Tape Measure Test Guide
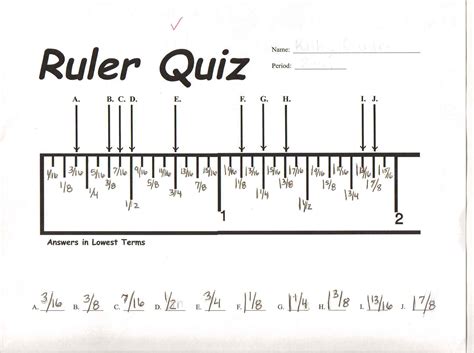
Introduction to Tape Measure Tests
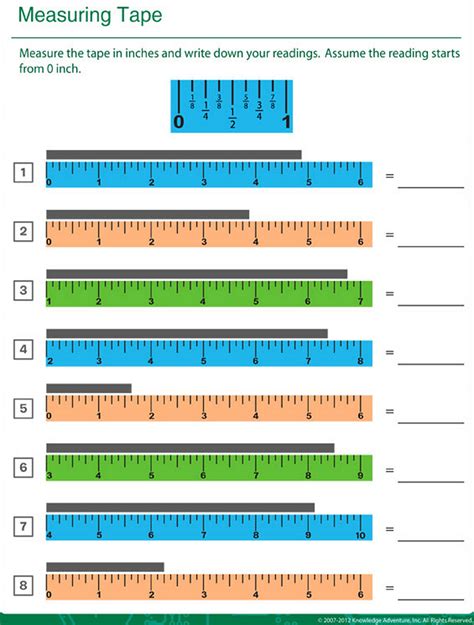
A tape measure is a flexible ruler used to measure distance, height, width, and depth of objects. It is a common tool found in many industries, including construction, carpentry, and engineering. However, have you ever wondered how tape measures are tested for accuracy and reliability? In this guide, we will explore the world of tape measure testing and provide an in-depth look at the various methods used to ensure the accuracy of these essential tools.
Importance of Tape Measure Testing
Tape measure testing is crucial to ensure that the measurements taken are accurate and reliable. Inaccurate measurements can lead to costly mistakes, delays, and even safety hazards. In construction, for example, incorrect measurements can result in poorly fitted materials, structural weaknesses, and compromised safety. Therefore, it is essential to test tape measures regularly to ensure they are functioning correctly and providing accurate readings.
Types of Tape Measure Tests
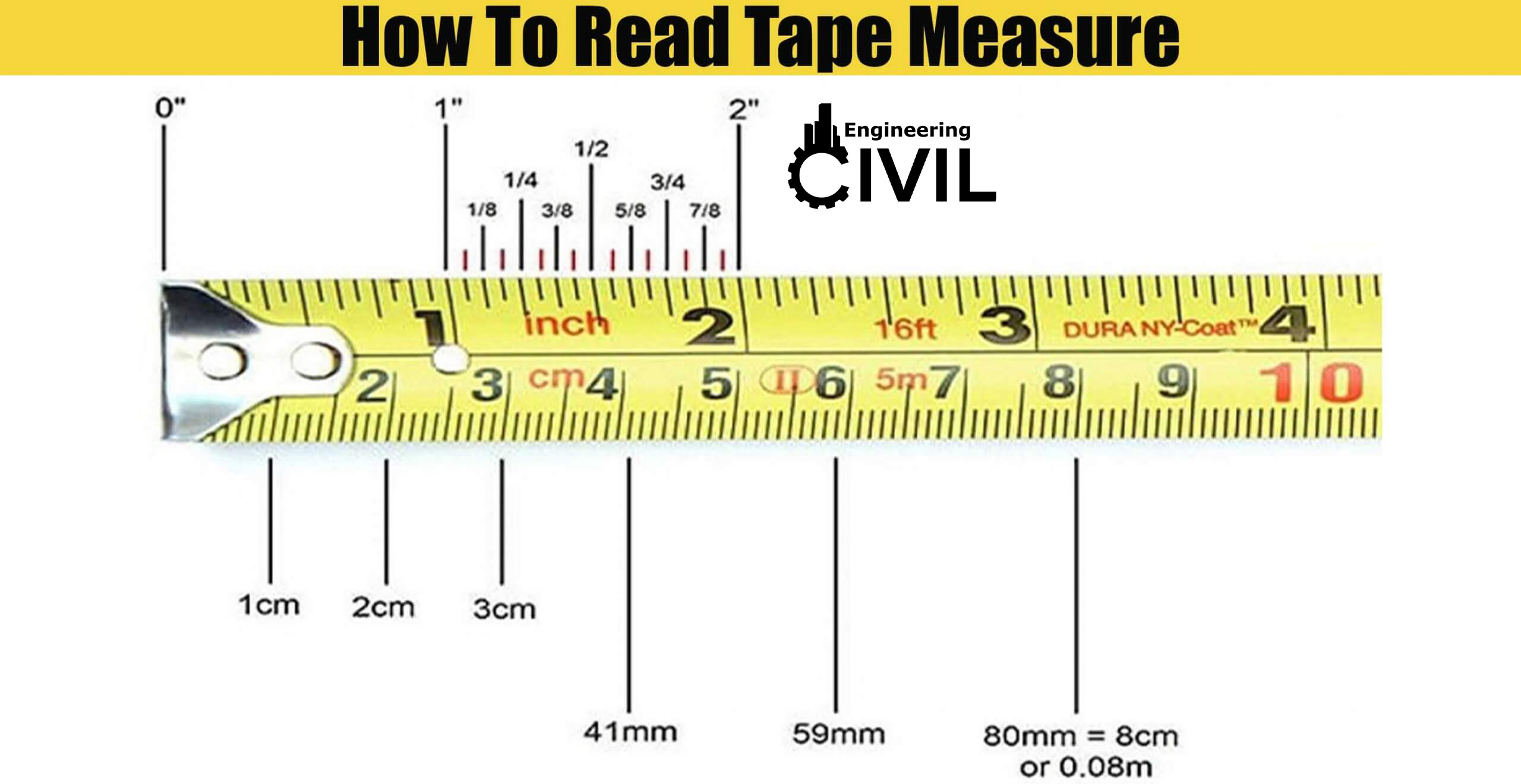
There are several types of tests used to evaluate the accuracy and reliability of tape measures. These include: * Calibration tests: These tests involve comparing the tape measure’s readings to a known standard to ensure accuracy. * Tension tests: These tests evaluate the tape measure’s ability to withstand various levels of tension and stress. * Temperature tests: These tests assess the tape measure’s performance in extreme temperatures. * Drop tests: These tests evaluate the tape measure’s durability and ability to withstand drops and impacts. * Usage tests: These tests simulate real-world usage scenarios to evaluate the tape measure’s performance over time.
Calibration Test Procedure
The calibration test procedure involves several steps: 1. Prepare the test environment: Ensure the test area is free from distractions and interference. 2. Select a reference standard: Choose a calibrated reference standard, such as a precision ruler or calibrator. 3. Set up the tape measure: Attach the tape measure to a fixed point and ensure it is level and plumb. 4. Take readings: Take multiple readings with the tape measure and record the results. 5. Compare readings: Compare the tape measure’s readings to the reference standard and calculate the error. 6. Adjust the tape measure: If necessary, adjust the tape measure to minimize the error.
📝 Note: Calibration tests should be performed regularly to ensure the tape measure remains accurate and reliable.
Tension Test Procedure
The tension test procedure involves applying various levels of tension to the tape measure and evaluating its performance. The steps include: 1. Prepare the test equipment: Set up a tension testing device, such as a spring scale or tensiometer. 2. Attach the tape measure: Attach the tape measure to the testing device and ensure it is secure. 3. Apply tension: Apply various levels of tension to the tape measure, ranging from minimal to maximum. 4. Take readings: Take readings with the tape measure at each tension level and record the results. 5. Evaluate performance: Evaluate the tape measure’s performance and accuracy at each tension level.
Temperature Test Procedure

