Subnetting Mastery: Practice Worksheets for Network Pros

Understanding Subnetting

Subnetting is an essential skill for network professionals, enabling the efficient division of IP networks into smaller, manageable segments. This not only aids in organizing network traffic but also enhances security and management. In this blog, we delve into subnetting, offering practice worksheets to solidify your understanding and mastery of network subnetting.
Why Subnetting?
Subnetting serves multiple purposes:
- Efficient IP Address Allocation: Prevents wastage by allocating only the necessary number of addresses.
- Improved Network Performance: Reduces broadcast traffic, thereby decreasing congestion and enhancing performance.
- Enhanced Security: Segregates networks, reducing the attack surface by isolating critical resources.
- Better Network Management: Makes it easier to manage and troubleshoot network issues due to smaller, more organized segments.
Subnetting also helps in scalability and flexibility, allowing networks to grow or adapt without the need for a complete overhaul.
Basic Concepts of Subnetting
Before diving into practice, let's grasp some fundamental concepts:
- Classful vs. Classless: The transition from classful networks, where network classes dictated address allocation, to classless networks, allowing for Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM), significantly improved efficiency.
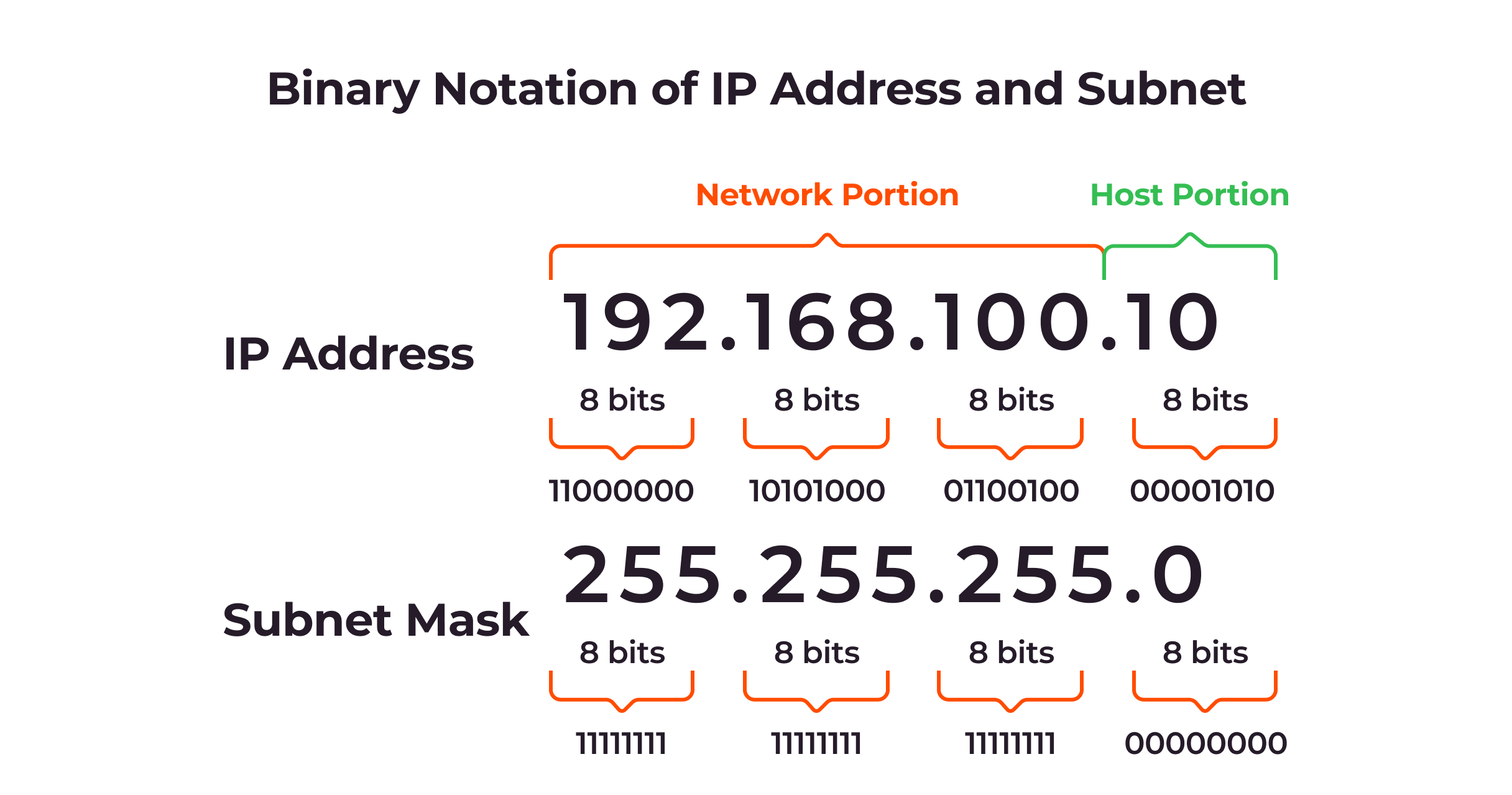
- Subnet Mask: A 32-bit number used to divide an IP address into network and host portions. CIDR notation (e.g., /24) is commonly used to represent subnet masks.
- Subnetting Process:
- Identify the class of the IP address to find the default mask.
- Determine the number of subnets needed and the number of hosts per subnet.
- Calculate the necessary bits to borrow from the host portion to create subnets.
- Formulate new subnet masks and calculate the range of each subnet.
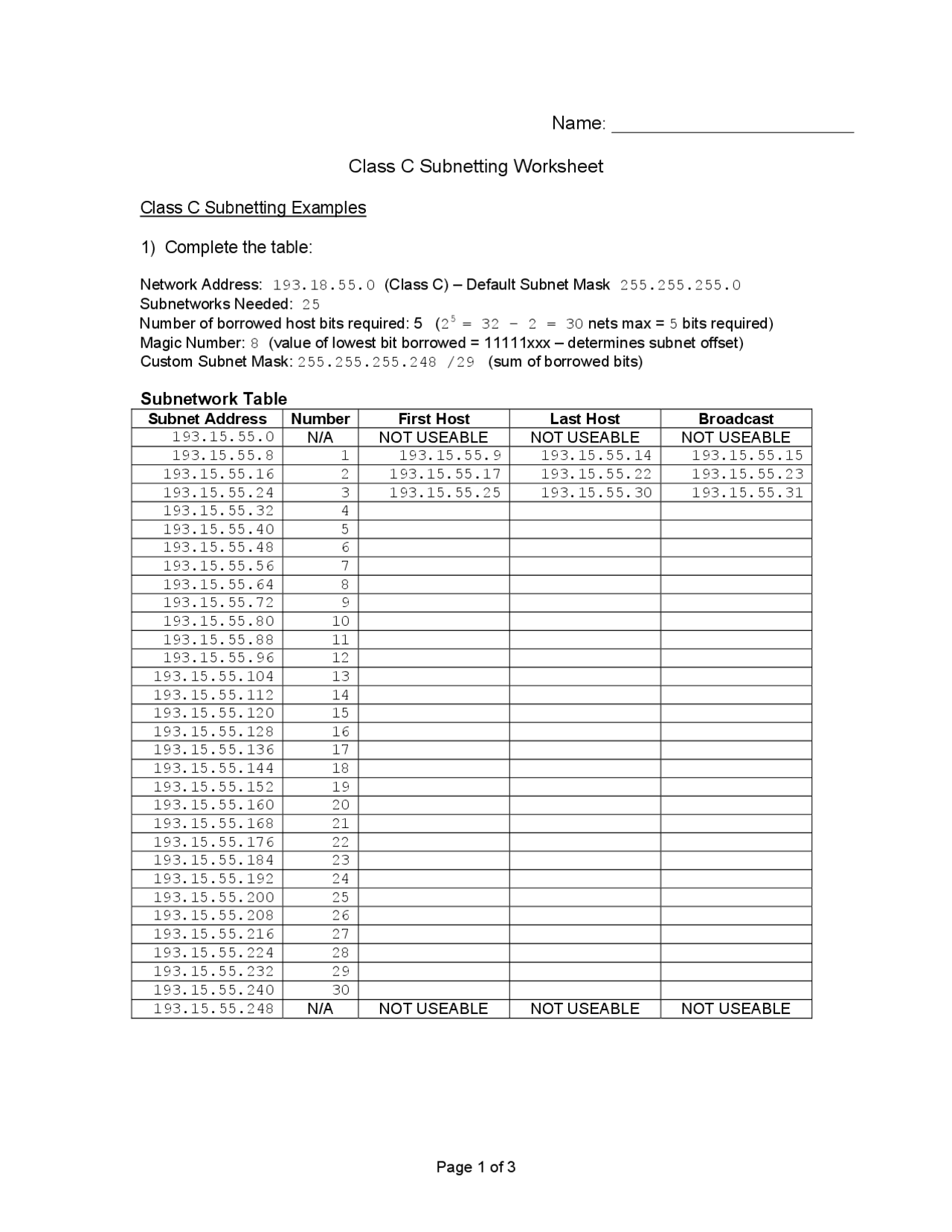
Practice Worksheets for Subnetting Mastery

