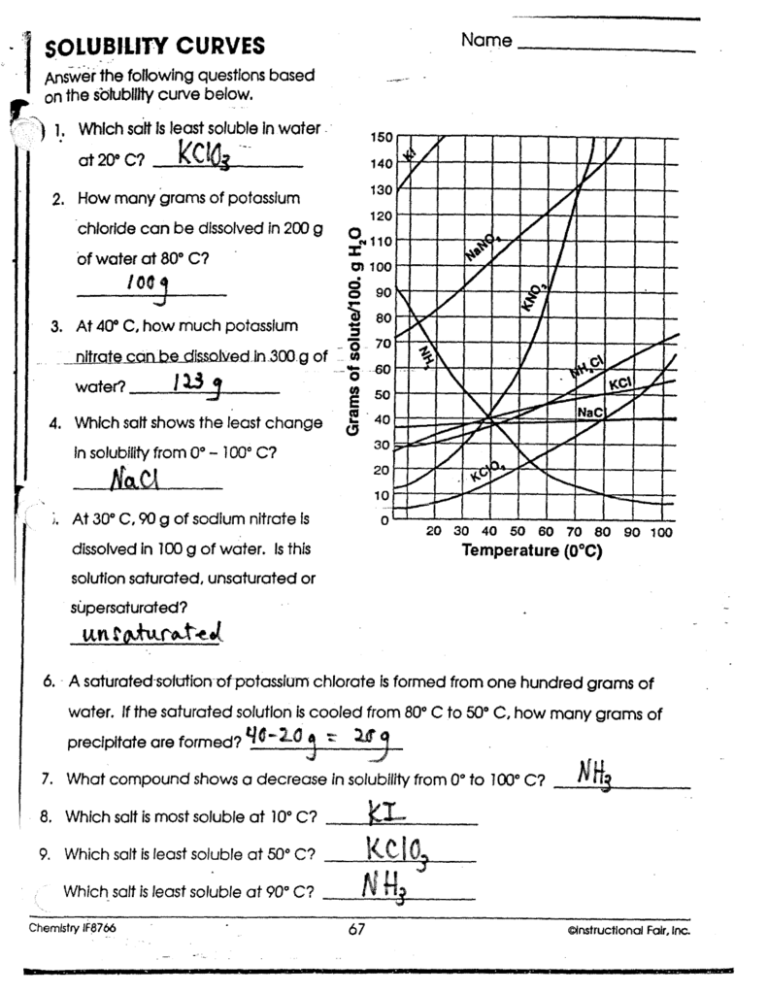
5 Tips for Mastering Solubility Curve Worksheets
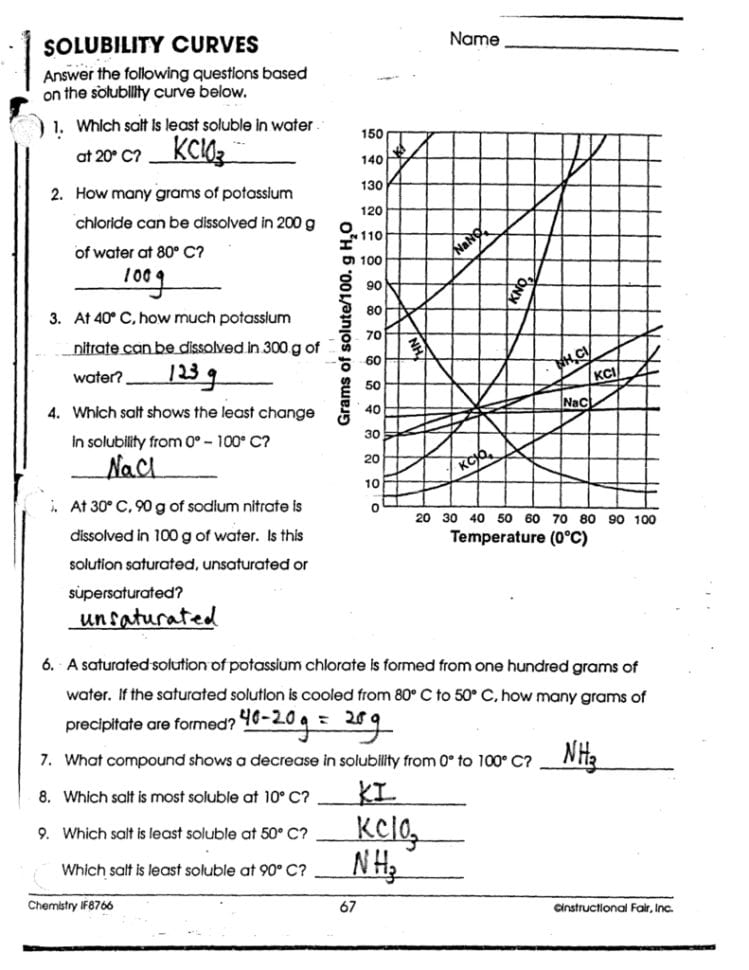
Solubility curve worksheets are an essential tool in chemistry education, providing students with a visual representation of how different substances dissolve at varying temperatures. Mastering these worksheets not only aids in understanding solubility but also enhances analytical skills in science. This blog post will guide you through five crucial tips to excel in working with solubility curve graphs and worksheets.
