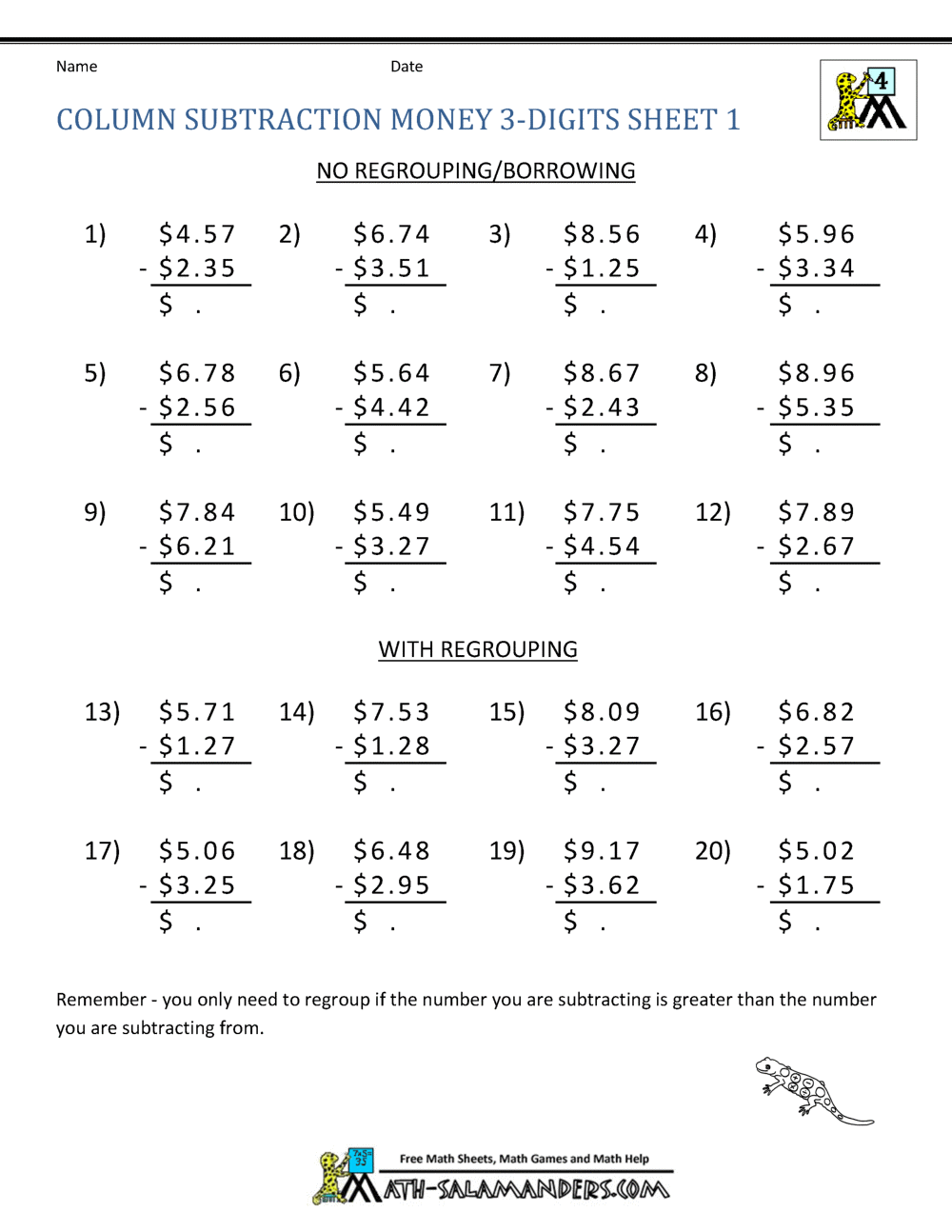
5 Tips for Mastering Subtraction With 3-Digit Borrowing
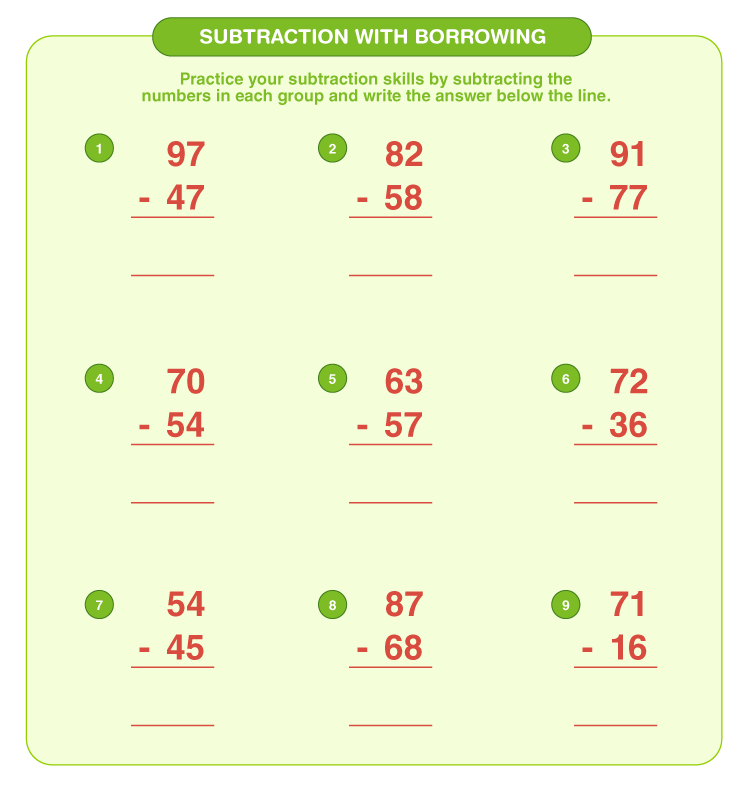
Subtraction can be a challenging arithmetic operation, particularly when dealing with three-digit numbers and borrowing. While the concept is straightforward, the execution often trips up students and adults alike. In this detailed guide, we will explore five essential tips to master subtraction with three-digit borrowing, ensuring you understand not only how to perform it correctly but also why these techniques are effective.
Tip #1: Understand the Basics of Borrowing

Understanding the process of borrowing, sometimes called regrouping, is crucial for successful subtraction. Let's illustrate this with an example:
- Imagine you are tasked with solving 352 - 148.
- If you try to subtract 8 from 2 in the ones place, you'll realize you can't, as 8 is larger than 2.
- Here, you need to borrow from the next column. Borrowing means you take 1 from the tens place (5), making it 4, and add 10 to the ones place, making it 12.
- Now, subtract 8 from 12, which equals 4.
📝 Note: This process continues as needed for each column.
Tip #2: Align the Numbers Properly

Proper alignment of numbers is fundamental:
- Line up the digits in their correct place value columns.
- Ensure that the minuend (number being subtracted from) is on top and the subtrahend (number being subtracted) is underneath.
- Use a subtraction worksheet or grid to keep numbers organized.
Aligning numbers helps in identifying where borrowing is necessary, making the subtraction process more intuitive.
