Solubility Worksheet Answers: Boost Your Chemistry Skills
The Concept of Solubility

Solubility is a pivotal concept in chemistry, both for students and professionals in various fields. Understanding solubility can unlock a myriad of chemical phenomena, from the daily dissolution of sugar in tea to industrial processes like wastewater treatment. This blog post aims to enhance your grasp of solubility, providing detailed solubility worksheet answers to common exercises, along with explanations to boost your chemistry skills.
What is Solubility?

Solubility refers to the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a solvent at a specific temperature and pressure, forming a solution. Here’s a more detailed look:
- Solute: The substance being dissolved.
- Solvent: The medium in which the solute dissolves, typically a liquid like water.
- Solution: The resultant mixture where particles are evenly distributed.
Factors Affecting Solubility
Several factors influence solubility:
- Temperature: For solid solutes, solubility generally increases with temperature, while for gases, it decreases.
- Pressure: Pressure mainly affects the solubility of gases in liquids; increased pressure leads to higher solubility.
- Nature of Solute and Solvent: Like dissolves like. Polar solvents dissolve polar solutes, and non-polar solvents dissolve non-polar solutes.
- Solute Concentration: As you add more solute, the rate of dissolving decreases until a point of saturation.
Solubility Worksheet Exercises

Let’s delve into some common solubility worksheet questions and their answers to help solidify your understanding:
Exercise 1: Calculating Solubility

Calculate the solubility of sodium chloride (NaCl) at 25°C if 36 grams dissolve in 100 grams of water.
Answer:
| Component | Mass (g) |
|---|---|
| Sodium Chloride (NaCl) | 36 |
| Water | 100 |
| Total Mass | 136 |

The solubility of NaCl in this scenario is 36 grams per 100 grams of water.
📌 Note: Remember, solubility is often expressed in terms of grams per 100 grams of solvent, especially in worksheet problems.
Exercise 2: Effect of Temperature on Solubility