1. Understand the Basics
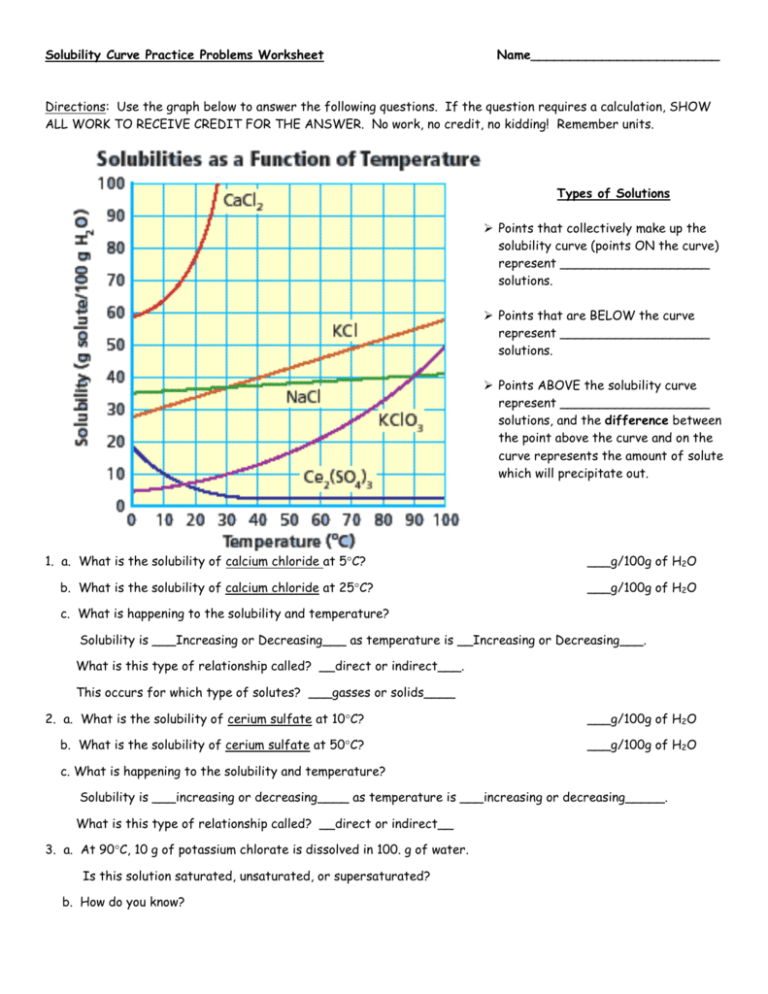
Before diving into complex solubility curve worksheets, it’s imperative to understand what solubility curves represent:
- Solubility Curves: These are graphical representations of how the solubility of a solute in a solvent changes with temperature.
- Key Features: You’ll encounter the solubility line, saturation points, and sometimes the supersaturation curve.
📘 Note: Remember, solubility curves usually show solubility in grams of solute per 100 grams of water at different temperatures.

2. Practice Reading the Graph

Accurate reading of solubility curves is fundamental:
- Identify points where the curve crosses specific temperature lines.
- Understand how to interpolate between points for approximate solubility values.
