Speed Of Light In Mach
The Speed of Light in Mach: Understanding the Relationship
The speed of light is a fundamental constant in physics, denoted by the letter c, and is approximately equal to 299,792,458 meters per second in a vacuum. This speed is a crucial component of the theory of special relativity proposed by Albert Einstein. On the other hand, Mach is a unit of measurement used to express the speed of an object relative to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium, usually air. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of the speed of light in Mach and delve into the relationship between these two seemingly disparate entities.
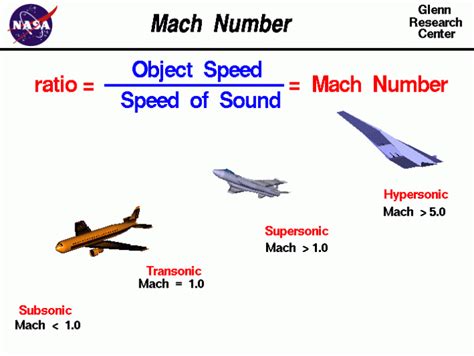
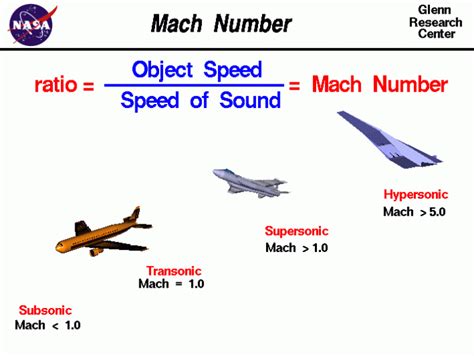
What is Mach?

Mach is a dimensionless quantity named after the Austrian physicist Ernst Mach. It is defined as the ratio of an object’s speed to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium. For example, if an object is traveling at Mach 1, it is moving at the speed of sound, which is approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius).
Converting the Speed of Light to Mach
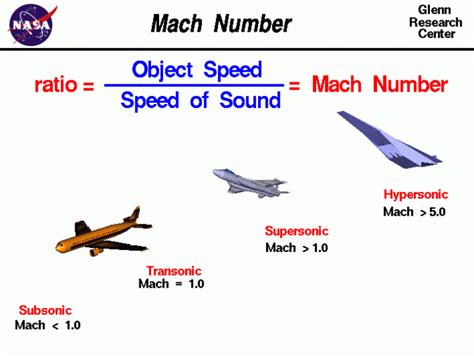
To express the speed of light in Mach, we need to divide the speed of light by the speed of sound. Let’s use the approximate values mentioned earlier:
Speed of light © ≈ 299,792,458 meters per second Speed of sound (Mach 1) ≈ 768 miles per hour
First, we need to convert the speed of sound from miles per hour to meters per second:
1 mile = 1609.34 meters 1 hour = 3600 seconds
So, the speed of sound in meters per second is:
768 miles/hour × (1609.34 meters/mile) / (3600 seconds/hour) ≈ 331.46 meters/second
Now, we can calculate the speed of light in Mach:
c ≈ 299,792,458 meters/second ÷ 331.46 meters/second ≈ 904,259 Mach
Therefore, the speed of light is approximately 904,259 Mach.
Why is the Speed of Light so Fast Compared to Mach?

The speed of light is an incredibly large value compared to the speed of sound, which is why the speed of light in Mach is so enormous. This disparity arises from the fundamental differences between the two types of waves.
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, which can propagate through a vacuum at an incredible speed. In contrast, sound waves require a medium, such as air, water, or solids, to propagate. The speed of sound is limited by the properties of the medium, such as its density, elasticity, and temperature.
In addition, the speed of light is a universal constant, meaning it remains the same regardless of the observer’s frame of reference. In contrast, the speed of sound is relative to the observer and the medium.
Implications of the Speed of Light in Mach

The vast difference between the speed of light and the speed of sound has significant implications for various fields, including physics, engineering, and astronomy.
In physics, the speed of light is a fundamental constant that plays a crucial role in the theory of special relativity. The speed of light in Mach highlights the enormous gap between the speed of light and the speed of sound, which is essential for understanding relativistic phenomena.
In engineering, the speed of light is used in the design of high-speed communication systems, such as fiber optic cables. The speed of light in Mach emphasizes the importance of considering relativistic effects in the design of these systems.
In astronomy, the speed of light is used to measure the vast distances between celestial objects. The speed of light in Mach underscores the immense scales involved in astronomical phenomena.
🚀 Note: The speed of light is always constant, but the speed of sound can vary depending on the medium and environmental conditions.
Comparison of Speeds

To put the speed of light in Mach into perspective, let’s compare it with some other speeds:
- Speed of sound (Mach 1) ≈ 768 mph (1,236 km/h)
- Speed of a commercial airliner ≈ 915 km/h (567 mph) ≈ Mach 0.8
- Speed of a bullet ≈ 1,700 mph (2,700 km/h) ≈ Mach 2.2
- Speed of a spacecraft (e.g., Apollo 11) ≈ 25,000 mph (40,200 km/h) ≈ Mach 30
- Speed of light ≈ 299,792,458 m/s ≈ 904,259 Mach
As we can see, the speed of light is vastly greater than any other speed, including the speed of sound.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the speed of light in Mach is an enormous value that highlights the fundamental differences between the speed of light and the speed of sound. Understanding this relationship is crucial for various fields, including physics, engineering, and astronomy.
By exploring the concept of the speed of light in Mach, we gain a deeper appreciation for the incredible scales involved in the universe and the importance of considering relativistic effects in our designs and calculations.
What is the speed of light in Mach?

+
The speed of light is approximately 904,259 Mach.
Why is the speed of light so fast compared to Mach?

+
The speed of light is an electromagnetic wave that can propagate through a vacuum, whereas sound waves require a medium and are limited by its properties.
What are the implications of the speed of light in Mach?

+
The speed of light in Mach has significant implications for physics, engineering, and astronomy, including the design of high-speed communication systems and the measurement of vast distances in the universe.
Related Terms:
- Speed of sound in Mach
- Speed of light in mph
- How fast is Mach 100000000000000