Squid Dissection Worksheet: A Guide for Students

In the fascinating journey of understanding marine life, dissecting a squid provides students with an enriching educational experience. Not only does it offer a hands-on approach to studying anatomy, but it also deepens our appreciation for the complexity and adaptations of sea creatures. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you in navigating through the dissection process:
Preparation for Dissection


The first step in any dissection is thorough preparation. Here’s what you should do:
- Gather Tools: You’ll need:
- Dissection tray or board
- Scissors
- Forceps
- Scalpel or razor blade
- Gloves
- Safety goggles
- Prepare Workspace:
- Clean and disinfect the work area
- Ensure good lighting
- Have a bucket or sink nearby for disposing biological material
🔬 Note: Safety should always come first. Make sure to follow all lab safety protocols, including wearing safety goggles and gloves to prevent contamination.
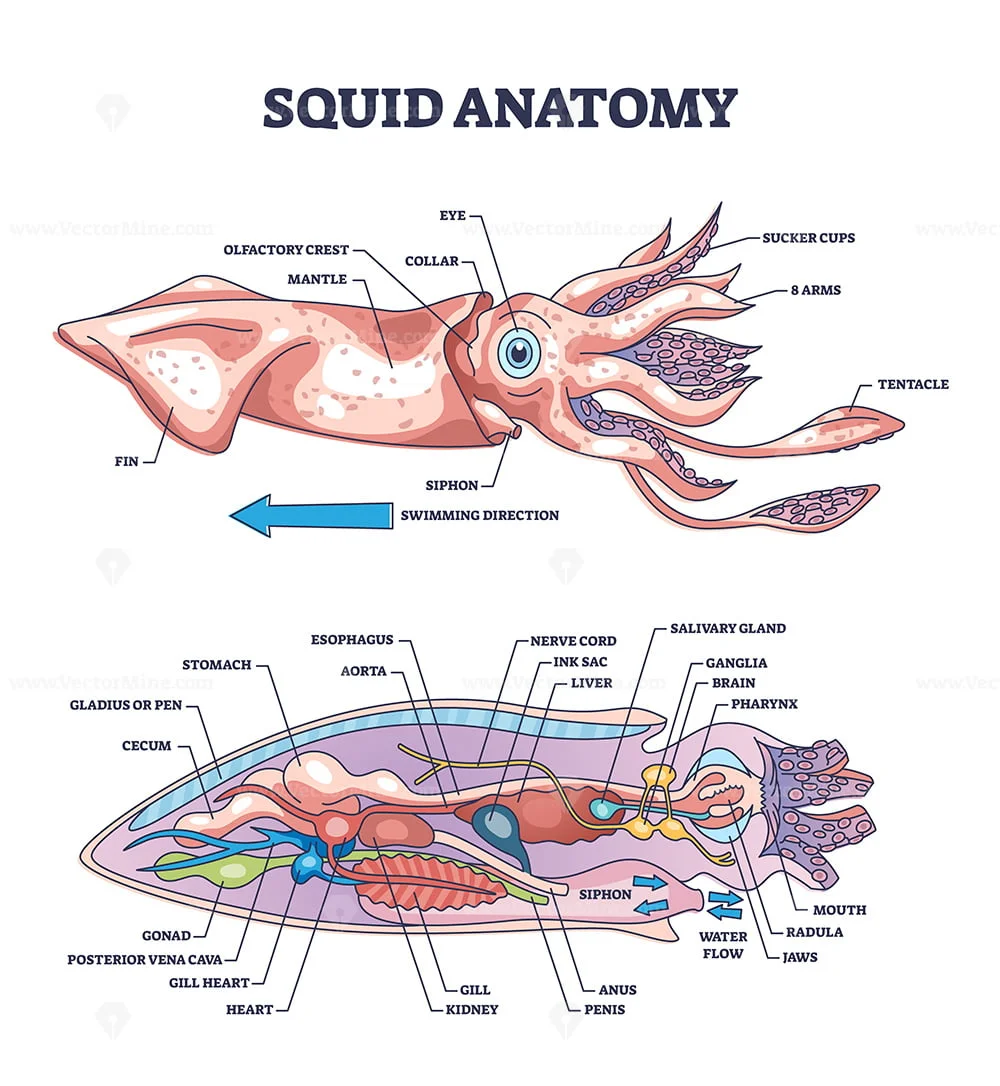
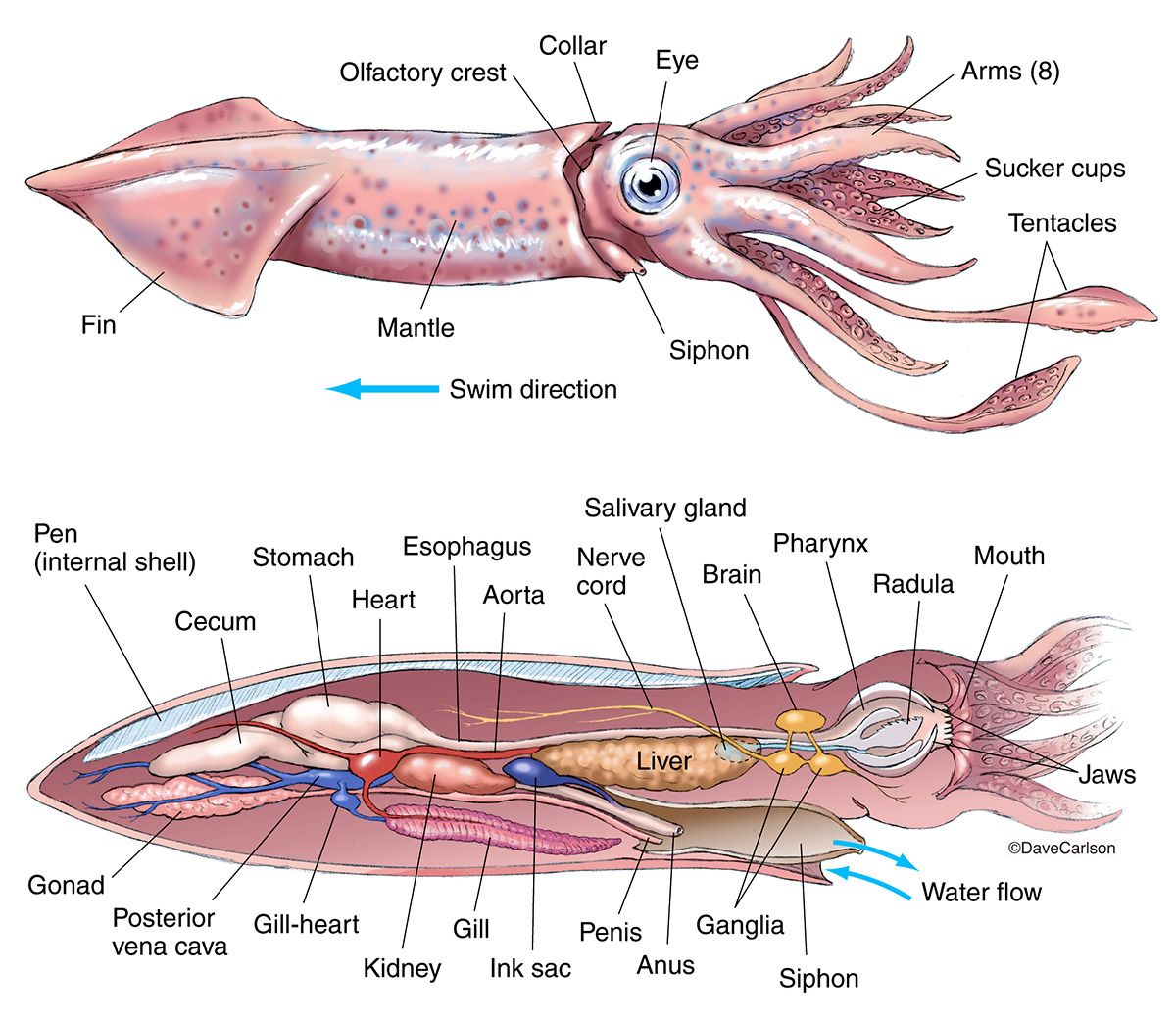
External Anatomy Exploration


