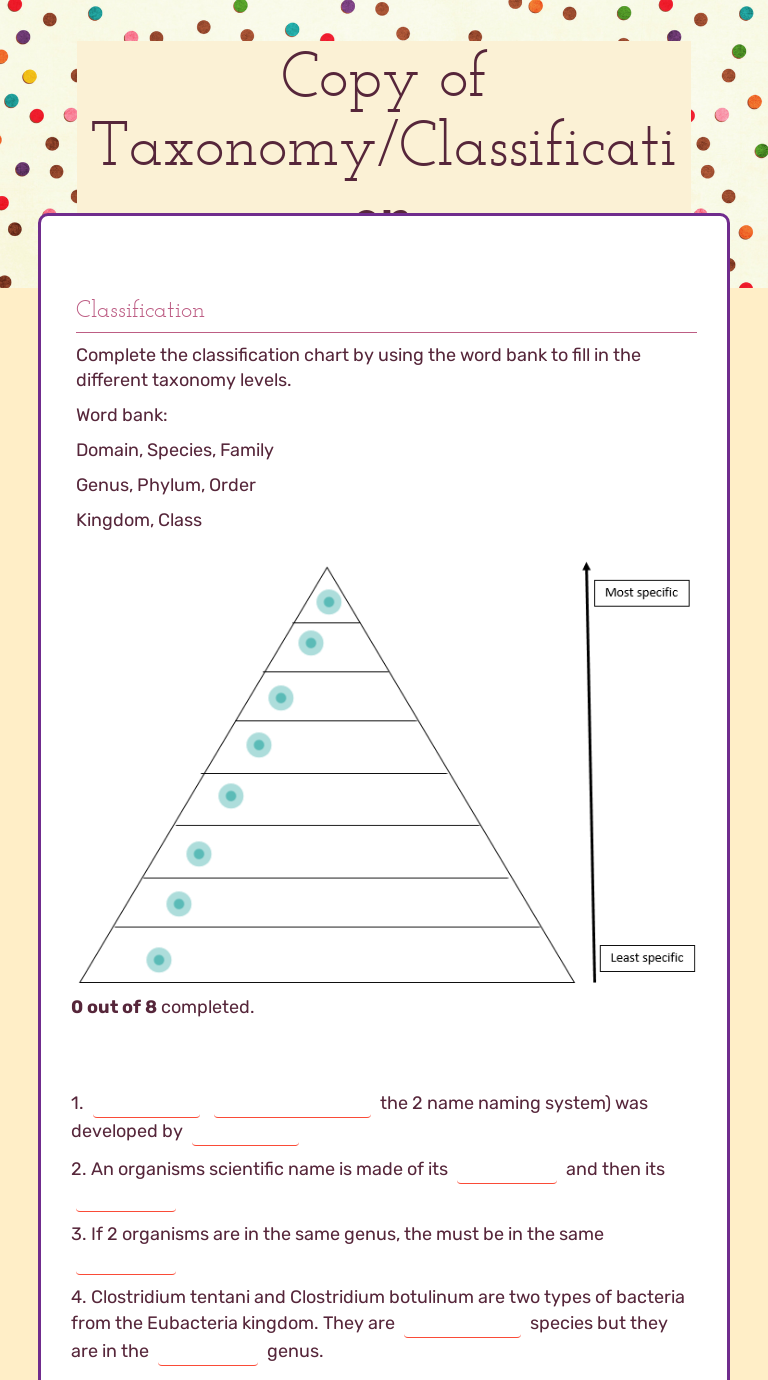
The Levels of Taxonomy

| Taxonomic Rank | Description |
|---|---|
| Domain | The broadest classification, encompassing Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. |
| Kingdom | Divides life forms into major groups like Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, and Monera. |
| Phylum | Subdivides kingdoms into smaller, related groups. |
| Class | Further categorizes phyla. |
| Order | Groups similar classes together. |
| Family | Closely related orders are combined here. |
| Genus | A group of closely related species. |
| Species | The most specific level, where individual organisms share the most similarities. |

🌿 Note: Taxonomy uses a hierarchical system to sort organisms in order of increasing specificity. Each rank groups organisms based on shared traits or ancestry.
Key Taxonomy Worksheet Answers

