Unlock the Mystery of Atoms with Our Subatomic Particles Worksheet Answers

Welcome to our enlightening exploration into the fundamental building blocks of matter - atoms and their subatomic particles. Understanding the intricate dance of electrons, protons, and neutrons within the atom not only satisfies the curiosity of those eager to comprehend the universe at its most basic level but also equips learners with essential knowledge for careers in science and technology. In this post, we delve deep into the key components of atoms, providing a comprehensive guide complete with worksheets, answers, and educational insights.
What are Atoms?

Atoms are the smallest units of an element that retain the chemical properties of that element. They consist of:
- Protons - Positively charged particles
- Electrons - Negatively charged particles
- Neutrons - Uncharged or neutral particles
Let’s start with an overview:
| Particle | Charge | Location | Mass (amu)* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proton | +1 | Nucleus | 1.0073 |
| Electron | -1 | Orbitals around nucleus | 0.00055 |
| Neutron | 0 | Nucleus | 1.0087 |
*Atomic Mass Unit (amu) is used to express the mass of atoms and subatomic particles.
🔬 Note: Understanding the structure of an atom is crucial for grasping how elements interact and form compounds.
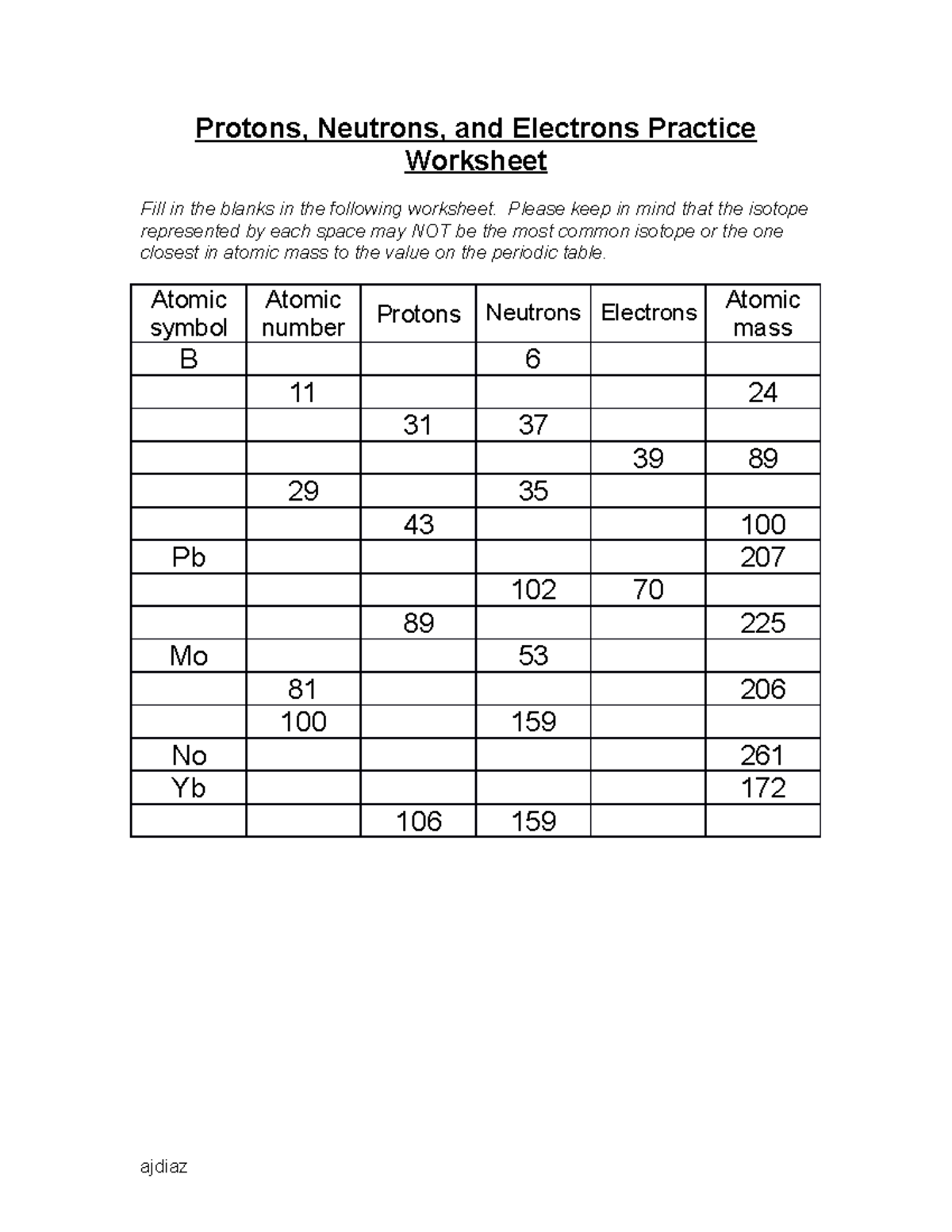
Worksheet on Subatomic Particles

Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s dive into a practical exercise:
Worksheet Instructions:
- Identify the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons for each element provided.
- Complete the atomic model diagrams given below.
Questions:

- Element: Carbon (Atomic Number: 6, Mass Number: 12)
- Element: Sodium (Atomic Number: 11, Mass Number: 23)
- Element: Oxygen (Atomic Number: 8, Mass Number: 16)
🔍 Note: The atomic number indicates the number of protons, while the mass number gives us the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Worksheet Answers:

- Carbon:
- Protons: 6
- Electrons: 6
- Neutrons: 6
- Sodium:
- Protons: 11
- Electrons: 11
- Neutrons: 12
- Oxygen:
- Protons: 8
- Electrons: 8
- Neutrons: 8
Electron Configuration

Understanding how electrons arrange themselves around the nucleus is vital:
Key Concepts:

- Energy Levels or Shells - Electrons occupy different energy levels or shells around the nucleus.
- Subshells and Orbitals - Shells contain subshells, which in turn contain orbitals, each capable of holding a specific number of electrons.
✏️ Note: The electron configuration of an atom dictates its chemical behavior, bonding tendencies, and reactivity.
Isotopes and Atomic Mass

Atoms of the same element can vary slightly in their mass due to a different number of neutrons, these are called isotopes:
Important Points:

- The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of all its isotopes, weighted by their natural abundance.
- Isotopes can affect an element’s physical and chemical properties.
🧪 Note: Isotopes are key in fields like medicine, where radioactive isotopes are used in diagnostics and treatment.
The Role of Electrons

Electrons play a pivotal role in:
- Electrical Conductivity - The movement of electrons forms the basis for electricity.
- Chemical Bonds - Electrons are shared, donated, or taken to form various bonds.
- Spectroscopy - Electrons absorb or emit energy, leading to observable spectral lines.
Atomic Theory Over Time

The concept of the atom has evolved:
- John Dalton’s atomic theory laid the groundwork in the early 19th century.
- J.J. Thomson’s discovery of the electron added complexity to the model.
- Rutherford’s gold foil experiment redefined the atom’s structure.
- Bohr’s atomic model introduced fixed electron orbits.
- Quantum mechanics has since provided a more nuanced understanding.
In this comprehensive overview, we've not only addressed the basic components of atoms but also provided a step-by-step guide to understanding their subatomic particles, their configuration, and their significance. The worksheets and answers offer a practical approach to mastering these concepts, while the notes underscore the importance of each section for further study. By understanding the subatomic particles of atoms, we gain insight into the invisible world that dictates the behavior of matter, facilitating innovations in technology, chemistry, and countless other fields.
Why do atoms have the same number of electrons and protons?

+
Atoms have the same number of electrons and protons to maintain electrical neutrality. The positive charge from protons in the nucleus is balanced by the negative charge of the electrons in the electron cloud.
What is the significance of neutron number in isotopes?

+
Neutrons contribute to an atom’s mass but not its charge. Different neutron counts in isotopes can change an element’s atomic mass, stability, and sometimes its chemical behavior.
How do subatomic particles affect atomic behavior?
+
Electrons in the outer shells are primarily responsible for an atom’s chemical behavior, engaging in bonding. Protons and neutrons, while not directly involved in bonding, affect the atom’s overall mass and nuclear stability, which indirectly influence atomic behavior.