7 Quick Standard Deviation Worksheet Solutions
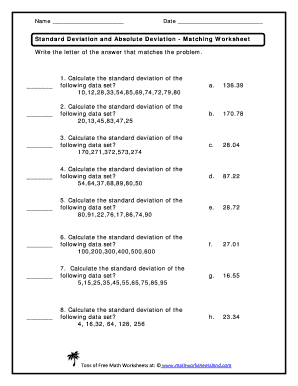
Introduction to Standard Deviation

Standard deviation is a crucial statistical measure that quantifies the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of data values. Understanding standard deviation can provide deep insights into the variability of data, making it an indispensable tool in fields ranging from finance to psychology, and from quality control to research science. This blog post will guide you through seven practical worksheets designed to solidify your understanding of standard deviation through hands-on calculations.
Worksheet 1: Basic Calculation of Standard Deviation

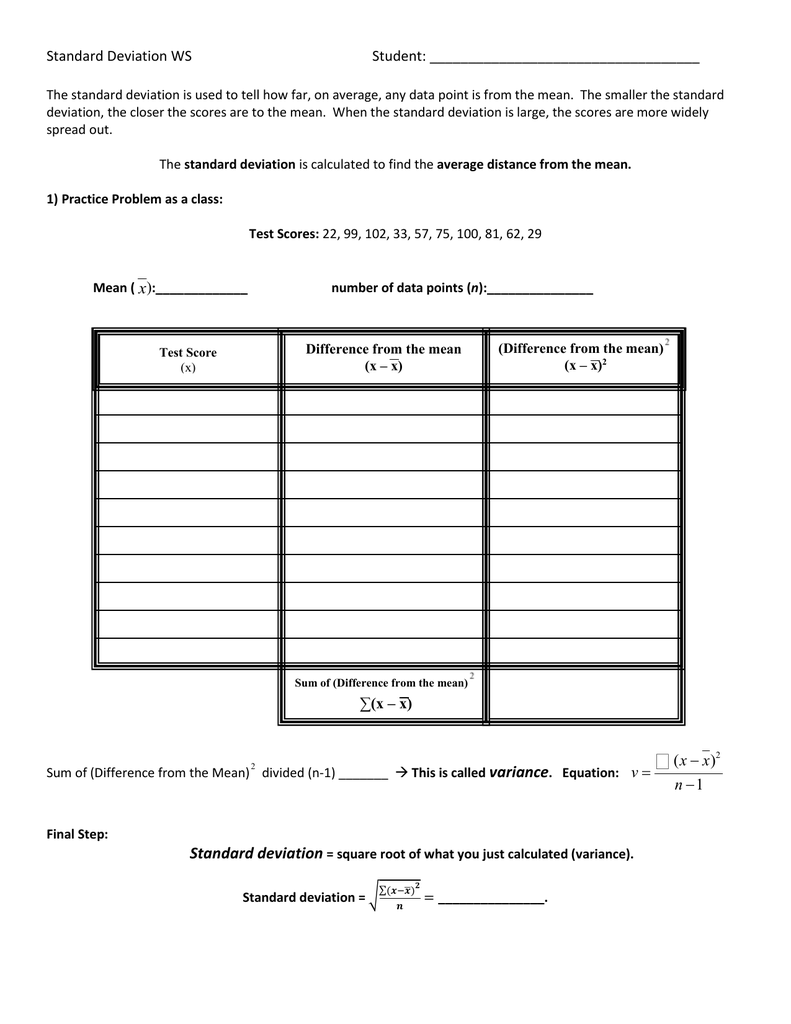
In this first worksheet, we’ll work through the calculation of standard deviation for a simple dataset.
- List the dataset values.
- Calculate the mean (average) of these values.
- Subtract the mean from each value and square the result.
- Sum these squared differences.
- Divide by the number of observations minus one (n - 1) for sample standard deviation.
- Finally, take the square root of this value.
🧮 Note: For larger datasets, using a calculator or software can reduce the chance of arithmetic errors.
Worksheet 2: Understanding Variance and Standard Deviation

