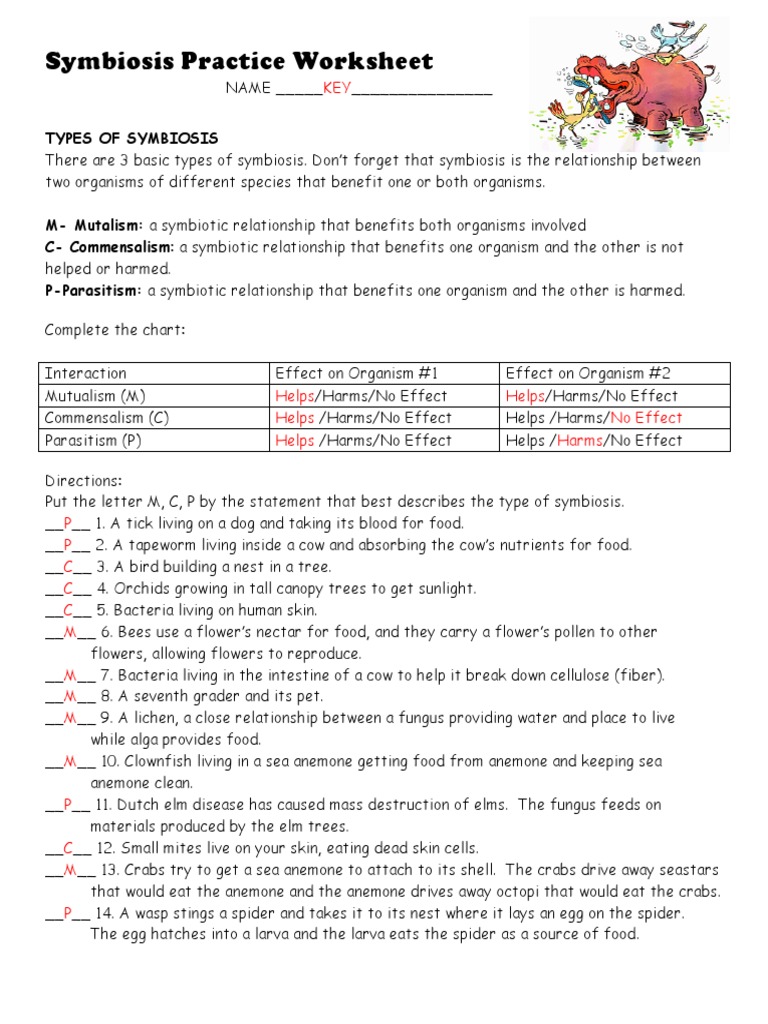
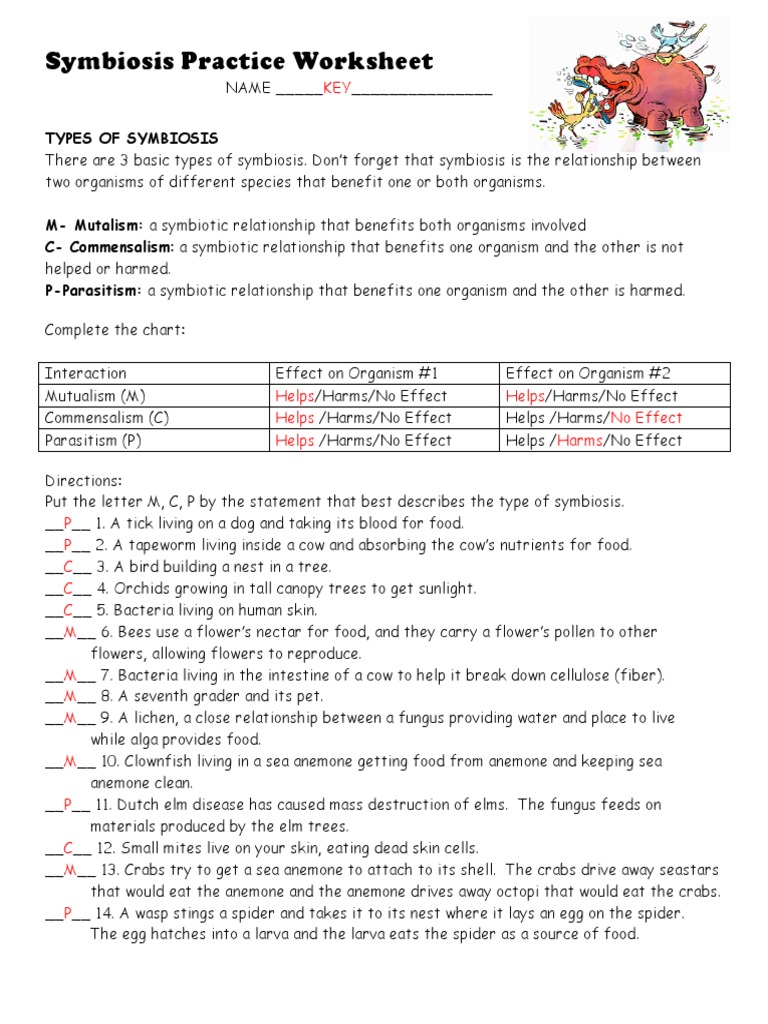
Symbiosis Practice Worksheet Answers Key Revealed

