5 Must-Know Facts About Animal Cells Worksheets

Understanding the basics of animal cells is an essential part of biology education. From understanding cellular structure to grasping the functional intricacies, students often use animal cells worksheets to reinforce their knowledge. This blog post delves into five must-know facts that every student should be aware of when working with these educational tools.
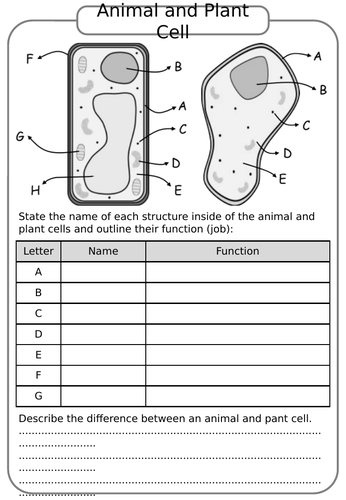
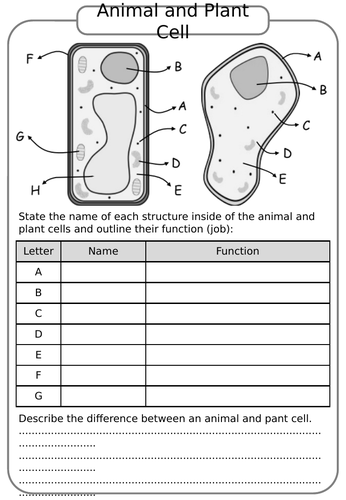
1. Structure and Function of Organelles

The animal cell is a masterpiece of cellular architecture, with each organelle playing a distinct role:
- Nucleus: Often referred to as the “control center,” the nucleus contains DNA, which dictates cellular activity.
- Mitochondria: Known as the powerhouse, mitochondria produce ATP, the cell’s energy currency.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Involved in protein and lipid synthesis, the ER comes in two types - rough, which has ribosomes, and smooth, which lacks ribosomes.
- Golgi Apparatus: It modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or use within the cell.
- Lysosomes: These are the digestive centers, breaking down waste materials and cellular debris.
- Cytoskeleton: Comprises microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules, providing structure, mobility, and internal organization.
- Ribosomes: The protein synthesis factories, found either free in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER.
- Cell Membrane: A semi-permeable barrier that regulates what enters and leaves the cell, crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis.
🔬 Note: Understanding the structure and function of each organelle helps in comprehending how cells maintain life processes.
2. Cellular Processes and Homeostasis

Animal cells are dynamic entities, continuously engaging in processes that ensure their survival and functionality:
- Cell Division (Mitosis): A crucial process for growth, repair, and reproduction, involving the replication of DNA and division of the cell into two identical daughter cells.
- Cell Respiration: Mitochondria carry out aerobic respiration, converting glucose into ATP, releasing energy stored in its chemical bonds.
- Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes read the DNA-encoded instructions from mRNA to produce proteins, which are essential for cellular function.
- Exocytosis and Endocytosis: These are methods through which the cell moves substances in and out. Exocytosis expels substances, while endocytosis allows substances to enter the cell.
- Maintaining Homeostasis: Cells work to keep an optimal internal environment, adjusting to changes in pH, temperature, and nutrient levels.
3. The Role of Enzymes

Enzymes are not just catalysts; they are critical to the efficiency of cellular processes:
- Catalysis: Enzymes speed up reactions, making them occur at a rate suitable for cellular function.
- Energy Efficiency: By lowering the activation energy, enzymes help cells use energy more effectively.
- Regulation: Many metabolic pathways are regulated by enzymes, which can be activated or inhibited to control the flow of reactions.
- Precision: Enzymes are highly specific, often working on a single substrate or class of substrates.
📝 Note: While not typically the focus of worksheets, enzymes play a pivotal role in understanding cellular function.
4. Differentiation and Specialization

One of the most fascinating aspects of animal cells is their ability to differentiate and specialize:
- Stem Cells: These are undifferentiated cells with the potential to become various cell types during early life and growth.
- Differentiation: Cells can change in structure and function to form tissues like muscle, nerve, or skin cells, through processes like gene expression control.
- Specialization: Cells become specialized for specific functions, ensuring organs can work together to perform complex tasks.
| Cell Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Neuron | Transmission of nerve impulses |
| Muscle Cell | Contraction to enable movement |
| Red Blood Cell | Transport of oxygen |

5. Interactive Learning through Worksheets
Worksheets are more than just paper and pencil exercises; they are interactive learning tools:
- Reinforcement: They allow students to review and apply their knowledge through various activities.
- Engagement: Worksheets can include puzzles, labeling exercises, and color-coded diagrams, keeping students engaged.
- Visualization: Visual aids in worksheets help students to understand the three-dimensional structure of cells.
- Critical Thinking: Questions that require analysis and synthesis encourage deeper thinking about cellular functions.
Understanding the complexity and elegance of animal cells can be made accessible and engaging through well-designed worksheets. From dissecting the roles of organelles to exploring cellular processes, these tools help students not only memorize facts but also appreciate the interconnectedness of cellular life. Whether through color-coded diagrams, puzzles, or step-by-step explanations, animal cells worksheets provide a robust platform for learning. In this way, students can bridge the gap between textbook theory and the intricate reality of biology.
Why are animal cell worksheets important?

+
Animal cell worksheets help students visualize and interact with the structures and processes of cells, making abstract concepts more tangible and easier to understand.
How do I use animal cell worksheets effectively?
+
Worksheets are most effective when used as a supplement to lectures, labs, and other educational resources. Engage with diagrams, label structures, and answer questions that encourage critical thinking about cellular functions.
Can I find animal cell worksheets online?

+
Yes, there are numerous resources online, from educational websites, biology forums, to academic portals where you can download or print animal cell worksheets.
Are animal cell worksheets suitable for all educational levels?

+
Worksheets can be adapted for different educational levels, from elementary students learning basic cell structure to advanced biology students exploring cellular physiology and molecular biology.
How can teachers enhance learning with animal cell worksheets?

+
Teachers can introduce hands-on activities, incorporate models, and use multimedia to complement worksheets, providing a multi-sensory approach to understanding animal cells.