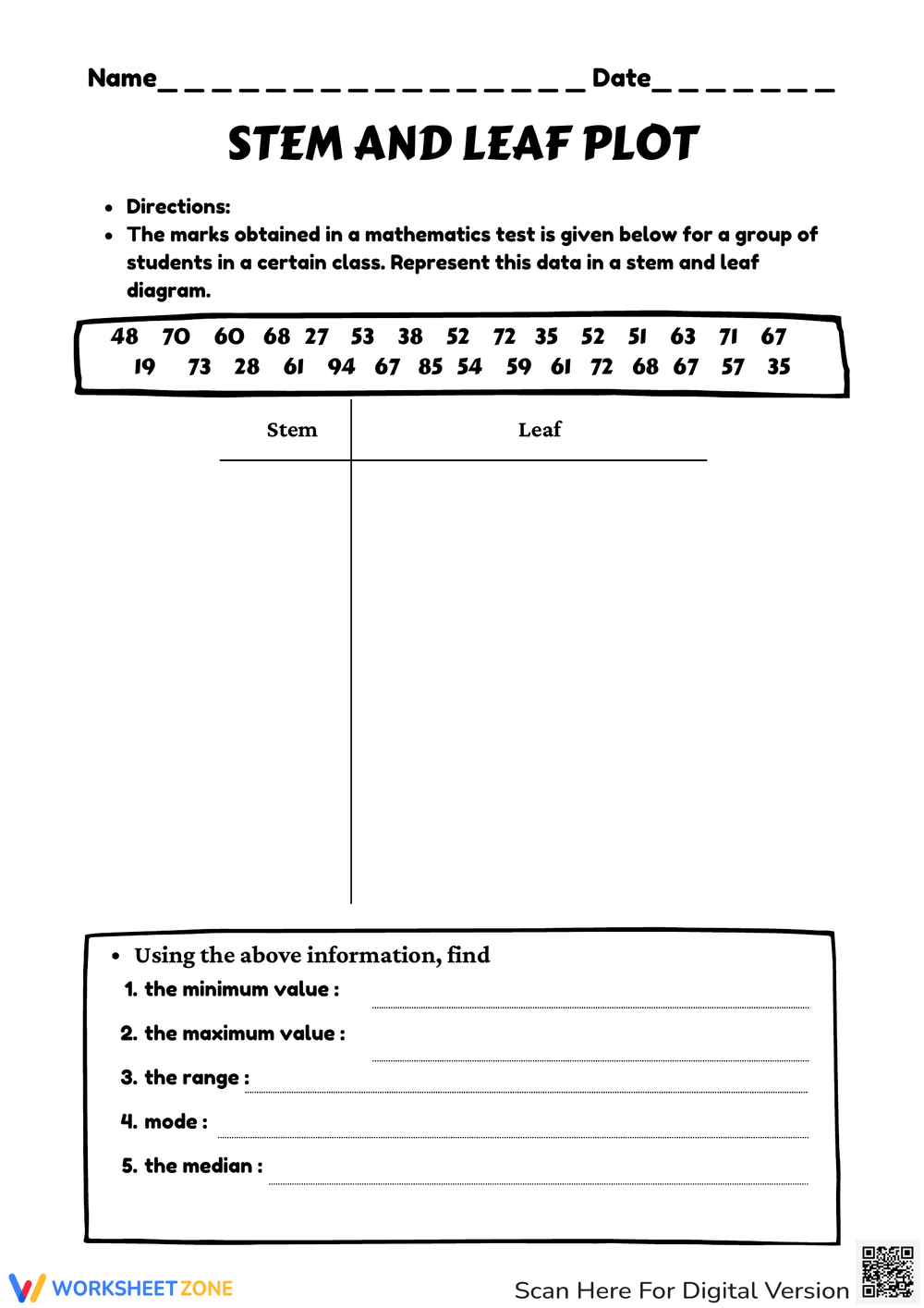
Stem and Leaf Plot Worksheet: Quick Guide for Easy Learning

Understanding data visualization tools is crucial in both academic and professional settings where statistical analysis is required. Among these tools, the Stem and Leaf Plot stands as a simple yet effective method for summarizing and displaying data. This guide aims to provide you with a thorough understanding of how to create, interpret, and analyze data using a Stem and Leaf Plot, ensuring easy learning for students and professionals alike.
What is a Stem and Leaf Plot?


A Stem and Leaf Plot is a graphical representation method that displays both the quantitative and qualitative nature of data. It’s essentially a table where each data point is broken into two parts: the stem (usually the first digit or digits) and the leaf (the last digit). This technique allows for immediate identification of patterns, distributions, and outliers within a dataset. Here’s how it works:
- Stems: These are listed vertically and represent the leading digits of the numbers in the dataset.
- Leaves: Positioned to the right of each stem, they show the trailing digits of the numbers.
Creating a Stem and Leaf Plot

Step-by-Step Guide:

- Gather Your Data: Have your dataset ready. Ensure the numbers are sorted or you will need to sort them for easier construction.
- Identify Stems and Leaves: Determine how many digits to use as stems and leaves. For example, for numbers between 5 and 129, use tens as stems and units as leaves.
- Create the Plot: Draw the stems vertically and plot the leaves accordingly.
Stem Leaves 5 3, 7 6 1, 2, 8 
📚 Note: Always list leaves in numerical order from left to right to maintain the plot's readability.
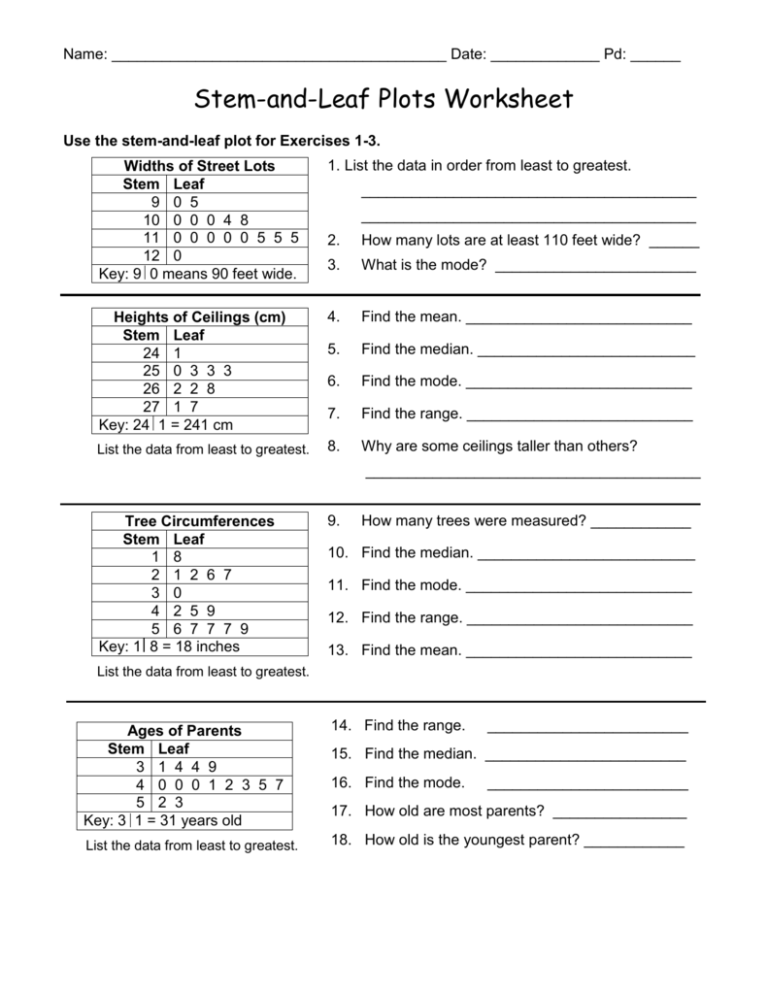
Interpreting Your Stem and Leaf Plot
- Distribution of Data: Look for the shape of the distribution - whether it’s symmetrical, skewed left or right, or uniform.
- Outliers: Identify numbers far from the main cluster of leaves.
- Mode: The leaf with the highest frequency can often indicate the mode of the dataset.
- Median: If there are an odd number of data points, the median will be found by counting halfway through the stems and leaves.
Advantages of Stem and Leaf Plots

- Preserves Data Details: Unlike histograms, stem and leaf plots retain the original data values, making it easier to retrieve specific numbers. - Small Datasets: They are particularly useful for datasets with a limited number of data points, where histograms might be less informative. - Visual Representation: Provides a visual sense of the data distribution while also allowing for precise analysis.
Limitations of Stem and Leaf Plots

- Limited Range: For very large datasets or datasets with a wide range of values, these plots can become unwieldy and less readable. - Not Suitable for Continuous Data: They work best with discrete data sets. - Interpretation Complexity: For those unfamiliar, interpreting can take time to learn.
Real-World Applications of Stem and Leaf Plots

Stem and leaf plots have practical applications in various fields:
- Business Analytics: For analyzing sales figures, customer ratings, or employee performance metrics.
- Education: Teachers can use them to display test scores and discuss distribution.
- Healthcare: To understand the distribution of patient recovery times or disease occurrence.
- Finance: For visualizing stock price changes or financial ratios over time.
🌟 Note: Stem and Leaf Plots are excellent for educational purposes, helping students visually understand data distribution and statistics concepts.
Having navigated through the complexities of creating, interpreting, and leveraging the advantages and limitations of Stem and Leaf Plots, we can conclude that this simple statistical tool is indispensable for quick data analysis. Whether you're a student learning the basics of statistics, an analyst diving into data trends, or a professional trying to make sense of business metrics, understanding how to use a Stem and Leaf Plot effectively can significantly enhance your ability to draw insights from raw data. They provide a bridge between raw data and sophisticated analysis, making statistics accessible to beginners while still useful for experts.
Can Stem and Leaf Plots handle negative numbers?
+
Yes, by using a special convention like placing negative numbers on the left side of the stem and positive on the right, or splitting the stem into two parts - one for negative leaves and one for positive.
How do you determine which digits to use as stems and leaves?

+
The decision largely depends on the range and distribution of your data. For smaller ranges, use tens as stems and units as leaves. For larger ranges or datasets with many small numbers, you might use hundreds or even thousands as stems.
What is the difference between a Stem and Leaf Plot and a Histogram?

+
While both display data distribution, a Histogram groups data into bins, losing individual data points, whereas Stem and Leaf Plots preserve the exact data values, showing the distribution more precisely.
Can Stem and Leaf Plots show multiple data sets?

+
Yes, by using different symbols or colors for leaves from different datasets, or splitting the stem into separate columns, one for each dataset.