The temperature test procedure involves evaluating the tape measure’s performance in extreme temperatures. The steps include: 1. Prepare the test environment: Set up a temperature-controlled test chamber or environment. 2. Set up the tape measure: Attach the tape measure to a fixed point and ensure it is level and plumb. 3. Expose to temperature extremes: Expose the tape measure to extreme temperatures, ranging from very cold to very hot. 4. Take readings: Take readings with the tape measure at each temperature extreme and record the results. 5. Evaluate performance: Evaluate the tape measure’s performance and accuracy at each temperature extreme.
Drop Test Procedure
The drop test procedure involves evaluating the tape measure’s durability and ability to withstand drops and impacts. The steps include: 1. Prepare the test equipment: Set up a drop testing device, such as a drop tower or impact tester. 2. Attach the tape measure: Attach the tape measure to the testing device and ensure it is secure. 3. Drop the tape measure: Drop the tape measure from various heights, ranging from minimal to maximum. 4. Take readings: Take readings with the tape measure after each drop and record the results. 5. Evaluate performance: Evaluate the tape measure’s performance and accuracy after each drop.
Usage Test Procedure
The usage test procedure involves simulating real-world usage scenarios to evaluate the tape measure’s performance over time. The steps include: 1. Prepare the test environment: Set up a test environment that simulates real-world usage scenarios. 2. Set up the tape measure: Attach the tape measure to a fixed point and ensure it is level and plumb. 3. Simulate usage: Simulate real-world usage scenarios, such as measuring distances, heights, and widths. 4. Take readings: Take readings with the tape measure at regular intervals and record the results. 5. Evaluate performance: Evaluate the tape measure’s performance and accuracy over time.
💡 Note: Usage tests should be performed regularly to ensure the tape measure remains accurate and reliable over time.
Results and Analysis

