Sonographer: Unlocking the Secrets of the Human Body

Unlocking the Secrets of the Human Body: The Role of a Sonographer
Sonographers, also known as ultrasound technologists, play a vital role in the medical field by using specialized imaging equipment to create images of the human body. These images help healthcare professionals diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions. In this article, we will delve into the world of sonography, exploring the role of a sonographer, the different types of sonography, and the skills required to succeed in this field.
What is Sonography?

Sonography, also known as ultrasonography, is a diagnostic medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the body’s internal structures. These images are created by sending sound waves into the body and measuring the echoes that bounce back. Sonography is commonly used to examine organs, tissues, and blood vessels, and is a valuable tool for diagnosing and treating a range of medical conditions, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, and musculoskeletal disorders.
Types of Sonography
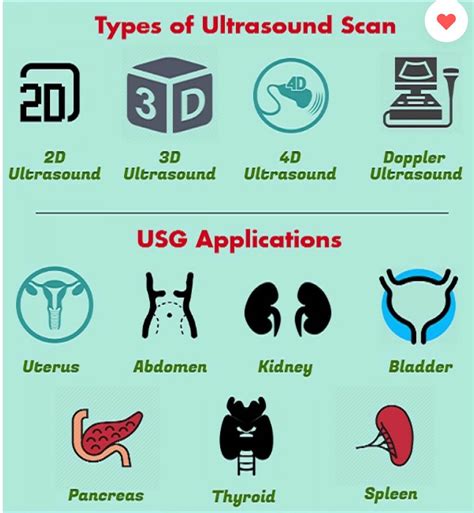
There are several types of sonography, each with its own unique application and purpose. Some of the most common types of sonography include:
- Diagnostic Medical Sonography: This type of sonography is used to diagnose and treat medical conditions. Diagnostic medical sonographers use ultrasound equipment to create images of the body’s internal structures, which are then used to diagnose conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and musculoskeletal disorders.
- Cardiovascular Sonography: This type of sonography is used to examine the heart and blood vessels. Cardiovascular sonographers use ultrasound equipment to create images of the heart and blood vessels, which are then used to diagnose conditions such as heart disease and blood clots.
- Obstetric and Gynecologic Sonography: This type of sonography is used to examine the female reproductive system. Obstetric and gynecologic sonographers use ultrasound equipment to create images of the uterus, ovaries, and fetus during pregnancy.
- Musculoskeletal Sonography: This type of sonography is used to examine the muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Musculoskeletal sonographers use ultrasound equipment to create images of the muscles, tendons, and ligaments, which are then used to diagnose conditions such as tendinitis and ligament sprains.
The Role of a Sonographer
Sonographers play a vital role in the medical field by using specialized imaging equipment to create images of the human body. Some of the key responsibilities of a sonographer include:
- Preparing Patients for Exams: Sonographers prepare patients for exams by explaining the procedure, answering questions, and ensuring that patients are comfortable and relaxed.
- Operating Ultrasound Equipment: Sonographers operate ultrasound equipment to create images of the body’s internal structures.
- Analyzing Images: Sonographers analyze images to identify any abnormalities or conditions.
- Providing Results to Healthcare Professionals: Sonographers provide results to healthcare professionals, who use the information to diagnose and treat medical conditions.
Skills Required to Succeed as a Sonographer

To succeed as a sonographer, individuals must possess a range of skills, including:
- Technical Skills: Sonographers must have strong technical skills, including the ability to operate ultrasound equipment and analyze images.
- Communication Skills: Sonographers must have excellent communication skills, including the ability to communicate effectively with patients and healthcare professionals.
- Analytical Skills: Sonographers must have strong analytical skills, including the ability to analyze images and identify abnormalities.
- Attention to Detail: Sonographers must have attention to detail, including the ability to ensure that images are of high quality and that patients are comfortable and relaxed during exams.
Education and Training Requirements

To become a sonographer, individuals typically need to complete a post-secondary education program in diagnostic medical sonography. These programs are typically offered at community colleges, universities, and vocational schools, and may lead to a certificate, diploma, or associate’s degree.
- Certificate Programs: Certificate programs in diagnostic medical sonography are typically one year in length and provide students with the technical skills and knowledge needed to succeed as a sonographer.
- Diploma Programs: Diploma programs in diagnostic medical sonography are typically two years in length and provide students with a more comprehensive education in diagnostic medical sonography.
- Associate’s Degree Programs: Associate’s degree programs in diagnostic medical sonography are typically two years in length and provide students with a comprehensive education in diagnostic medical sonography, as well as general education courses.
Certification and Licensure Requirements
To practice as a sonographer, individuals must obtain certification or licensure in their state. Certification is typically obtained through the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS), while licensure requirements vary by state.
- ARDMS Certification: The ARDMS offers certification in several areas of sonography, including diagnostic medical sonography, cardiovascular sonography, and obstetric and gynecologic sonography.
- State Licensure: Some states require sonographers to be licensed to practice. Licensure requirements vary by state, but typically involve passing a certification exam and completing continuing education requirements.
📚 Note: Certification and licensure requirements may vary by state and employer, so it's essential to check with your state and employer for specific requirements.
Salary and Job Outlook

The salary and job outlook for sonographers are promising, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) predicting a 14% increase in employment opportunities through 2028.
- Salary: The median annual salary for sonographers is around $62,000, according to the BLS.
- Job Outlook: The BLS predicts a 14% increase in employment opportunities for sonographers through 2028, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
Conclusion
Sonographers play a vital role in the medical field by using specialized imaging equipment to create images of the human body. To succeed as a sonographer, individuals must possess a range of skills, including technical skills, communication skills, analytical skills, and attention to detail. Education and training requirements typically involve completing a post-secondary education program in diagnostic medical sonography, while certification and licensure requirements vary by state. With a promising salary and job outlook, sonography is a rewarding and challenging career for individuals who are passionate about healthcare and technology.
What is the role of a sonographer in the medical field?

+
Sonographers play a vital role in the medical field by using specialized imaging equipment to create images of the human body. These images help healthcare professionals diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions.
What are the different types of sonography?
+
There are several types of sonography, including diagnostic medical sonography, cardiovascular sonography, obstetric and gynecologic sonography, and musculoskeletal sonography.
What education and training requirements are needed to become a sonographer?

+
To become a sonographer, individuals typically need to complete a post-secondary education program in diagnostic medical sonography. These programs are typically offered at community colleges, universities, and vocational schools, and may lead to a certificate, diploma, or associate’s degree.
Related Terms:
- Who does ultrasounds for pregnancy
- Sonographer
- Types of sonography specialties
- ob gyn sonography
- Pediatric sonographers
- Musculoskeletal sonographer