Stratigraphy Worksheet Answers: Easy Guide for Students

Understanding the complexities of stratigraphy can be a daunting task for students embarking on their journey into the geosciences. However, mastering this foundational discipline is not just about memorization but about recognizing patterns, understanding geological processes, and interpreting the historical record of Earth's layers. This blog post serves as your comprehensive guide to answering common questions and tackling worksheets on stratigraphy effectively.
What is Stratigraphy?

Before diving into the specifics of stratigraphy worksheets, let's refresh our understanding of what stratigraphy entails:
- Stratigraphy is the study of rock layers, or strata, and their relationships.
- It involves principles like the Law of Superposition, which states that in an undisturbed sequence of sedimentary rocks, the older layers will be beneath the younger layers.
- Stratigraphers use these layers to decipher Earth's history, looking at aspects like depositional environments, time scales, and geological events.
🌟 Note: Remember that the focus of stratigraphy is not just on the rock layers themselves but on what they tell us about the Earth's past, including climatic changes, sea level variations, and even prehistoric life.
Common Stratigraphy Worksheet Questions
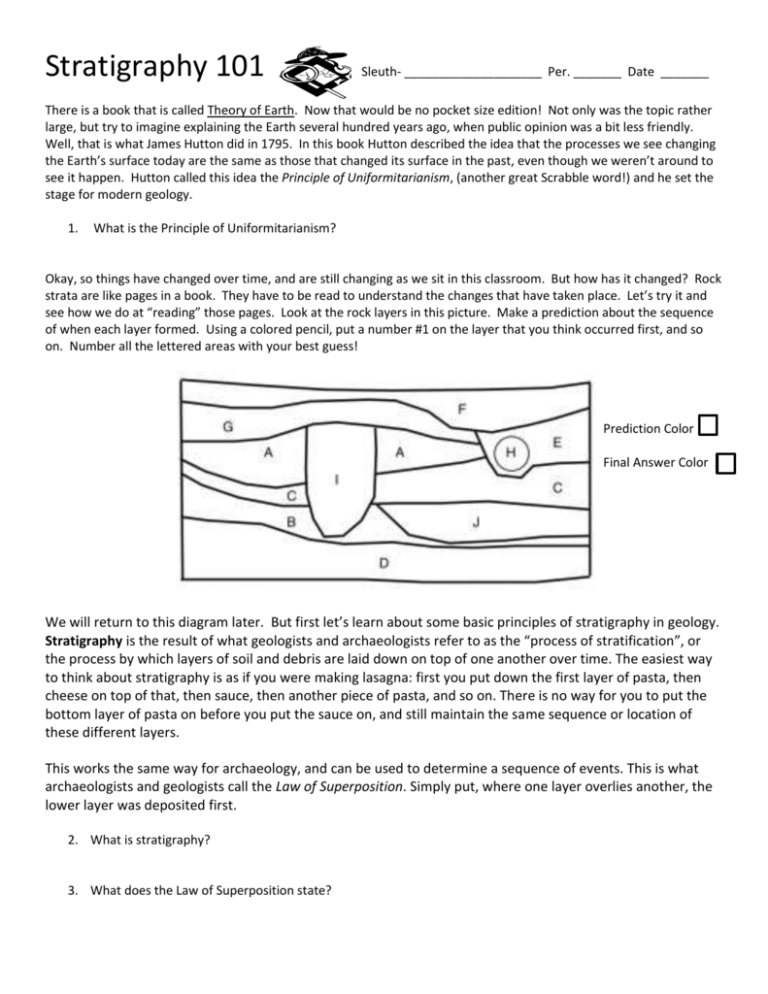
Stratigraphy worksheets often include questions aimed at testing your ability to apply the basic principles of stratigraphy. Here are some common types of questions:
1. Correlation of Strata

Worksheets might present several columns of rock layers and ask you to correlate these strata:
- Identify key marker beds that can be traced across different sections.
- Use fossil evidence or index fossils to correlate layers from different locations.
- Apply the principle of lateral continuity to infer that layers once extended laterally.
| Location A | Location B | Location C |
|---|---|---|
| Layer 3: Sandstone | Layer 2: Shale | Layer 1: Limestone |
| Layer 2: Shale | Layer 3: Sandstone | Layer 2: Shale |
| Layer 1: Limestone | Layer 4: Marl | Layer 3: Sandstone |

📚 Note: When correlating strata, always consider multiple types of evidence, not just one.
2. Age Determination

Questions might ask you to determine the age of specific layers or events using:
- Relative dating methods like superposition or cross-cutting relationships.
- Absolute dating methods like radiometric dating (e.g., using isotopes like Carbon-14 for younger deposits or Uranium-Lead for older ones).
🧪 Note: While relative dating methods can determine which layer is older, absolute dating gives an actual numerical age.
3. Interpretation of Geological History

Some tasks might ask you to interpret the geological history based on the strata:
- Identify periods of erosion, non-deposition, or unconformities.
- Analyze the types of sediment and infer the depositional environment.
- Reconstruct past sea levels or tectonic events.
Strategies for Tackling Stratigraphy Worksheets

Here are some strategic tips to help you through:
- Understand the basics: Ensure you are familiar with the fundamental principles of stratigraphy.
- Use visual aids: Sketch out the strata if it helps you visualize the layers and their relationships.
- Correlate first: Start by correlating the layers before attempting more complex interpretations.
- Examine evidence: Look for all possible evidence before making a decision.
🎨 Note: Visualizing the rock layers in 3D can provide better insights into their lateral continuity and potential interruptions like faults.
As we come to the end of our exploration into stratigraphy worksheets, remember that patience, attention to detail, and a deep understanding of geological processes are key. By following the strategies outlined, you can not only answer the questions effectively but also gain a richer understanding of Earth's history. Let the layers of rock guide you through time, revealing secrets of the past and teaching you to read the Earth's language through its very foundation. Keep practicing, and you'll find that stratigraphy becomes not just a subject to study but a fascinating story to uncover.
What are the primary methods used for correlating strata?

+
The primary methods include: using key marker beds or index fossils, applying the principle of lateral continuity, and examining physical characteristics like lithology or color.
Why is the Law of Superposition important in stratigraphy?

+
This law provides a fundamental framework for determining the relative ages of rock layers, making it crucial for stratigraphic analysis and understanding Earth’s history.
How can I differentiate between erosion and non-deposition?

+
Erosion involves the removal of pre-existing rock or sediment, often leaving an erosional surface or unconformity. Non-deposition occurs when sediment does not accumulate, creating a gap in the sedimentary record, without evidence of erosion.