In the intricate dance of life, symbiosis plays a pivotal role, showcasing the interplay between different species for mutual benefit or coexistence. This blog post unravels the complexities of symbiosis by providing an in-depth guide to the "Symbiosis Practice Worksheet", offering answers that not only clarify the concepts but also deepen understanding.
Introduction to Symbiosis

Symbiosis is defined as a close, long-term interaction between two or more species, where at least one benefits. The relationship can range from mutualism, where both species benefit, to parasitism, where one species benefits at the expense of another. Here’s how we categorize symbiosis:
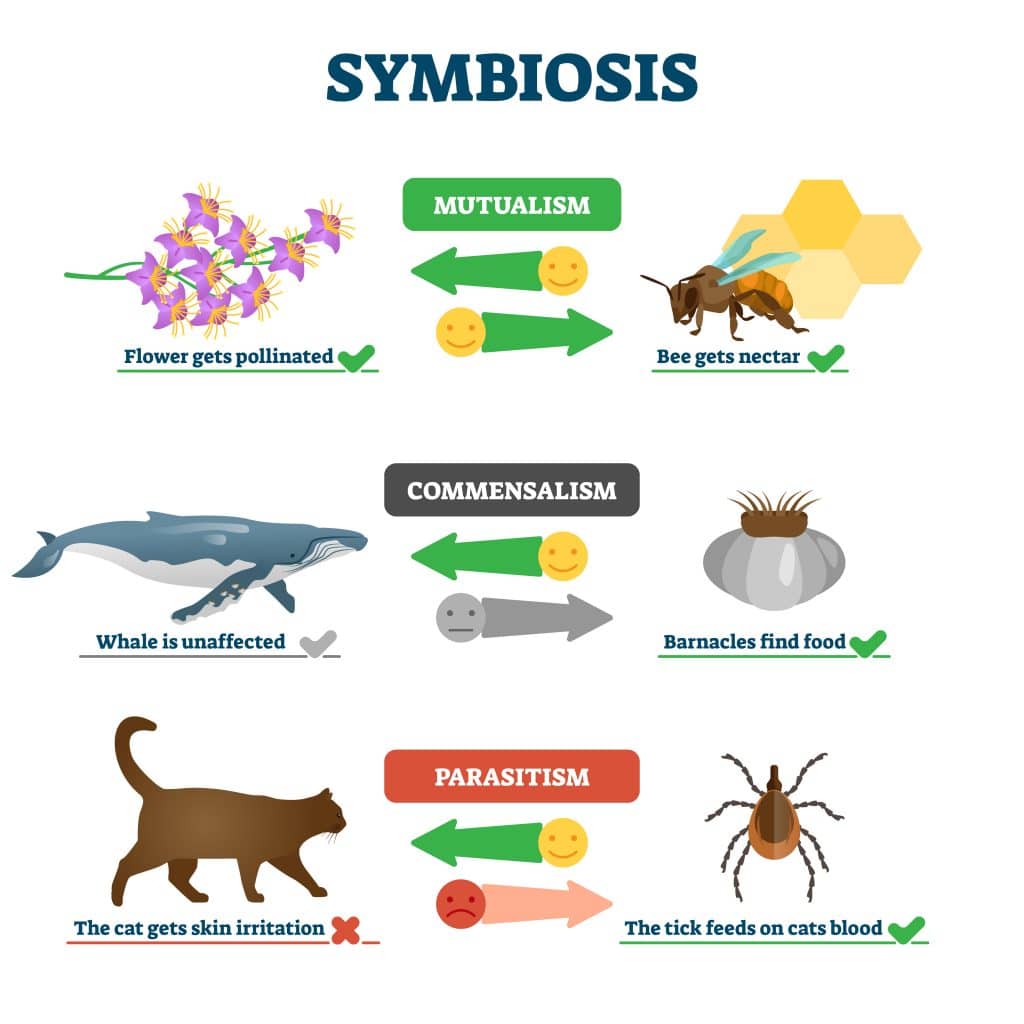
- Mutualism - Both species benefit.
- Commensalism - One species benefits while the other is neither helped nor harmed.
- Parasitism - One species benefits at the other's cost.
- Amensalism - One species is harmed while the other is unaffected.
- Competition - Both species are negatively impacted by the interaction.
Answering the Worksheet: A Closer Look