Here, we’ll explore how variance relates to standard deviation, and why both are important in statistical analysis.
- Variance is simply the average of squared deviations from the mean.
- Standard deviation is the square root of variance, providing a measure in the same units as the data.
✨ Note: Variance helps in understanding spread, while standard deviation is often more intuitive for practical applications.
Worksheet 3: Population vs. Sample Standard Deviation
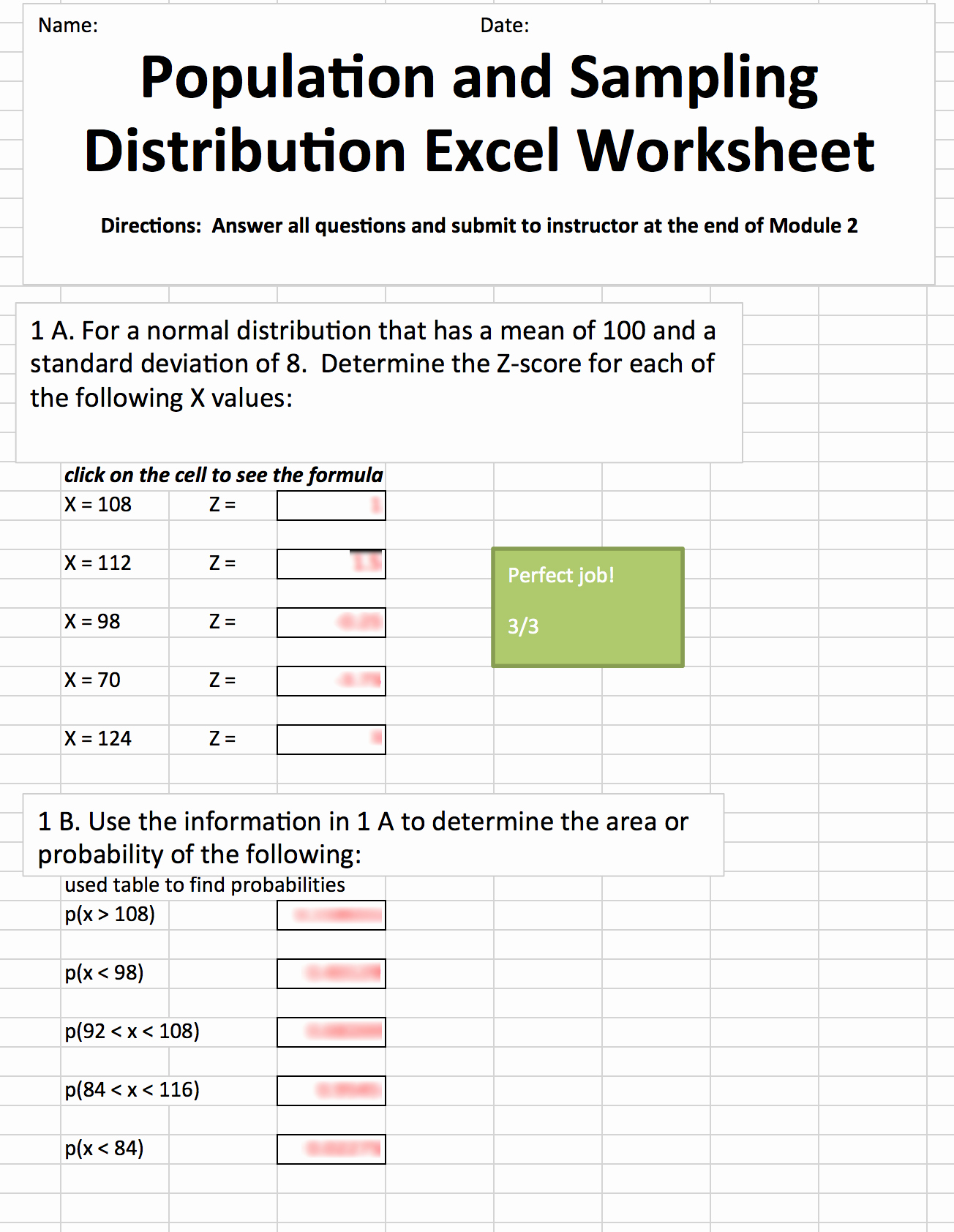
This worksheet differentiates between population standard deviation and sample standard deviation.
- Population Standard Deviation uses (N - 1) as the denominator where N is the total number of items in the population.
- Sample Standard Deviation uses (n - 1) where n is the sample size. This is called Bessel’s correction and provides an unbiased estimate of the population standard deviation.
| Scenario | Formula |
|---|---|
| Population | √[∑(X - μ)²/N] |
| Sample | √[∑(X - μ)²/(n-1)] |
💡 Note: Always be clear on whether you're dealing with a population or a sample before calculating standard deviation.
Worksheet 4: Standard Deviation with Grouped Data