At 40°C, 50 grams of glucose can dissolve in 100 grams of water. If the temperature is increased to 60°C, how does the solubility change?
Answer:
- Solubility usually increases with an increase in temperature for most solid solutes like glucose. Hence, at 60°C, more than 50 grams of glucose would be able to dissolve in 100 grams of water.
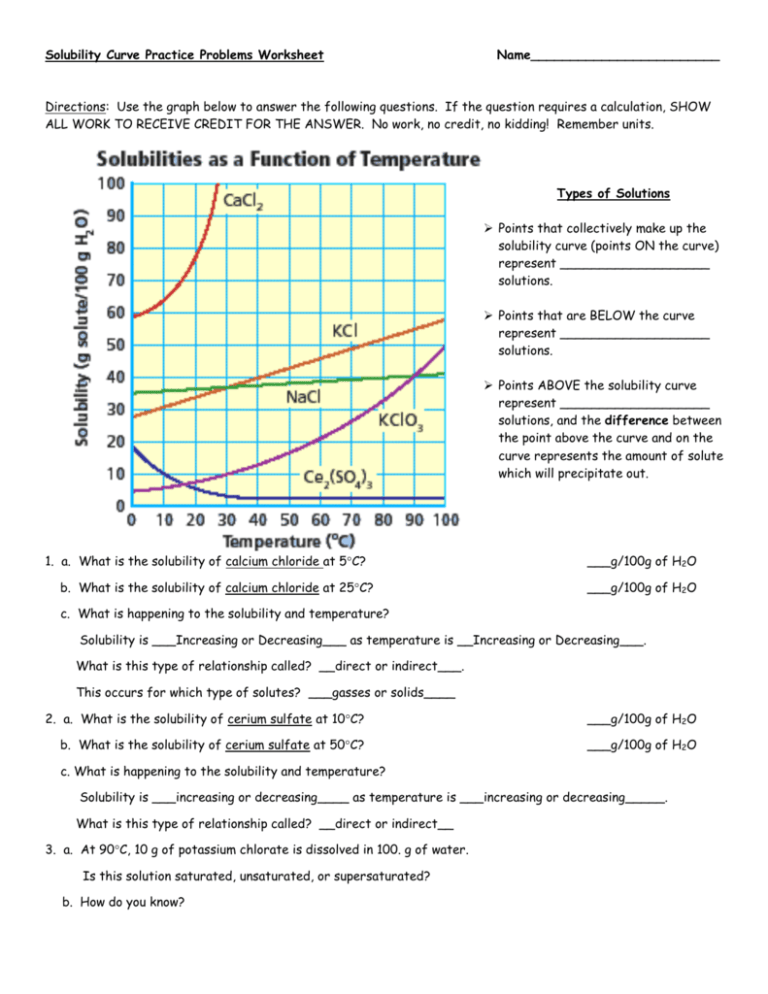
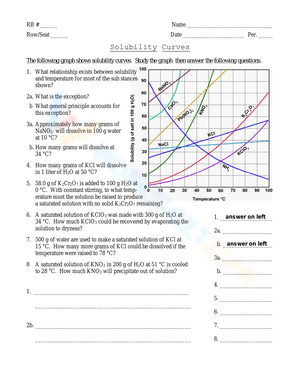
Analyzing Solubility Graphs
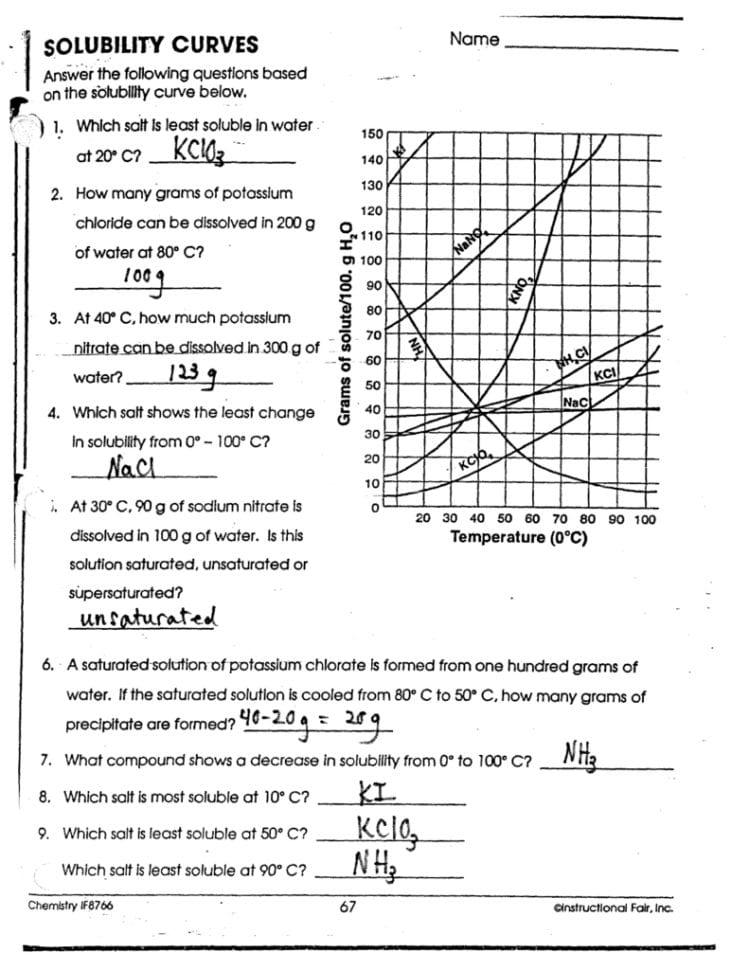
Graphs are a great tool for visualizing solubility trends over a range of temperatures. Here’s how to read a solubility graph:
- Identify the temperature on the x-axis and the solubility on the y-axis.
- Follow the line or curve representing the solute to find its solubility at the given temperature.
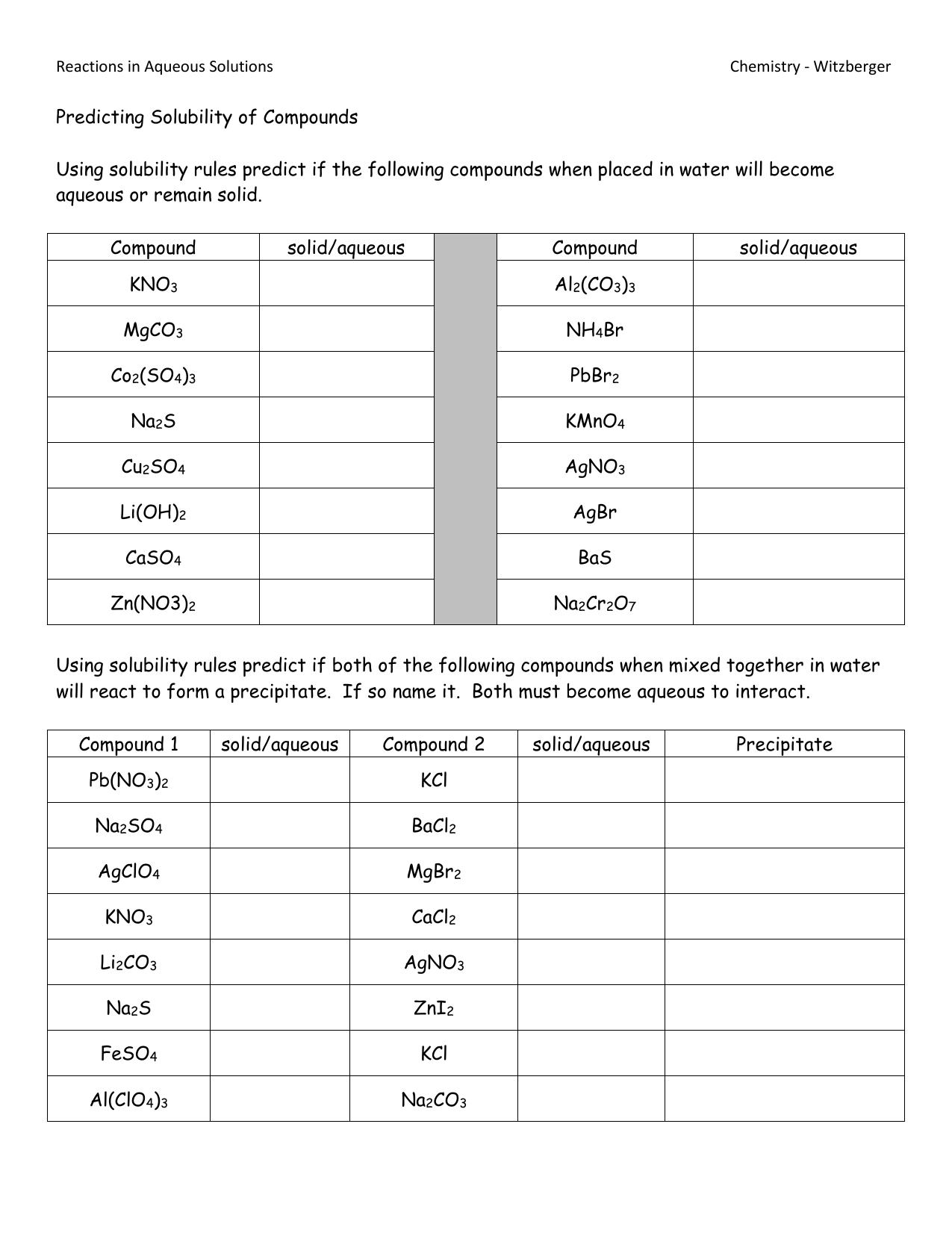
Example Graph Reading
Consider a graph showing the solubility of potassium nitrate (KNO3) versus temperature:
- At 20°C, the solubility is approximately 31.6 grams per 100 grams of water.
- At 80°C, the solubility increases to about 169 grams per 100 grams of water.
📌 Note: When reading from graphs, approximate values might be necessary, especially if the graph doesn’t have fine increments.
Applications of Solubility