To solidify your understanding, here are some practice scenarios:
Scenario 1: Simple Subnetting

| IP Address | Subnet Mask | No. of Subnets Required | No. of Hosts per Subnet |
|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.0 | 255.255.255.0 (/24) | 4 | 60 |

Calculate:
- The new subnet mask.
- List the first 4 subnets along with their usable host ranges.
Scenario 2: VLSM Subnetting

| IP Address | Subnet Mask | Networks Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1.1.0 | 255.255.255.0 (/24) |
|
Determine:
- Subnets for each network requirement.
- The smallest subnets with the given host counts.
🚨 Note: Remember that with VLSM, you allocate subnets to meet specific host requirements, avoiding unnecessary address space wastage.
Scenario 3: Subnetting for Summarization

| Subnets | Masks |
|---|---|
| 172.16.1.0 172.16.2.0 172.16.3.0 |
/24 |
Find:
- A summary address that will encompass all given subnets.
Essential Tips for Subnetting

Here are some crucial tips to consider:
- Understand the binary system thoroughly; this will simplify calculations.
- Practice converting decimal IP addresses to binary for an intuitive understanding of subnet masks.
- Start with classful networks and progress to classless networks to appreciate the evolution of subnetting.
- Use subnet calculators initially, but wean off as you become more comfortable.
Conclusion

Subnetting mastery is not just about theoretical knowledge but also about hands-on practice and understanding network design principles. With these practice worksheets and the foundational concepts outlined, you're well on your way to becoming proficient in network subnetting. Regular practice and exposure to real-world scenarios will further enhance your skills, enabling you to design and manage networks with confidence.
Why is subnetting necessary for network professionals?

+
Subnetting is crucial for optimizing network performance, ensuring efficient use of IP addresses, improving network security, and simplifying management. It allows for segmentation of large networks into smaller, more manageable units, reducing broadcast domains and enhancing overall network stability.
What is VLSM, and why is it important in subnetting?

+
Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM) allows a network to be further subdivided into various sizes of subnets, each with its own unique mask. This approach is vital because it enables more efficient allocation of IP addresses, reducing waste by matching subnet sizes to the number of hosts required.
How can subnetting impact network security?

+
Subnetting can enhance security by isolating different network segments, thereby limiting the spread of malware or unauthorized access attempts. It helps in containing breaches within smaller network segments, reducing the potential attack surface.