- Recognize trends, like whether solubility increases, decreases, or remains constant with temperature.
3. Analyze Solubility Data

Here are some key aspects to focus on:
- Maximum Solubility: Determine at what temperature a solute reaches its maximum solubility.
- Unsaturated vs. Saturated Solutions: Identify where on the graph a solution would be saturated at given conditions.
- Comparison: Compare the solubility of different solutes at the same temperature or the same solute at different temperatures.
4. Apply Scientific Concepts
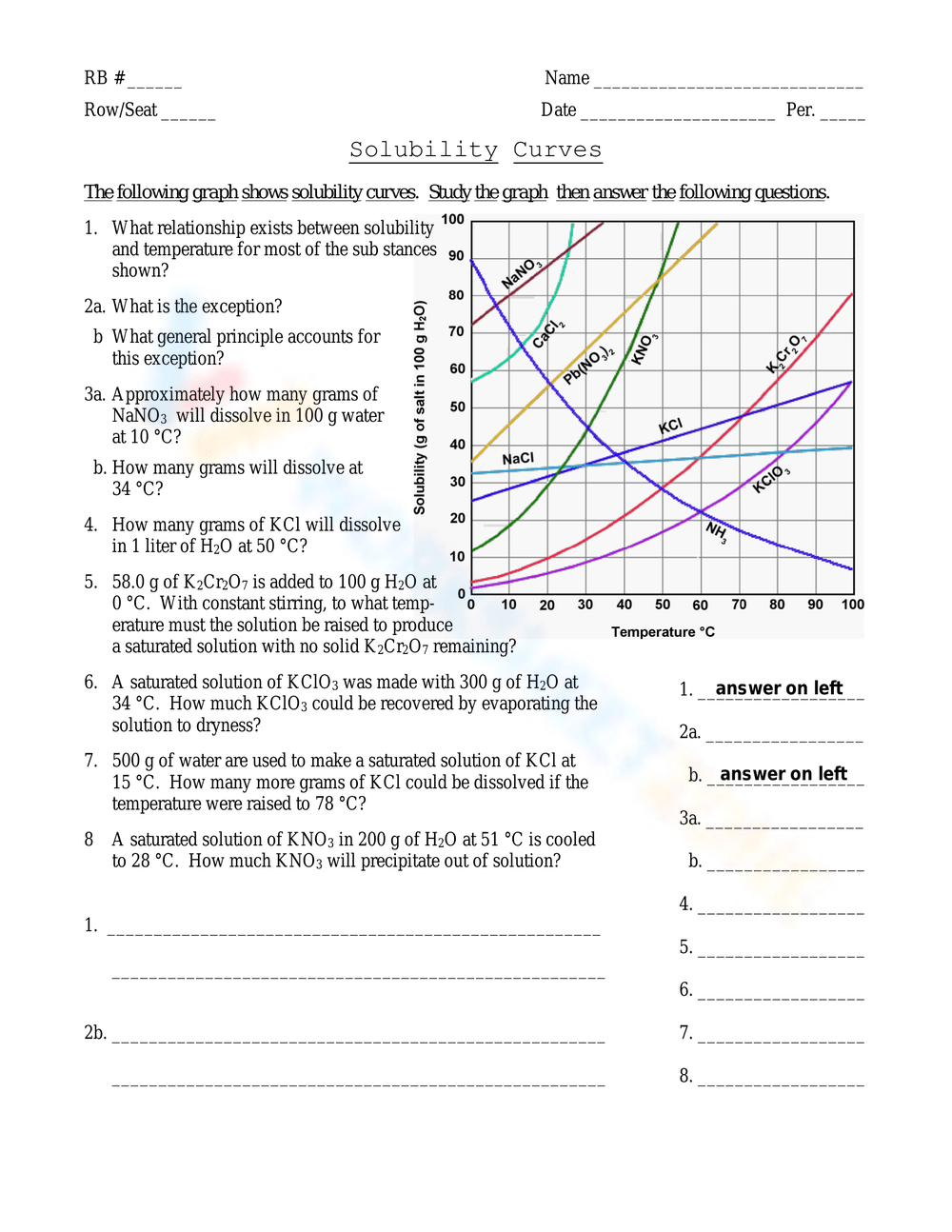
Link solubility data with broader chemical principles:
- Le Chatelier’s Principle: Understand how changes in temperature affect solubility.