Solubility is not just a theoretical concept; it has numerous applications:
- Pharmaceuticals: Understanding solubility helps in developing drugs that can dissolve in the body’s fluids.
- Agriculture: Solubility of fertilizers determines how plants can absorb nutrients.
- Environmental Science: Solubility of pollutants can predict how they will spread in water bodies.
- Industrial Processes: From crystallizing compounds to purifying solutions, solubility plays a critical role.
Wrapping Up

Throughout this post, we've delved into the essence of solubility, offering detailed solubility worksheet answers to illustrate key concepts. Understanding solubility isn't just about memorizing values or formulas; it's about grasping how different variables like temperature, pressure, and the nature of solute and solvent impact the dissolution process. This knowledge aids in both academic chemistry studies and real-world applications. Always remember to consider not just the numbers but the underlying principles when solving solubility problems. Keep practicing, and you'll find that your ability to interpret and solve solubility issues will sharpen significantly.
What affects the solubility of a substance?

+
Key factors include temperature, pressure, the nature of solute and solvent, and the concentration of solute already in solution.
Why does temperature usually increase solubility?

+
Increased kinetic energy at higher temperatures facilitates the breaking of bonds in the solute, allowing more particles to enter the solution.
What is meant by ‘like dissolves like’ in solubility?

+
This principle suggests that polar solutes dissolve well in polar solvents, and non-polar solutes in non-polar solvents, due to their similar molecular interactions.
Can you have solubility with gases?

+
Yes, gases also exhibit solubility in liquids, and this can be influenced by temperature, pressure, and chemical nature of the gas and solvent.