The results of the tape measure tests should be analyzed and compared to the manufacturer’s specifications and industry standards. Accurate and reliable tape measures should meet or exceed these standards, while inaccurate or unreliable tape measures may require calibration, adjustment, or replacement.
| Test Type | Pass/Fail Criteria |
|---|---|
| Calibration Test | ±0.1% of reading |
| Tension Test | ±0.5% of reading |
| Temperature Test | ±0.2% of reading |
| Drop Test | No damage or malfunction |
| Usage Test | ±0.1% of reading over time |

In conclusion, tape measure testing is a critical process that ensures the accuracy and reliability of these essential tools. By following the test procedures outlined in this guide, manufacturers and users can ensure that their tape measures meet the required standards and provide accurate readings. Regular testing and calibration can help prevent costly mistakes, delays, and safety hazards, making it an essential part of any industry that relies on accurate measurements.
What is the purpose of tape measure testing?

+
The purpose of tape measure testing is to ensure the accuracy and reliability of tape measures, which is crucial in various industries, including construction, carpentry, and engineering.
What types of tests are used to evaluate tape measures?

+
There are several types of tests used to evaluate tape measures, including calibration tests, tension tests, temperature tests, drop tests, and usage tests.
How often should tape measures be tested?
+
Tape measures should be tested regularly, depending on usage and industry requirements. Calibration tests should be performed at least once a year, while usage tests should be performed every 6-12 months.
What are the consequences of using an inaccurate tape measure?
+
The consequences of using an inaccurate tape measure can include costly mistakes, delays, and safety hazards. Inaccurate measurements can lead to poorly fitted materials, structural weaknesses, and compromised safety.
Can tape measures be adjusted or calibrated?
+
Yes, tape measures can be adjusted or calibrated to ensure accuracy. However, this should only be done by a qualified professional or according to the manufacturer’s instructions.