- Heat of Solution: Consider if dissolving the solute is endothermic or exothermic to predict solubility trends.
- Concentration Effects: Assess how changing the solute concentration impacts solubility.
⚠️ Note: Remember to account for any anomalous solubility curves where solubility might decrease with temperature, like for gases in liquids.
5. Engage in Problem-Solving
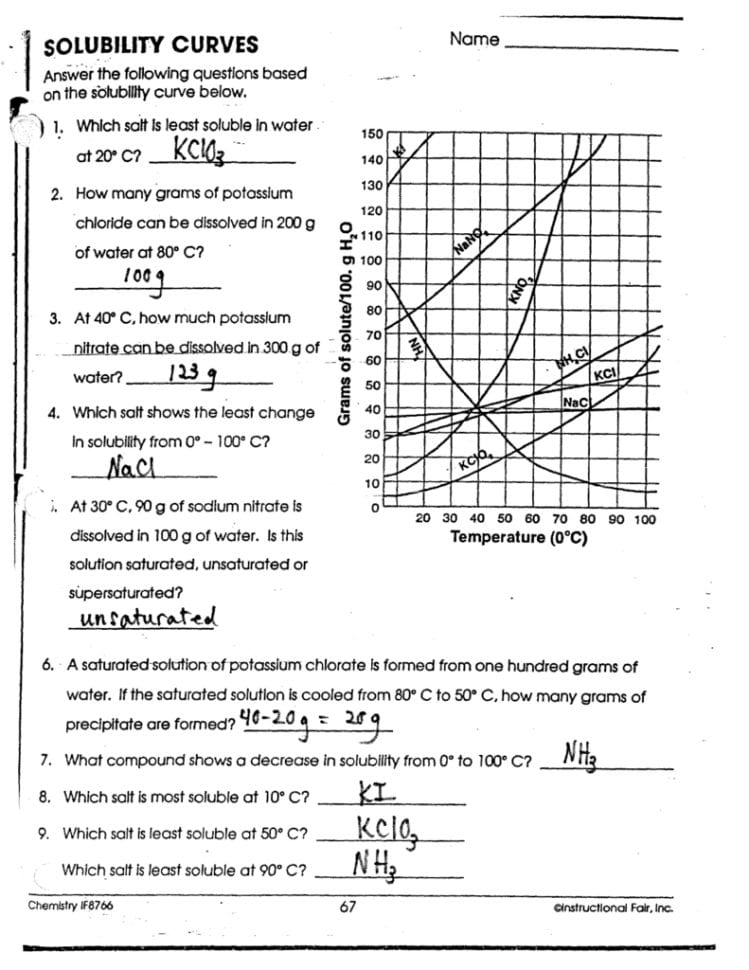
Developing problem-solving skills is vital for mastering solubility curve worksheets:
- Questions and Scenarios: Work through typical questions that involve solubility graphs, such as calculating the amount of solute dissolved at different temperatures.
- Graphical Analysis: Use the graph to infer information like the temperature at which a supersaturated solution would crystallize.
Here’s a quick example table for reference:
| Solute | Temp (°C) | Solubility (g/100g H₂O) |
|---|---|---|
| Salt | 0 | 36 |
| Salt | 100 | 45 |

These tips are not just about mastering solubility curve worksheets; they are about deepening your understanding of solubility and its relationship to temperature. By applying these concepts, you'll be well-equipped to handle any solubility curve problem thrown your way, making you a proficient chemistry student.
Why do some substances have different solubility curves?

+
Different substances have unique chemical properties that influence their solubility. For instance, ionic compounds often dissolve more readily in water (endothermic) as temperature increases, while gases decrease in solubility (exothermic) due to changes in molecular interactions.
How do I determine the solubility at a non-standard temperature?

+
Use the graph to interpolate between known points. For example, if you know solubility at 0°C and 50°C, you can estimate at 25°C by drawing a line between these points and reading the value where it intersects with the 25°C line.
Can I use solubility curves to predict crystallization?
+
Absolutely. If you know the amount of solute dissolved and the temperature, you can determine if it falls into the supersaturated region on the solubility curve, indicating potential for crystallization as the solution cools.