Master Hydrocarbons Easily with Our Simple Worksheet

The world of hydrocarbons might seem complex and overwhelming at first glance, especially for those just stepping into the realms of chemistry or environmental science. However, understanding the basics of these compounds is both fascinating and surprisingly straightforward when broken down into simple terms. This blog post is designed to master hydrocarbons easily with the aid of a simple, interactive worksheet. We'll explore the fundamental aspects of hydrocarbons, their classifications, applications, and environmental impact, providing you with a worksheet that you can use to reinforce your learning and make the process both fun and educational.
What Are Hydrocarbons?

Hydrocarbons are the simplest organic compounds, consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. They form the backbone of organic chemistry, as they are the primary constituents of fossil fuels, plastics, and countless other materials that shape our modern world. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Definition: Molecules containing only carbon © and hydrogen (H).
- Significance: They are key in energy production, materials science, and as a foundational concept in chemistry.
Types of Hydrocarbons
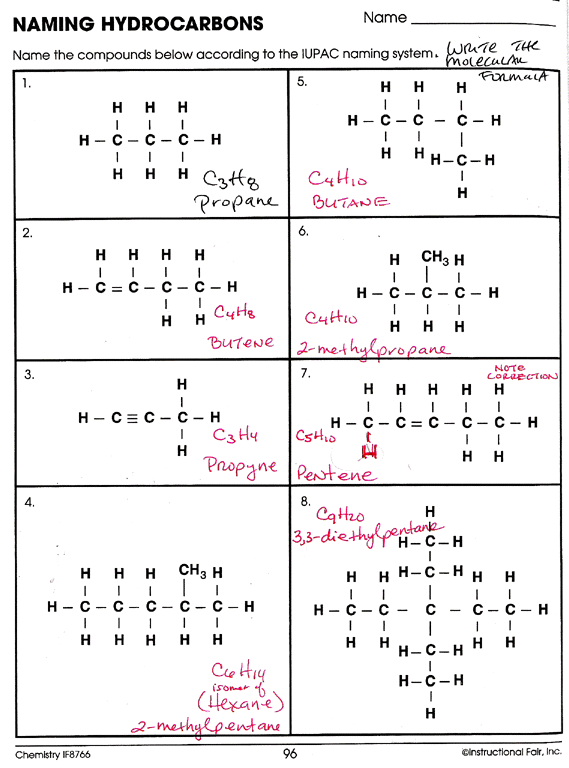
Hydrocarbons can be classified into several groups, each with unique structures and properties. Let’s delve into the different types:
Alkanes
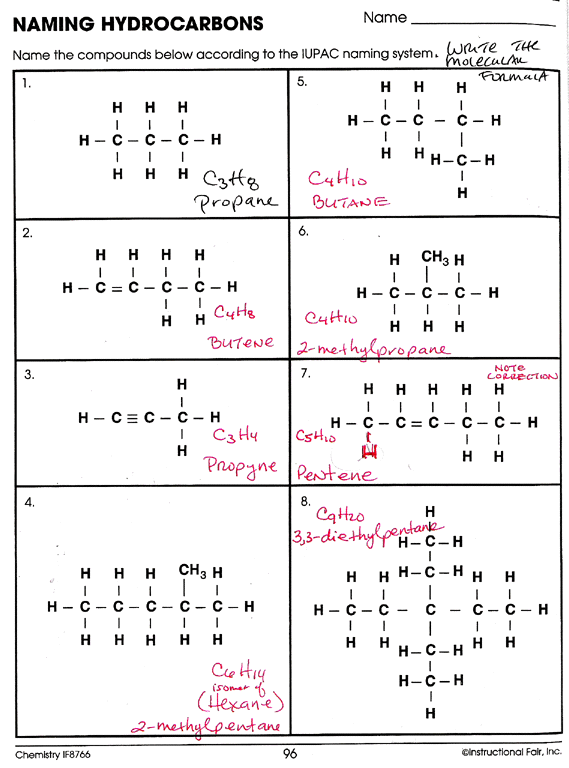
- Also known as: Paraffins
- Characteristics: Single bonded, saturated hydrocarbons.
- General Formula: CnH2n+2
- Examples: Methane (CH4), Ethane (C2H6)
Alkenes
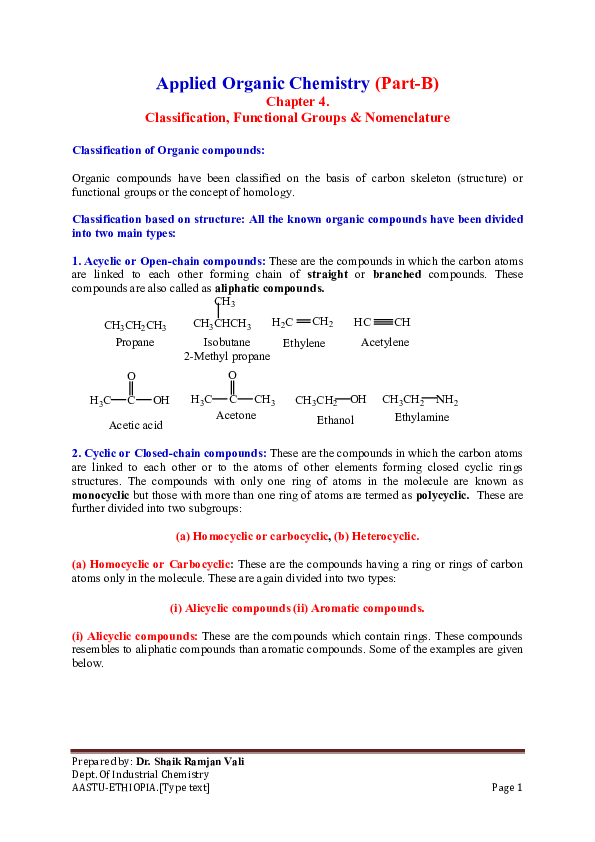
- Also known as: Olefins
- Characteristics: Contain at least one double bond, making them unsaturated.
- General Formula: CnH2n
- Examples: Ethene (C2H4), Propene (C3H6)
Alkynes

