Solubility Graph Worksheet Answers: 5 Key Insights

Understanding solubility graphs is not just an academic exercise; it's a cornerstone for both theoretical understanding and practical applications in various sciences. Whether you're tackling chemistry experiments or learning about physical properties in environmental science, solubility graphs provide insights into how substances interact with solvents at different temperatures. Here are five key insights that you can glean from working through a solubility graph worksheet, enhancing your comprehension of this fundamental concept.
1. The Nature of Solubility


First and foremost, solubility graphs visually depict the relationship between temperature and solubility. Here’s what you need to know:
- Positive Slope: Typically, solubility of most solids in liquids increases with temperature, creating an upward slope on the graph.
- Negative Slope: Some substances exhibit reverse solubility; their solubility decreases with temperature.
- Inflection Points: At certain temperatures, there might be drastic changes in solubility, indicating a phase transition or chemical change.
2. Understanding Saturation Points
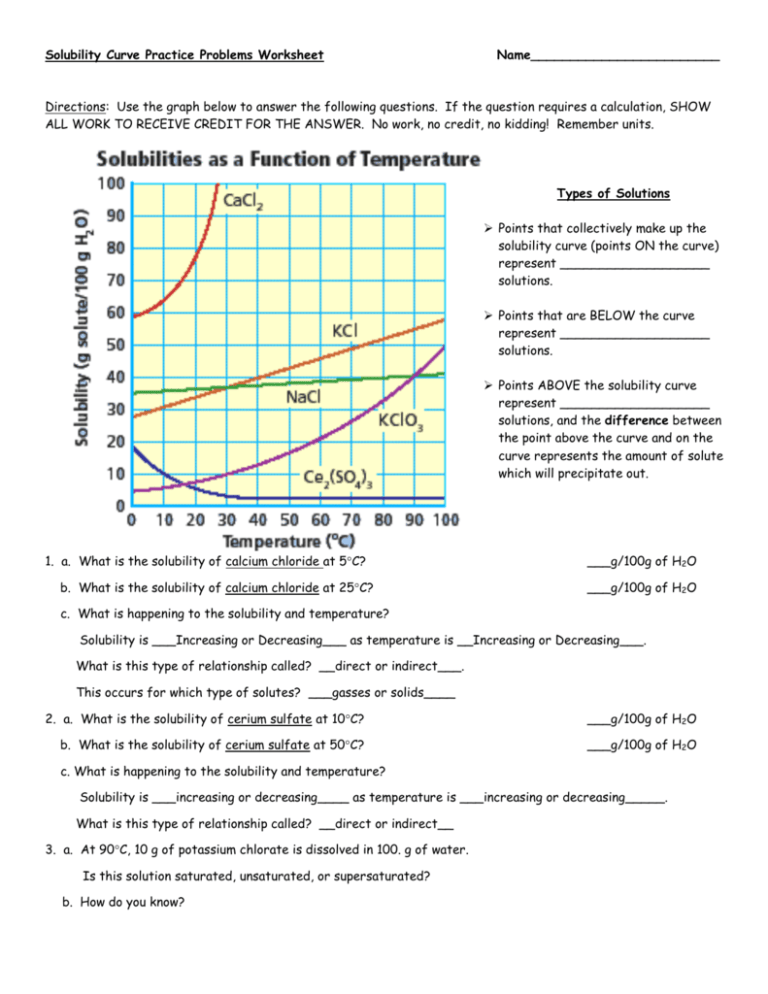
Saturation refers to the point at which no more solute can be dissolved in the solvent. Solubility graphs help identify:
- At what temperature a solution becomes saturated.
- How to calculate the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved.
- The impact of changing temperature on a saturated solution.
For instance, if you have a beaker of water at 50°C, a solubility graph can quickly tell you how much sodium chloride you can dissolve without reaching saturation.
3. Extrapolation and Interpolation

Solubility graphs are not only informative for known data points but also for estimating solubility at temperatures not explicitly measured:
- Interpolation: Predicting solubility at temperatures within the range of the graph’s data.
- Extrapolation: Estimating solubility beyond the data range, although this must be done cautiously.
🔎 Note: While interpolation is generally reliable, extrapolation can introduce inaccuracies as solubility behavior might not follow the same trend beyond the known data points.
4. Effects of Concentration

| Concentration | Effect on Solubility |
|---|---|
| Dilute | Increases solubility |
| Saturated | Maximum solubility at current temperature |
| Supersaturated | Exceeds normal solubility limit |