1. What is the Importance of Taxonomy?

Taxonomy provides a universal language for biology. Here are some reasons why taxonomy is crucial:
- It aids in identifying species for conservation efforts, ecological research, and medical purposes.
- It allows us to track evolution by understanding how species are related to one another.
- Biodiversity assessments and protection strategies are based on taxonomic classifications.
- Organisms are often named after key characteristics, which can provide insights into their nature.
2. How Do Taxonomists Classify Organisms?
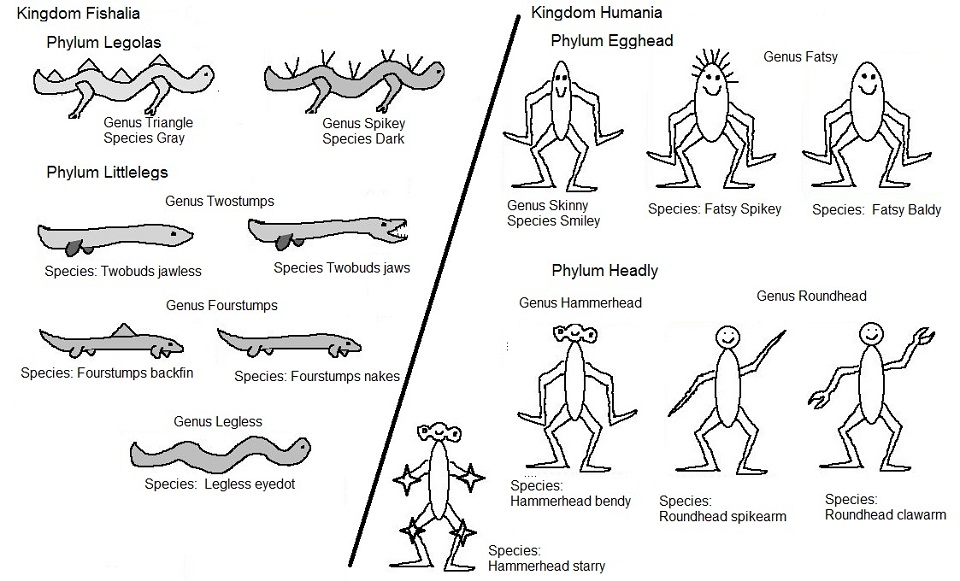
Taxonomists use multiple approaches:
- Morphological Characteristics: Physical appearance, structure, and development.
- Molecular Data: DNA, RNA, or protein sequences.
- Ecological and Behavioral Studies: How organisms interact with their environment or each other.
- Fossil Records: To understand extinct species and their connections to living ones.
3. What are the Different Ranks in Taxonomy?

The taxonomic ranks form a hierarchical system that reflects the evolutionary history of organisms:
- Domain
- Kingdom
- Phylum
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
Additional sub-ranks like Subphylum, Infraclass, and Subfamily exist to provide more granularity when necessary.
4. What is Binomial Nomenclature?

Binomial nomenclature, proposed by Carl Linnaeus, provides a unique name for each species using:
- The Genus name: The first part of the species name, capitalized.
- The Specific epithet: The second part of the name, not capitalized, describing the species further.
5. How Has Taxonomy Evolved Over Time?
The study of taxonomy has progressed from:
- Classical Taxonomy: Based on external characteristics.
- Numerical Taxonomy: Utilizes algorithms and statistics to classify organisms.
- Phylogenetic Taxonomy: Incorporates molecular biology and aims to reflect evolutionary history accurately.
- Cybertaxonomy: Modern taxonomic studies using digital tools and databases.
🔎 Note: Modern taxonomy often employs genetic sequencing to resolve classification issues where traditional morphology may not suffice.
In wrapping up, taxonomy remains an evolving science. Its significance in understanding biodiversity, evolutionary biology, and ecological systems cannot be overstated. Whether you're a student deciphering taxonomy worksheet answers or a researcher navigating the complexities of systematic biology, grasping these fundamental principles is vital for success. Each organism we classify adds to the tapestry of life, and each taxonomic breakthrough provides insight into the intricate web of life on Earth.
What is the purpose of taxonomy?

+
The primary purpose of taxonomy is to provide a standardized system for the identification, classification, and naming of organisms, aiding in understanding their relationships, evolution, and aiding in conservation and medical research.
How do taxonomists decide which rank an organism belongs to?

+
Taxonomists analyze characteristics like morphology, genetics, behavior, and ecological roles. These traits, combined with phylogenetic analysis, determine where an organism fits in the taxonomic hierarchy.
What is the difference between a class and an order in taxonomy?

+
A class is a rank above order and groups organisms with more general characteristics, while an order groups organisms with more specific traits or relationships within a class.
Why might a species have more than one name?

+
Synonyms exist due to historical naming differences, discovery by multiple scientists, or taxonomic reclassification. The most scientifically accepted name prevails, but older names might still appear in literature.
Is taxonomy only applicable to living organisms?

+
Taxonomy also includes fossils and extinct organisms. Paleontology uses taxonomy to classify and understand evolutionary patterns in ancient life forms.