- Also known as: Acetylenes
- Characteristics: Contain at least one triple bond.
- General Formula: CnH2n-2
- Examples: Ethyne (C2H2)
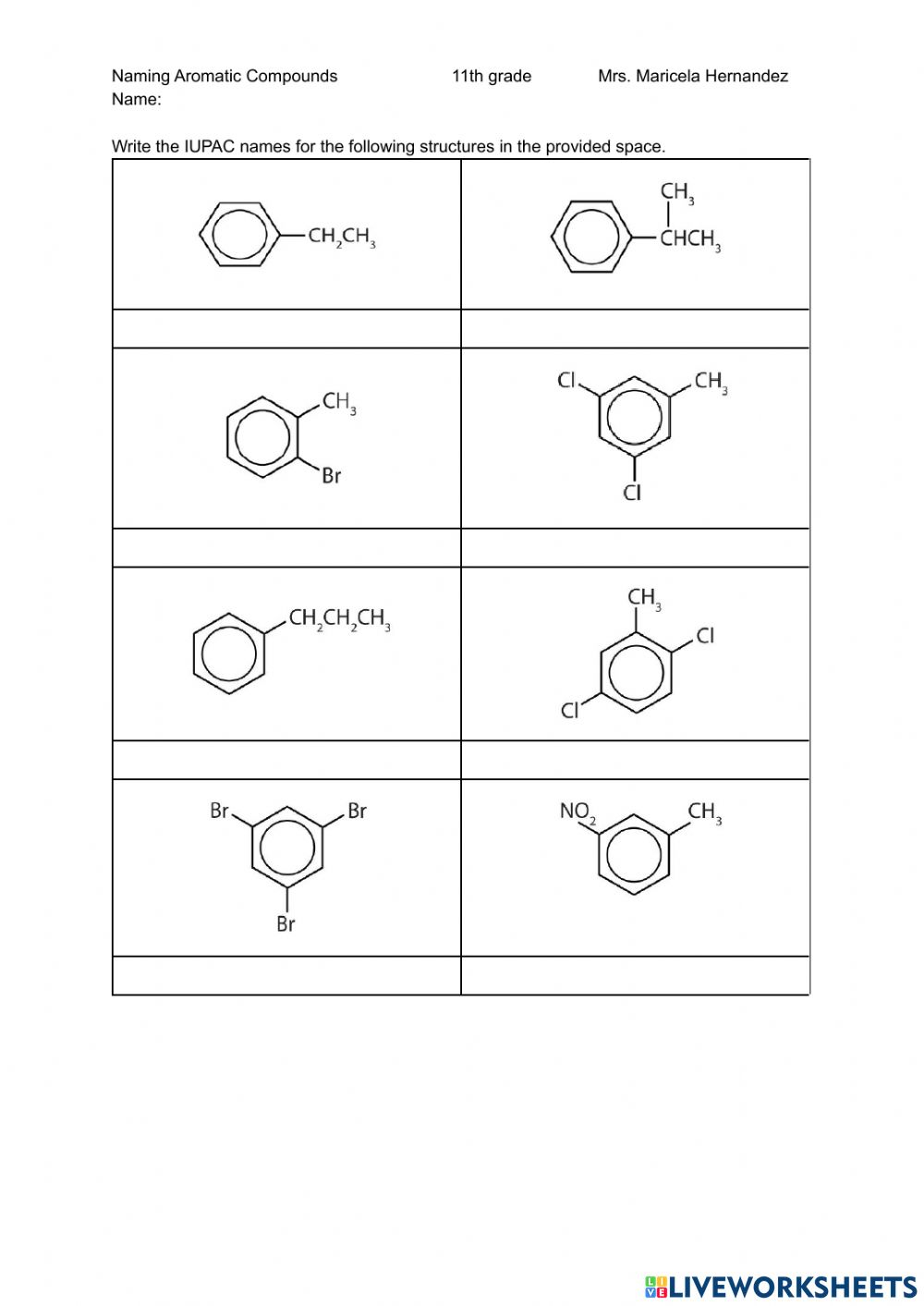
Aromatic Hydrocarbons