By studying a solubility graph, you can understand:
- The role of concentration on how much solute can be dissolved.
- How the addition of solute beyond saturation can result in precipitation or crystallization.
5. Real-World Applications

Applying solubility graphs in real life goes beyond the lab:
- Crystal Growth: Industries use solubility data to control crystal growth for pharmaceuticals and semiconductor manufacturing.
- Water Treatment: Understanding solubility aids in designing efficient water purification systems.
- Geological Processes: Solubility information helps predict the formation of mineral deposits or the erosion of rock formations.
From these insights, we can see that solubility graphs are much more than mere academic tools. They are essential for process control, experimental predictions, and understanding natural phenomena. The intricate dance between solute and solvent at different temperatures, as depicted on these graphs, provides a window into the fundamental interactions driving both chemical and physical processes. By mastering the interpretation of solubility graphs, one can unlock a wealth of knowledge, leading to better predictions, innovations, and applications across diverse scientific fields.
Why does solubility increase with temperature for most substances?

+
Increasing temperature typically provides more energy to the solvent molecules, allowing them to overcome the forces holding the solute particles together, thus increasing solubility.
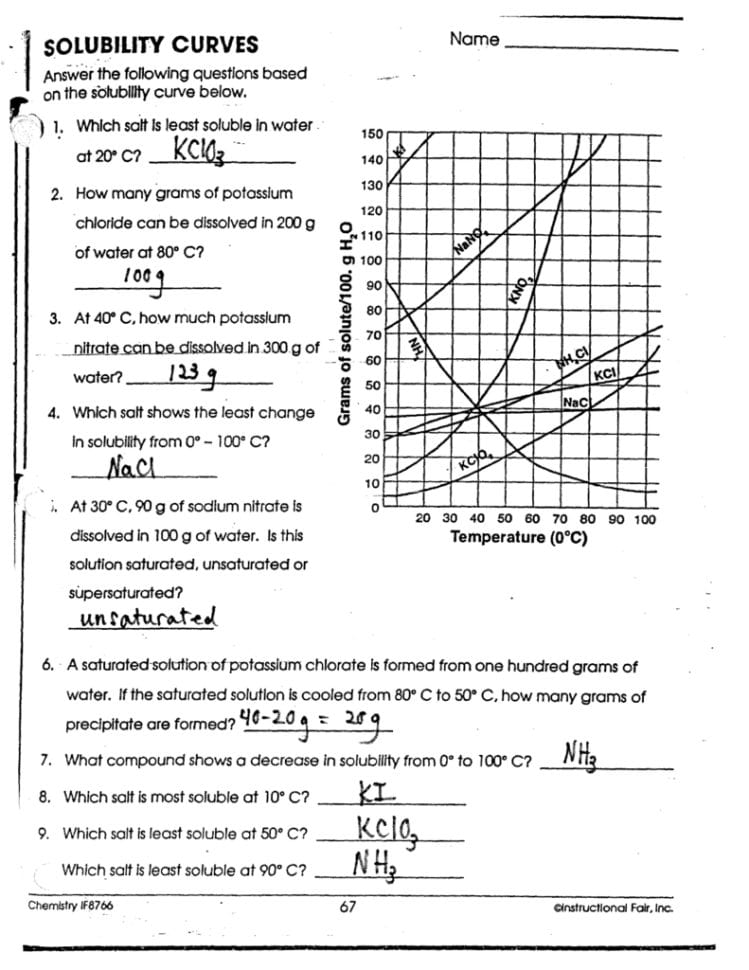
How do you determine the solubility of a substance from a graph?
+
Locate the temperature on the x-axis, find the corresponding solubility on the y-axis, and read the intersection. This point represents the solubility of the substance at that temperature.
Can solubility be increased beyond saturation?

+
Yes, by creating a supersaturated solution where more solute is dissolved than would normally be possible at a given temperature, usually by heating the solution and then cooling it slowly without agitation.
Related Terms:
- Solubility graph worksheet answers pdf
- Solubility graph Worksheet PDF
- Solubility curve questions and answers
- Solubility curve PDF