Before making any incisions, observe the squid’s exterior:
- Body Shape: Notice the streamlined, torpedo-shaped body designed for swift movement through water.
- Mantle: This is the squid’s main body part where internal organs are housed.
- Fins: Look for the triangular or wing-like fins used for stability and maneuvering.
- Eyes: Observe the large eyes, an adaptation for living in various depths with low light.
- Arms and Tentacles: Identify the difference between the eight arms, lined with suckers, and the two longer feeding tentacles.
Dissection Procedure


Now, let’s move on to the actual dissection:
- Incision: Make a longitudinal cut along the mantle from the tip to the opening of the funnel. Be careful not to cut through the organs underneath.
- Exposing the Digestive System:
- Open the mantle to reveal the squid’s internal organs. Look for:
- The large, ink sac
- Radula (the beak-like structure)
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Open the mantle to reveal the squid’s internal organs. Look for:
- Circulatory System:
- The heart is centrally located, often surrounded by other organs. You might also find:
- Gill hearts
- Aorta
- Venous sinuses
- The heart is centrally located, often surrounded by other organs. You might also find:
- Reproductive Organs: Depending on the squid’s gender, you’ll find either:
- Oviducts or testes
- Nidamental glands in females or spermatophoric sac in males
- Muscular Structures: The muscular mantle is not just for protection but also for propulsion. Note the funnel, used for expelling water to move the squid.
🧐 Note: Be gentle when handling the squid's delicate organs. Use forceps to move tissues without damaging them.
Documentation and Analysis

Recording your findings is an essential part of the learning process:
- Sketching: Create a sketch of the squid’s external and internal anatomy. Label each part.
- Data Collection: Note down observations on color, size, and any peculiarities in structure.
- Journaling: Document your dissection experience, challenges faced, and what you’ve learned about squid anatomy and biology.
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Ink Sac | Defense mechanism; releases ink to confuse predators |
| Radula | Used for feeding, like a tongue with teeth |
| Mantle | Houses organs, provides structure, and propels squid by jet propulsion |
Reflection and Cleanup
After completing your dissection:
- Cleanup: Dispose of the squid remains properly, clean the tools, and sanitize the workspace.
- Reflect: Think about what this experience taught you about marine biology, adaptations, and the complex systems of animals.
- Discuss: Engage with peers or instructors to discuss findings, observations, and any questions that arose during the dissection.
The experience of dissecting a squid is a journey through one of the ocean's most intriguing residents. It teaches us about their unique biological adaptations, how they navigate their environments, and how they interact with other species. This hands-on activity not only enhances our understanding but also fosters a deeper connection with the natural world, encouraging a lifelong curiosity and respect for marine life.
What is the purpose of dissecting a squid?

+
Dissecting a squid allows students to explore marine biology, understand anatomical structures, and learn about the functional adaptations of cephalopods in their natural environments.
How do you handle the ink sac during a squid dissection?

+
Be cautious not to rupture the ink sac. If ink spills, use gloves and clean it immediately to prevent staining and to ensure a clear view of the internal anatomy.
What can we learn from the squid’s reproductive system?
+
By examining the reproductive organs, students can understand the reproductive strategies of squids, including their unique method of fertilization and the sexual dimorphism present in these organisms.
Related Terms:
- Squid dissection worksheet pdf
- Squid dissection worksheet answers
- Internal squid anatomy
- Squid Dissection lab report
- External squid anatomy