- Also known as: Arenes
- Characteristics: Planar, cyclic structures with delocalized pi electrons.
- General Formula: Usually contains one or more benzene rings.
- Examples: Benzene (C6H6)
Applications of Hydrocarbons

Hydrocarbons play an instrumental role in various sectors:
- Energy: Primary source in the form of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas.
- Chemicals: They form the building blocks for many chemical processes and synthetic materials.
- Plastics: Many types of plastics are derived from hydrocarbon polymers.
- Lubricants: Lubricating oils and greases are hydrocarbons.
Environmental Impact of Hydrocarbons

While hydrocarbons are beneficial in many ways, they also have significant environmental implications:
- Greenhouse Gases: Combustion of hydrocarbons releases CO2, contributing to global warming.
- Spills: Oil spills can have devastating effects on marine ecosystems.
- Acid Rain: Burning fossil fuels releases sulfur oxides, leading to acid rain.
- Climate Change: Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, has a significant impact when released into the atmosphere.
📌 Note: It's crucial to understand the environmental impact of hydrocarbons as we move towards more sustainable energy sources.
Worksheet for Mastering Hydrocarbons

To help you master these concepts, we’ve created a worksheet. Here’s how you can use it:
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Structure | Identify and name hydrocarbons based on their structures. |
| Reactions | Learn about common reactions involving hydrocarbons, including combustion, substitution, and addition reactions. |
| Environmental Impact | Reflect on and discuss the environmental implications of hydrocarbon use and potential solutions. |
| Application | Explore real-world applications of hydrocarbons and their derivatives. |

By engaging with this worksheet, you'll not only solidify your understanding but also apply what you've learned in practical scenarios, which is an effective way to learn and remember.
Summing Up
Mastering hydrocarbons doesn’t have to be an arduous journey. By understanding the basic principles, classifications, applications, and environmental considerations, along with utilizing the provided worksheet, you can become proficient in these essential compounds. As we’ve explored, hydrocarbons are central to our daily lives, affecting everything from the energy we use to the products we consume. With this knowledge, you can better understand the world around you and contribute to discussions on sustainable energy, pollution, and materials science.
Why are hydrocarbons important in our daily lives?

+
Hydrocarbons are fundamental to energy production, plastics manufacturing, and are present in many products like lubricants, solvents, and fuels. They are integral to our way of life.
What’s the difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons?

+
Saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes) have only single bonds and are fully saturated with hydrogen atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons (alkenes and alkynes) contain multiple bonds, making them more reactive.
Can you suggest sustainable alternatives to traditional hydrocarbon fuels?
+
Alternatives include renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and biofuels derived from non-fossil hydrocarbon sources, reducing the carbon footprint.