| Numbers | Hundreds | Tens | Ones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minuend | 3 | 5 | 2 |
| Subtrahend | 1 | 4 | 8 |
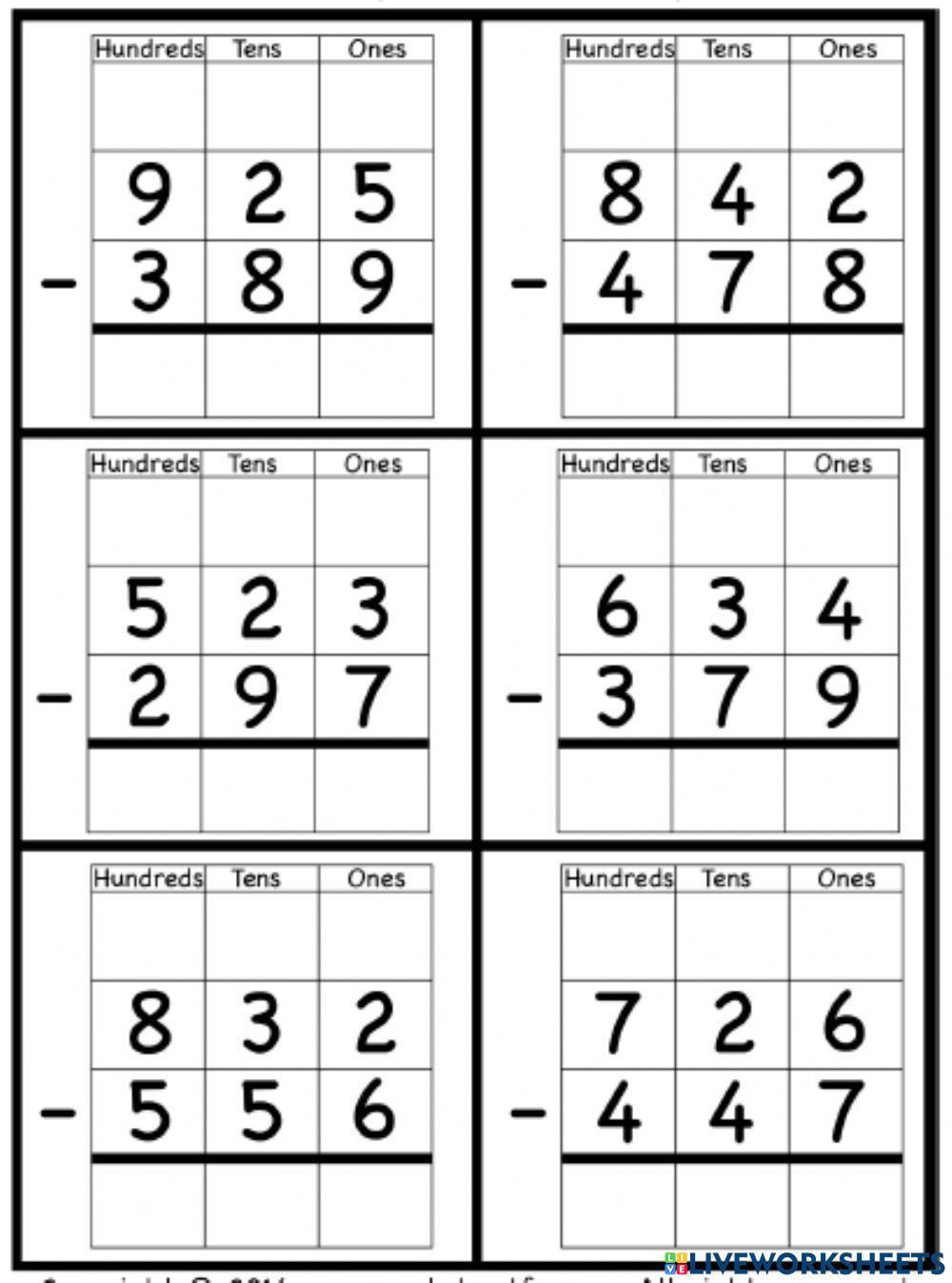
Tip #3: Use Visual Aids to Understand Borrowing
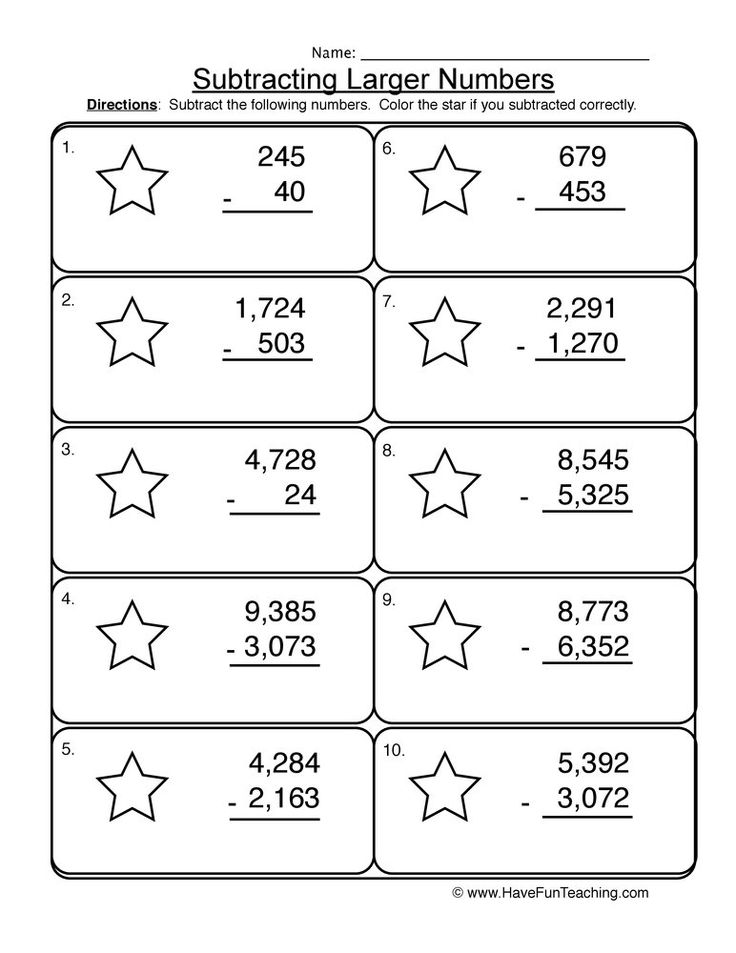
Visual aids are invaluable when learning or teaching subtraction:
- Draw blocks, number lines, or use physical manipulatives to represent borrowing.
- Show how borrowing transforms the number, making subtraction easier.
- Visual representations can bridge the gap between abstract number theory and practical application.
🔍 Note: Using diagrams can also help identify common errors in the subtraction process.
Tip #4: Practice with Real-Life Scenarios

Relate subtraction to real-life scenarios:
- Imagine you're tracking your expenses or working out change at a store.
- Use everyday activities like budgeting or shopping to apply subtraction skills.
- Linking math to everyday life makes learning more engaging and relevant.
When students see subtraction as part of their daily lives, they're more likely to develop a deeper understanding of how it works.
Tip #5: Create a Routine Practice Regimen
Repetition is key in mastering any skill:
- Develop a daily or weekly practice routine focused on subtraction with borrowing.
- Incorporate different difficulty levels, from simple to complex problems.
- Use online resources, printable worksheets, or apps designed to practice subtraction.
Regular practice not only reinforces the techniques but also helps in recognizing patterns and improving speed.
⚙️ Note: Ensure practice sessions are varied to avoid monotony and encourage comprehensive understanding.
Subtraction with three-digit borrowing might seem daunting at first, but with the right techniques and a systematic approach, it becomes manageable. Understanding the basics of borrowing, aligning numbers correctly, utilizing visual aids, relating to real-life scenarios, and consistent practice are all vital steps in mastering this skill. Whether you're a student, parent, or educator, these tips provide a roadmap to enhance understanding and proficiency in subtraction.
Why is borrowing in subtraction difficult for some learners?

+
Borrowing in subtraction can be difficult because it requires a conceptual leap from straightforward subtraction to understanding place value manipulation, which isn’t intuitive for everyone.
How can I help my child with subtraction with borrowing?

+
You can help by breaking down the process, using visual aids, and ensuring they understand the number system’s place values before introducing subtraction with borrowing.
What are some common mistakes in subtraction with borrowing?

+
Common mistakes include misaligning numbers, forgetting to borrow from the correct column, or borrowing incorrectly (like borrowing from a single digit instead of borrowing and carrying over).