For grouped or frequency distribution data, calculating standard deviation involves an extra step of considering frequency.
- Find the midpoint of each class interval.
- Calculate mean using these midpoints and their frequencies.
- Compute squared differences from the mean, then multiply by the frequency.
- Follow the standard deviation formula for the summation and division.
📌 Note: When working with grouped data, approximations in calculating mean and standard deviation are often necessary due to the loss of exact data points.
Worksheet 5: Using Software for Standard Deviation
In this digital age, software tools like Excel, Python, or R provide quick solutions for standard deviation:
- In Excel: Use the STDEV.P function for population and STDEV.S for sample.
- In Python, with libraries like numpy or pandas:
numpy.std(data, ddof=1)for sample. - In R, the base function is
sd(data).
🖥️ Note: Using software reduces calculation errors and time, but understanding the underlying concept remains crucial.
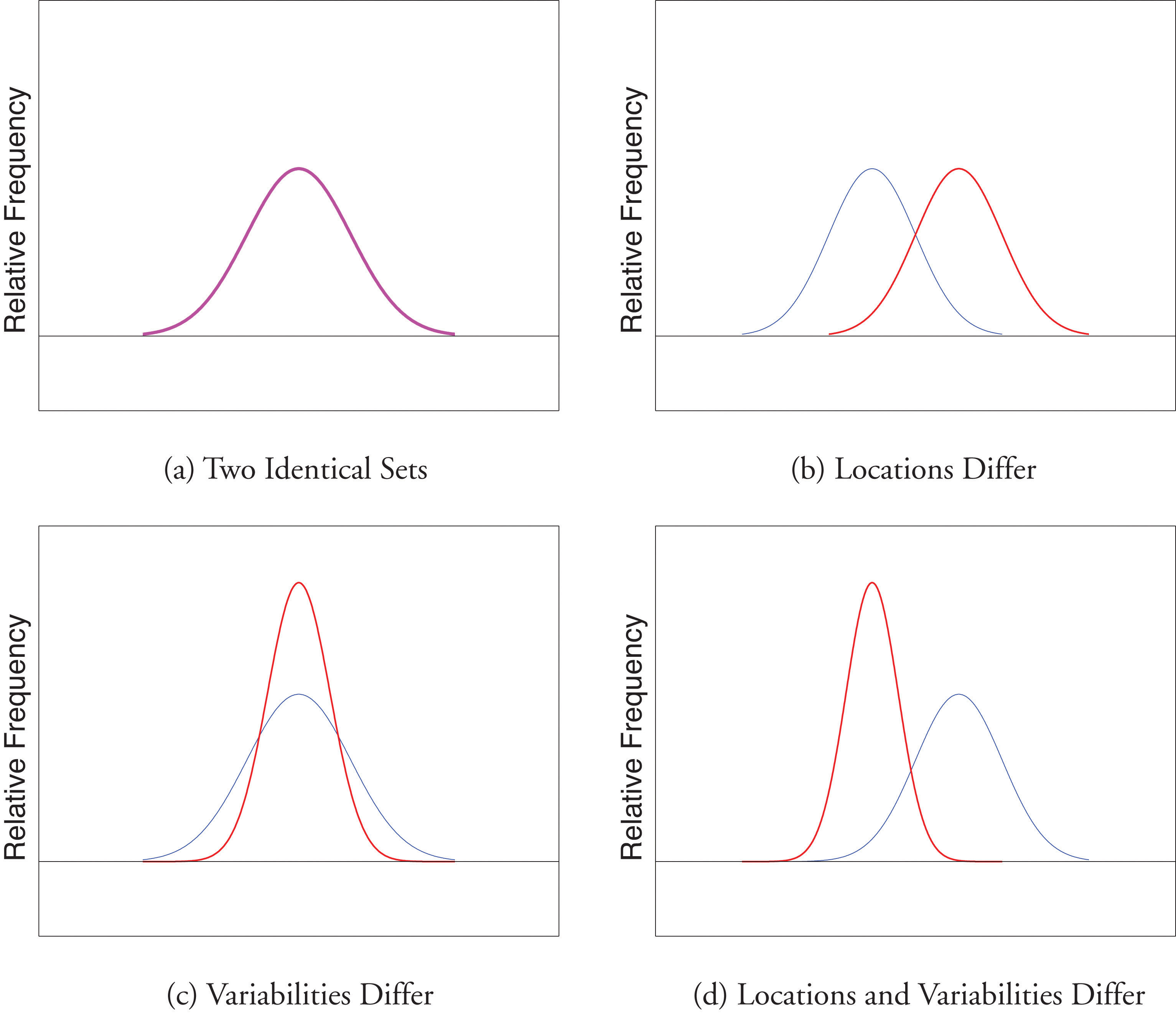
Worksheet 6: Interpreting Standard Deviation in Real Life