Let’s delve into the answers to the Symbiosis Practice Worksheet, exploring each relationship with detailed explanations:
Question 1: Barnacles and Whales
Relationship: Commensalism
Barnacles attach themselves to whales, gaining a free ride and a place to grow without hampering the whale’s movement. The whale remains unaffected by this association.

Question 2: Clownfish and Sea Anemones

Relationship: Mutualism
Clownfish live among the anemones’ tentacles, which protect them from predators. In return, the clownfish clean the anemones and drive away polyp-eating fish. Both species thrive from this interaction.
Question 3: Tapeworms and Humans

Relationship: Parasitism
Tapeworms live in the human gut, feeding off nutrients, thereby depriving the host of essential nourishment. This relationship is detrimental to humans.
Question 4: Lichen

Relationship: Mutualism
Lichen is a perfect example of symbiosis where fungi provide structure and moisture retention, while algae or cyanobacteria photosynthesize to provide food. Both partners are dependent on each other for survival.
💡 Note: Lichens can be found in some of the most inhospitable environments, demonstrating the resilience of symbiotic relationships.
Question 5: Trees and Epiphytes
Relationship: Commensalism
Epiphytes like bromeliads or orchids use trees for support to reach sunlight, without taking nutrients from the tree. This is a classic example of commensalism.
| Relationship | Example |
|---|---|
| Mutualism | Clownfish and Sea Anemones |
| Commensalism | Barnacles and Whales, Epiphytes and Trees |
| Parasitism | Tapeworms and Humans |
Why Understanding Symbiosis is Crucial

Understanding symbiosis is not just academic; it has real-world implications:
- Ecosystem Health: Symbiotic relationships contribute to the stability and diversity of ecosystems, which are vital for ecological balance.
- Agricultural Practices: Farmers can leverage mutualistic relationships to enhance crop yield, like pollination services or soil health through mycorrhizal fungi.
- Medical Research: Parasitism insights help in understanding disease transmission and developing strategies against parasites.
In Summation

The analysis of symbiosis through worksheets not only helps students grasp these concepts but also fosters an appreciation for the interconnectedness of life. Symbiotic relationships are vital for survival, innovation in ecosystems, and even human health. They reveal the delicate balance of nature, where cooperation and competition coexist, shaping the biodiversity of our planet.
What are some common examples of symbiotic relationships?

+
Common examples include bees and flowers (mutualism), barnacles on whales (commensalism), and ticks on dogs (parasitism).
How does symbiosis influence ecosystem stability?
+
Symbiotic relationships contribute to ecosystem stability by promoting biodiversity, enhancing species survival, and facilitating nutrient cycling.
Can symbiosis be negative?

+
Yes, when the relationship is parasitic, it can lead to negative impacts on one of the species involved, like diseases in humans caused by parasites.
How can we study symbiosis in the wild?

+
Field observations, ecological surveys, and laboratory studies of captive species are common methods to study symbiotic relationships in nature.
Is symbiosis only between animals?
+
No, symbiosis includes relationships between plants, fungi, and bacteria as well, like mycorrhizal fungi with tree roots.