Let’s see how standard deviation applies in real-world scenarios:
- Stock Market: It indicates the volatility or risk of an investment.
- Education: Test scores; a low standard deviation suggests consistent performance.
- Quality Control: Helps in determining if a process is stable or if it needs adjustments.
🧠 Note: Standard deviation provides a measure of consistency, which is key in decision-making and process improvement.
Worksheet 7: Common Pitfalls and Tips
Here are some common mistakes and tips when dealing with standard deviation:
- Not differentiating between sample and population standard deviation.
- Confusing mean with median when calculating deviations.
- Using a biased estimate when dealing with samples (dividing by n instead of n-1).
🔍 Note: Careful application of standard deviation principles ensures accurate interpretation of data variability.
This exploration through these worksheets has highlighted how standard deviation serves as a fundamental tool in statistical analysis. By understanding and correctly applying the steps to calculate standard deviation, you can better comprehend data variability, aiding in more informed decision-making. Each worksheet has provided a step-by-step guide, from basic calculations to interpreting results in real-world contexts, ensuring that you have a robust toolkit for tackling variability in any dataset. Remember, standard deviation is not just a number; it's a window into the consistency and reliability of your data.
What does a high standard deviation imply in a dataset?
+
A high standard deviation implies that the data points are spread out over a larger range of values, indicating greater variability or dispersion from the mean.
Can standard deviation be negative?

+
No, standard deviation is always non-negative because it involves calculating the square root of variance, which is the sum of squared differences from the mean. Squaring eliminates negative signs.
Why do we divide by n-1 when calculating sample standard deviation?

+
Dividing by n-1 instead of n (called Bessel’s correction) provides an unbiased estimate of the population standard deviation, accounting for the fact that a sample only represents a part of the population.
How does outliers affect standard deviation?

+
Outliers can significantly increase the standard deviation by skewing the distribution of data points further from the mean, thus indicating higher variability in the dataset.
What are the limitations of using standard deviation?

+
Standard deviation has limitations like being sensitive to extreme values, not differentiating between positive and negative deviations, and assuming a symmetric distribution which might not always be true for real-world data.



